Visual Brain
... Figure 4.24 How a tree creates an image on the retina and a pattern of activation on the cortex. ...
... Figure 4.24 How a tree creates an image on the retina and a pattern of activation on the cortex. ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Existence of distinct agnosias for aspects of perception suggests that these abilities are localized to areas selectively damaged. Achromatopsia – good perception of form despite inability to distinguish hues. Prosopagnosia – inability to recognize faces as particular people (identity). Can recogniz ...
... Existence of distinct agnosias for aspects of perception suggests that these abilities are localized to areas selectively damaged. Achromatopsia – good perception of form despite inability to distinguish hues. Prosopagnosia – inability to recognize faces as particular people (identity). Can recogniz ...
Lectures on mathematical neuroscience
... • Simple models to analyze synchronous and anti-phase oscillations ...
... • Simple models to analyze synchronous and anti-phase oscillations ...
We are investigating the use of novel stimulus
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...
Chapter 2 figures 2.7 to 2.12
... Figure 2.9. (a) Image with 4 bands of differing brightness. A to D are locations marks. (b) Physical brightness levels of image in (a). (c) Perceptual brightness of image (a) "seen" by viewer resulting from lateral inhibition. (d) Conceptual diagram of how lateral inhibition can enhance borders bet ...
... Figure 2.9. (a) Image with 4 bands of differing brightness. A to D are locations marks. (b) Physical brightness levels of image in (a). (c) Perceptual brightness of image (a) "seen" by viewer resulting from lateral inhibition. (d) Conceptual diagram of how lateral inhibition can enhance borders bet ...
Lecture S&P
... More cortex is devoted to areas of high acuity – like the disproportionate representation of sensitive body parts in somatosensory cortex About 25% of primary visual cortex is dedicated to input from the fovea ...
... More cortex is devoted to areas of high acuity – like the disproportionate representation of sensitive body parts in somatosensory cortex About 25% of primary visual cortex is dedicated to input from the fovea ...
Nervous System - Crossword Labs
... 7. rest and digest section of the autonomic nervous system 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All neural tissue outside CNS 20. cytoplasm of axon 21. Cell that receives message 22. ca ...
... 7. rest and digest section of the autonomic nervous system 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All neural tissue outside CNS 20. cytoplasm of axon 21. Cell that receives message 22. ca ...
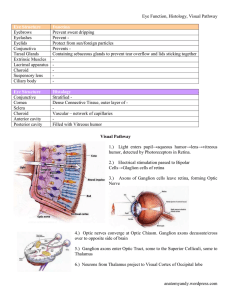
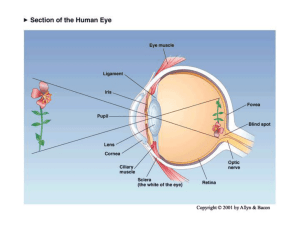
Eye Structure - WordPress.com
... Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
... Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
Nervous Systems
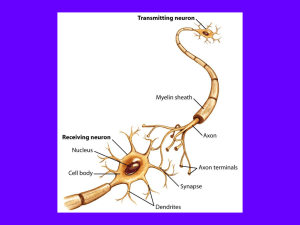
... Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body Sensory receptors: collect info Sensory neurons: body CNS Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons Nerves = bundles of neurons C ...
... Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body Sensory receptors: collect info Sensory neurons: body CNS Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons Nerves = bundles of neurons C ...
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... – Process information related to form, movement, depth, small changes in brightness – Connected mostly with rods ...
... – Process information related to form, movement, depth, small changes in brightness – Connected mostly with rods ...
The Brain and Behavior
... • Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have ...
... • Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... Arianna Maffei, Ph.D. Research Associate Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual ...
... Arianna Maffei, Ph.D. Research Associate Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual ...
Visual Cortical Dynamics Charles Gilbert The Rockefeller University
... the task being executed. Each cortical area represents an association field, whereby bits of information are dynamically linked via a plexus of long range horizontal connections. Although each neuron receives 105 inputs from other neurons, neurons are capable of selecting a small subset of task rele ...
... the task being executed. Each cortical area represents an association field, whereby bits of information are dynamically linked via a plexus of long range horizontal connections. Although each neuron receives 105 inputs from other neurons, neurons are capable of selecting a small subset of task rele ...
Ch 4 V Cortexb - Texas A&M University
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
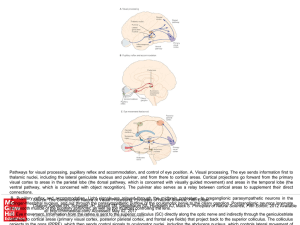
Slide ()
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
Document
... • Orientation tuning curves – Shows response of simple cortical cell for orientations of stimuli ...
... • Orientation tuning curves – Shows response of simple cortical cell for orientations of stimuli ...
Session 4
... Light is absorbed by the photoreceptors in the retina. Some processing is performed in the retina itself. The retinal ganglion cells are the final stage in the retinal processing. They send axons out of the eye to the LGN. ...
... Light is absorbed by the photoreceptors in the retina. Some processing is performed in the retina itself. The retinal ganglion cells are the final stage in the retinal processing. They send axons out of the eye to the LGN. ...
Auditory information processing at the cortical level
... Auditory information processing in the auditory cortex occurs due to a group of neurons organised in a vertical manner (columnar organisation). The most clear-cut parameter along which this organisation has been observed is the characteristic frequency of the nerve cells. Those neurons are sharply s ...
... Auditory information processing in the auditory cortex occurs due to a group of neurons organised in a vertical manner (columnar organisation). The most clear-cut parameter along which this organisation has been observed is the characteristic frequency of the nerve cells. Those neurons are sharply s ...
Lesson1 Powerpoint
... Many visual neurons have excitatory and inhibitory parts to their receptive field. Examples of retinal and LGN cells. ...
... Many visual neurons have excitatory and inhibitory parts to their receptive field. Examples of retinal and LGN cells. ...
Document
... Many visual neurons have excitatory and inhibitory parts to their receptive field. Examples of retinal and LGN cells. ...
... Many visual neurons have excitatory and inhibitory parts to their receptive field. Examples of retinal and LGN cells. ...
Nervous System
... When the CNS interprets the information from sensory neurons, integration takes place. This step involves neurons located entirely within the CNS (Brain & Spinal Cord) and between gray and white matter. ...
... When the CNS interprets the information from sensory neurons, integration takes place. This step involves neurons located entirely within the CNS (Brain & Spinal Cord) and between gray and white matter. ...