Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... _________________ functions such as heart rate, breathing and digestion. 29. The _____________________ controls balance, muscle tone, and ________________ movements. 30. The reticular formation or reticular __________________ system functions in regulating ________________ and __________________. 31 ...
... _________________ functions such as heart rate, breathing and digestion. 29. The _____________________ controls balance, muscle tone, and ________________ movements. 30. The reticular formation or reticular __________________ system functions in regulating ________________ and __________________. 31 ...
Etiopathogenesis of Alzem - Nursing Powerpoint Presentations
... are converted to long-term memories • Thalamus: receives sensory and limbic information and sends to cerebral cortex • Hypothalamus: monitors certain activities and controls body’s internal clock • Limbic system: controls emotions and instinctive behavior (includes the hippocampus and parts of the c ...
... are converted to long-term memories • Thalamus: receives sensory and limbic information and sends to cerebral cortex • Hypothalamus: monitors certain activities and controls body’s internal clock • Limbic system: controls emotions and instinctive behavior (includes the hippocampus and parts of the c ...
Slide ()
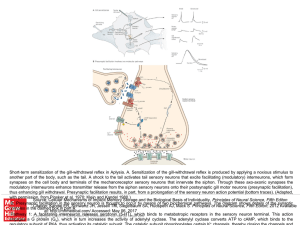
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... B) Complex Reflexes: “polysynaptic” Sensory neuron communicates with motor neuron via interneuron Slight delay between stimulus & response i.e.: Withdrawl reflex ...
... B) Complex Reflexes: “polysynaptic” Sensory neuron communicates with motor neuron via interneuron Slight delay between stimulus & response i.e.: Withdrawl reflex ...
Chapter Summary Visual Stimulus Light is part of the
... The optic nerve is called the optic tract beyond the optic chiasm. The optic track travels to the superior colliculus, which is important in the detection of movement, and to the lateral geniculate nucleus, which is an important way station for processing visual input. The lateral geniculate nucleus ...
... The optic nerve is called the optic tract beyond the optic chiasm. The optic track travels to the superior colliculus, which is important in the detection of movement, and to the lateral geniculate nucleus, which is an important way station for processing visual input. The lateral geniculate nucleus ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
03. Neurons and Nerves
... are many kinds of neurons. They differ in size, structure and function. ...
... are many kinds of neurons. They differ in size, structure and function. ...
Ch. 3 Discovering Psy Behaving Brain Video
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
Name
... 2. tumors formed by over-reproduction of glial cells; commonly known as brain tumors 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve ...
... 2. tumors formed by over-reproduction of glial cells; commonly known as brain tumors 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve ...
Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
Slide 1
... and tissue in the body. They are like a blank microchip that can ultimately be programmed to perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function, such as in the skin, muscle or brain. Additionally ...
... and tissue in the body. They are like a blank microchip that can ultimately be programmed to perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function, such as in the skin, muscle or brain. Additionally ...
Using Breakthroughs in Visual Neuroscience to
... neural circuits process and integrate visual signals. For example, recording the impulses from clusters of retinal ganglion cells, which transmit visual input from the eye to the brain, allows researchers to characterize completely the information presented to the visual parts of the brain. The next ...
... neural circuits process and integrate visual signals. For example, recording the impulses from clusters of retinal ganglion cells, which transmit visual input from the eye to the brain, allows researchers to characterize completely the information presented to the visual parts of the brain. The next ...
Study Guide 3
... 23. Describe two ways in which processing in the retina might affect our visual perception. 24, Which cells in the retina produce action potentials? Which do not? 25. What is accommodation? How does it occur? 26. What is light-adaptation? What causes it, and why do we need it? 27. What is dark-adapt ...
... 23. Describe two ways in which processing in the retina might affect our visual perception. 24, Which cells in the retina produce action potentials? Which do not? 25. What is accommodation? How does it occur? 26. What is light-adaptation? What causes it, and why do we need it? 27. What is dark-adapt ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... 20. If a neuron can only send an ON or OFF signal, how can information about stimulus intensity be contained in that signal? (11.3) 21. How does an action potential from one neuron create a graded potential in a target neuron? (11.5) 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what ...
... 20. If a neuron can only send an ON or OFF signal, how can information about stimulus intensity be contained in that signal? (11.3) 21. How does an action potential from one neuron create a graded potential in a target neuron? (11.5) 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what ...
How Does the Brain Work?
... of the axon releases neurotransmitters —chemicals that cross a microscopic gap, or synapse — to stimulate other neurons nearby. The process may be repeated thousands of times to create a circuit of electrical signals that produces movement, emotion, a sensory experience or thought. Actually, a neuro ...
... of the axon releases neurotransmitters —chemicals that cross a microscopic gap, or synapse — to stimulate other neurons nearby. The process may be repeated thousands of times to create a circuit of electrical signals that produces movement, emotion, a sensory experience or thought. Actually, a neuro ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... • Acetylcholine (ACh): stimulates muscles, memory formation, learning • Epinephrine: (adrenaline) fight-or-flight • Norepinephrine: fight-or-flight • Dopamine: reward, pleasure (“high”) – Loss of dopamine Parkinson’s Disease • Serotonin: well-being, happiness – Low levels Depression • GABA: inhi ...
... • Acetylcholine (ACh): stimulates muscles, memory formation, learning • Epinephrine: (adrenaline) fight-or-flight • Norepinephrine: fight-or-flight • Dopamine: reward, pleasure (“high”) – Loss of dopamine Parkinson’s Disease • Serotonin: well-being, happiness – Low levels Depression • GABA: inhi ...
White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections
... spontaneous recovery. I hypothesize that the migrated white blood cells serve to recover neuronal damage. In this project, I focus on this interesting phenomenon, which can be detected rarely, but occurs spontaneously, and aim to clarify the physiological significance. 4. Anticipated effects and fut ...
... spontaneous recovery. I hypothesize that the migrated white blood cells serve to recover neuronal damage. In this project, I focus on this interesting phenomenon, which can be detected rarely, but occurs spontaneously, and aim to clarify the physiological significance. 4. Anticipated effects and fut ...
Getting on your Nerves
... They can be classified according to their structure, (which is closely related to their function) ...
... They can be classified according to their structure, (which is closely related to their function) ...