ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... Nerve impulses pass down the dendrite, through the cell body, and down the axon. At the end of the axon, the signal reaches a fluid-filled space (synapse) separating the end of the axon from the dendrite of the ...
... Nerve impulses pass down the dendrite, through the cell body, and down the axon. At the end of the axon, the signal reaches a fluid-filled space (synapse) separating the end of the axon from the dendrite of the ...
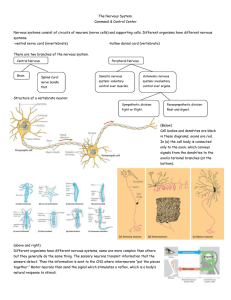
Nervous System
... animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of the brain and spinal cord. The cranial nerves, sp ...
... animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of the brain and spinal cord. The cranial nerves, sp ...
28.1_Responses
... Review List three body systems that work together to create a response to a stimulus Sequence What is the correct sequence of the following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups ...
... Review List three body systems that work together to create a response to a stimulus Sequence What is the correct sequence of the following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups ...
Biology Option Review Section E
... birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the beaches where they were born as they were able to survive themselves, thus t ...
... birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the beaches where they were born as they were able to survive themselves, thus t ...
Researchers find that neurons in the primary visual cortex listen to
... Researchers find that neurons in the primary visual cortex listen to just a small subset of synaptic inputs 5 February 2015, by Bob Yirka has not been clear is the relative importance each neuron places on the information received from each of the inputs. The difficulty in solving this mystery has b ...
... Researchers find that neurons in the primary visual cortex listen to just a small subset of synaptic inputs 5 February 2015, by Bob Yirka has not been clear is the relative importance each neuron places on the information received from each of the inputs. The difficulty in solving this mystery has b ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam1_050117_final_solution
... and smooth muscle receive this regulatory tone directly from …postganglionic fibers…… that are linked to the central units. The efferent segment of the pupillary reflex belongs to this system. Activation of the center called …Edinger-Westphal……... nucleus and its downstream ganglion called …… ………… r ...
... and smooth muscle receive this regulatory tone directly from …postganglionic fibers…… that are linked to the central units. The efferent segment of the pupillary reflex belongs to this system. Activation of the center called …Edinger-Westphal……... nucleus and its downstream ganglion called …… ………… r ...
Sensory Physiology
... – Did you activate neurons with low as well as high threshold for activation? ...
... – Did you activate neurons with low as well as high threshold for activation? ...
3-2_UniqueFt_of_Neurons
... connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the dendrites) axon: one long (depends on the specie and the service site) cable-like project ...
... connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the dendrites) axon: one long (depends on the specie and the service site) cable-like project ...
chapter 4
... neurons that carry information up the spinal cord to the medulla. From there, nerve tracts cross over, and the information is conveyed through the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex, which contains a map of the body. “Phantom limb” appears to originate in stimulation of adjacent somatorysensory ar ...
... neurons that carry information up the spinal cord to the medulla. From there, nerve tracts cross over, and the information is conveyed through the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex, which contains a map of the body. “Phantom limb” appears to originate in stimulation of adjacent somatorysensory ar ...
MAPPINGS BETWEEN BRAINS - Wichita State University
... process? Do the neurons fire just once or do they continue to take in input and evaluate it and fire another decision until the decisions are irrelevant? Why are the brains neurons able to receive many inputs at the same time, but only give one output at a time? ...
... process? Do the neurons fire just once or do they continue to take in input and evaluate it and fire another decision until the decisions are irrelevant? Why are the brains neurons able to receive many inputs at the same time, but only give one output at a time? ...
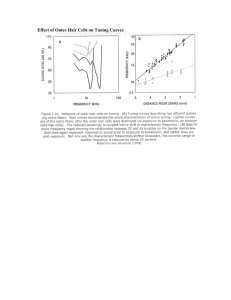
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... waves elicit maximal responses at the basal end of the membrane, near the stapes, whereas lowfrequency sounds induce maxima at the other end, near the apex of the cochlea. The membrane has been "uncoiled" in this illustration to show the sensory hair cells, each studded with stiff rods called stereo ...
... waves elicit maximal responses at the basal end of the membrane, near the stapes, whereas lowfrequency sounds induce maxima at the other end, near the apex of the cochlea. The membrane has been "uncoiled" in this illustration to show the sensory hair cells, each studded with stiff rods called stereo ...
Nervous System Notes - Mrs. Franco's Biology & Anatomy Page
... TYPES OF NEUROGLIA IN CNS Astrocytes – star shaped cells ...
... TYPES OF NEUROGLIA IN CNS Astrocytes – star shaped cells ...
