Name
... _____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands _____ 9. Sensory receptors found in muscle and tendons, which detect their degree of stretch _____ 10. Changes, occurring within or outside the body, that affect nervous system functioning. _____ 11. Neuron that conducts ...
... _____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands _____ 9. Sensory receptors found in muscle and tendons, which detect their degree of stretch _____ 10. Changes, occurring within or outside the body, that affect nervous system functioning. _____ 11. Neuron that conducts ...
Neural coding in the primary olfactory cortex
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
Other Receptive-Field Properties
... elongated receptive fields in striate cortex? Hubel and Wiesel Suggested concentric LGN cells that feed into a cortical cell are all in a row ...
... elongated receptive fields in striate cortex? Hubel and Wiesel Suggested concentric LGN cells that feed into a cortical cell are all in a row ...
Nerve cord
... Neuron: nerve cell with a unique structure for receiving and passing on information. Sensory Neuron: nerve cells that detect stimuli Interneurons: nerve cells that pass information between neurons Motor neurons: nerve cells that carry response information to muscles and other organs ...
... Neuron: nerve cell with a unique structure for receiving and passing on information. Sensory Neuron: nerve cells that detect stimuli Interneurons: nerve cells that pass information between neurons Motor neurons: nerve cells that carry response information to muscles and other organs ...
Why light
... Others were raised in environments comprised of mainly horizontally oriented stimuli. Both sets of kittens were then tested by placing them in an environment with both types of orientation. Kittens raised in vertical environments ignored the horizontally oriented parts of their environments. Kittens ...
... Others were raised in environments comprised of mainly horizontally oriented stimuli. Both sets of kittens were then tested by placing them in an environment with both types of orientation. Kittens raised in vertical environments ignored the horizontally oriented parts of their environments. Kittens ...
Slide ()
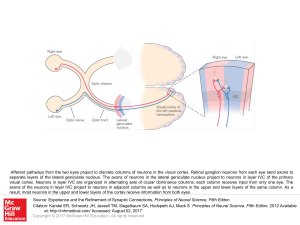
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
specimen jar craft - National Wildlife Federation
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
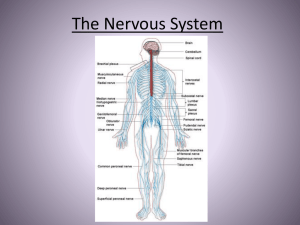
The Nervous System
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... question is the peripheral nervous system. Sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion are located along the spinal cord; they derive during development from common progenitor cells which differentiate into many types of neurons that are mediating sensory information (touch, pain, heat, cold, and pr ...
... question is the peripheral nervous system. Sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion are located along the spinal cord; they derive during development from common progenitor cells which differentiate into many types of neurons that are mediating sensory information (touch, pain, heat, cold, and pr ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Simplest nerve pathway Many psychologists think this is how all nervous systems work ...
... Simplest nerve pathway Many psychologists think this is how all nervous systems work ...
Abstract View ; The Salk Inst, San Diego, CA, USA
... visual system of Manduca sexta (Sphingidae, Lepidoptera) reveal two cell classes that are sensitive to the retreat or approach of an object. Stimulation with different looming stimuli and illusions (such as a rotating spiral) reveals that these cell types use different visual cues to determine direc ...
... visual system of Manduca sexta (Sphingidae, Lepidoptera) reveal two cell classes that are sensitive to the retreat or approach of an object. Stimulation with different looming stimuli and illusions (such as a rotating spiral) reveals that these cell types use different visual cues to determine direc ...
Plants and Pollinators
... bend projections of hair cells and stimulate the endings of sensory neurons ...
... bend projections of hair cells and stimulate the endings of sensory neurons ...
Ch. 2 the LGN and Striate Cortex
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can
... antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs. yellow) without being antagonistic for the location of the stimuli. Both are generated by neural processing in the retina. (C) In the auditory system, primary neurons are excited by single tones. The outline of this excitatory area is known as the tuning curve. ...
... antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs. yellow) without being antagonistic for the location of the stimuli. Both are generated by neural processing in the retina. (C) In the auditory system, primary neurons are excited by single tones. The outline of this excitatory area is known as the tuning curve. ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
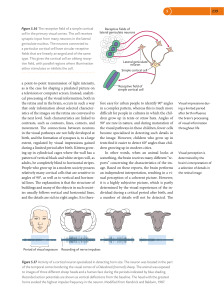
... Figure 5.56 The receptive field of a simple cortical cell in the primary visual cortex. The cell receives synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same ...
... Figure 5.56 The receptive field of a simple cortical cell in the primary visual cortex. The cell receives synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same ...
Slide ()
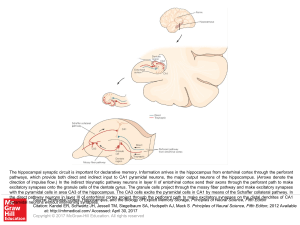
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
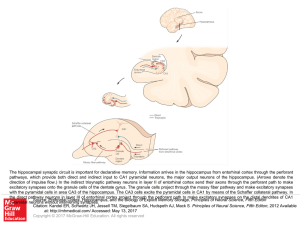
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
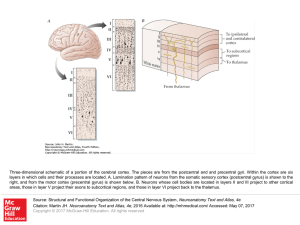
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
Lec17BioImProc
... 1. Light hyperpolarizes the rod and excites the bipolar cell below it 2. But inhibitory connections through horizontal cells suppress signals 3. Best response to localized “dot” 4. While stimulating surround only lowers firing rate What is this??? Convolution!!! Im*[-1 2 –1] ...
... 1. Light hyperpolarizes the rod and excites the bipolar cell below it 2. But inhibitory connections through horizontal cells suppress signals 3. Best response to localized “dot” 4. While stimulating surround only lowers firing rate What is this??? Convolution!!! Im*[-1 2 –1] ...
KC Kajander GJ Giesler, Jr. KJ Gingrich JH Byrne YS Chan J
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... and the role that sensory experience has in shaping cortical circuits. In a new line of research, further work focuses on the interaction between the neural and vascular systems Our results have shown that neurons participating in different pathways (eg. callosal – connecting the two hemispheres ver ...
... and the role that sensory experience has in shaping cortical circuits. In a new line of research, further work focuses on the interaction between the neural and vascular systems Our results have shown that neurons participating in different pathways (eg. callosal – connecting the two hemispheres ver ...
Lecture 5 - TeachLine
... What do we mean by “why” in science? What is the primary goal of neuroscience? ...
... What do we mean by “why” in science? What is the primary goal of neuroscience? ...
Lecture 3
... outweighs inhibition, the cell may reach threshold causing another action potential. The cycle begins again in the next cell. ...
... outweighs inhibition, the cell may reach threshold causing another action potential. The cycle begins again in the next cell. ...