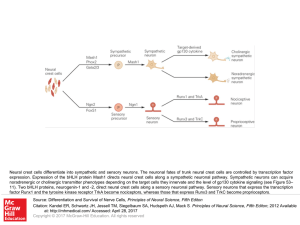
Slide ()
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... Receptive field 2 is less common and is antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs. yellow) without being antagonistic for the location of the stimuli. Both are generated by neural processing in the retina. (C) In the auditory system, primary neurons are excited by single tones. The outline of this excita ...
... Receptive field 2 is less common and is antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs. yellow) without being antagonistic for the location of the stimuli. Both are generated by neural processing in the retina. (C) In the auditory system, primary neurons are excited by single tones. The outline of this excita ...
Final Exam - UF Psychology
... b. inputs from the two eyes converge on neurons in the lateral geniculate body. c. form and color of an object are processed in parallel with its movement and location. d. the retinotectal pathway is critical to analysis of the biological relevance of a stimulus. e. primary visual cortex contains ce ...
... b. inputs from the two eyes converge on neurons in the lateral geniculate body. c. form and color of an object are processed in parallel with its movement and location. d. the retinotectal pathway is critical to analysis of the biological relevance of a stimulus. e. primary visual cortex contains ce ...
Psychophysics ppt. - Ms. Engel @ South
... the sensory receptor which causes a change in the release of NT which modifies the firing rate in neurons with which these cells form synapses and so on until the information reaches the brain • Sensory experience: see color, taste bitter, hear low tone ...
... the sensory receptor which causes a change in the release of NT which modifies the firing rate in neurons with which these cells form synapses and so on until the information reaches the brain • Sensory experience: see color, taste bitter, hear low tone ...
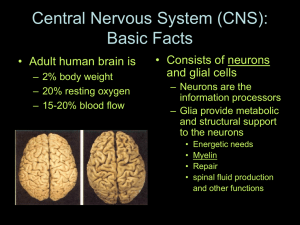
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
Temporal Cortex
... MT: 1. Direction-selective cells for moving bar or moving dots 2. Columnar organization of direction selectivity 3. RF larger than those of V1 cells 4. Some MT cells (20%) are “pattern direction-selective” 5. Lesion of MT cells impairs motion perception ...
... MT: 1. Direction-selective cells for moving bar or moving dots 2. Columnar organization of direction selectivity 3. RF larger than those of V1 cells 4. Some MT cells (20%) are “pattern direction-selective” 5. Lesion of MT cells impairs motion perception ...
Striate cortex April 2009
... • Livingstone and Hubel recorded from cells inside the blob regions, and found that they showed no orientation preference, but instead were concentric, and over half of them responded to color variation ...
... • Livingstone and Hubel recorded from cells inside the blob regions, and found that they showed no orientation preference, but instead were concentric, and over half of them responded to color variation ...
The visual system
... patients with no significant group improvement there was a correlation between the magnitude of the response to dose of Ldopa and the magnitude of the postsurgical improvement. 4) graft placement – grafts only innervate tissue 2-3 mm from the graft site so benefits will depend on the location of the ...
... patients with no significant group improvement there was a correlation between the magnitude of the response to dose of Ldopa and the magnitude of the postsurgical improvement. 4) graft placement – grafts only innervate tissue 2-3 mm from the graft site so benefits will depend on the location of the ...
What a Frog s Eye tells the Frog s brain
... 1. Local sharp edges and contrast 2. the curvature of edge of a dark contrast 3. the movement of edges 4. the local dimming produced by movement or rapid general darkening Each group of fibers serving one operation maps the retina continuously in a single sheet of endings in the frog’s brain. Th ...
... 1. Local sharp edges and contrast 2. the curvature of edge of a dark contrast 3. the movement of edges 4. the local dimming produced by movement or rapid general darkening Each group of fibers serving one operation maps the retina continuously in a single sheet of endings in the frog’s brain. Th ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... Information about these stimuli are transmitted to the central nervous system for processing and may trigger hormonal, chemical, or behavioral adjustments that maintain homeostasis. 2. The major types of sensory receptors are chemo-, photo-, mechano-, thermo-, proprio-, electro- and pain receptors. ...
... Information about these stimuli are transmitted to the central nervous system for processing and may trigger hormonal, chemical, or behavioral adjustments that maintain homeostasis. 2. The major types of sensory receptors are chemo-, photo-, mechano-, thermo-, proprio-, electro- and pain receptors. ...
P312Ch04C_BeyondV1
... 3) May be a separate area in the inferotemporal lobe containing neurons which respond to face-like stimuli. The fusiform face area has been identified in humans. It’s under the temporal lobe. 4) Ramachandran has suggested that there may be as many as 30 different processing modules. Each one contain ...
... 3) May be a separate area in the inferotemporal lobe containing neurons which respond to face-like stimuli. The fusiform face area has been identified in humans. It’s under the temporal lobe. 4) Ramachandran has suggested that there may be as many as 30 different processing modules. Each one contain ...