The Nervous System
... • In order to maintain homeostasis, organisms must be able to respond to internal and external stimuli. • In order to be able to respond to stimuli, the human body needs the nervous system to bring messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the ner ...
... • In order to maintain homeostasis, organisms must be able to respond to internal and external stimuli. • In order to be able to respond to stimuli, the human body needs the nervous system to bring messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the ner ...
Neural Tissue
... Lining of ventricles & central canal Some regions ciliated Some specialized to produce CSF ...
... Lining of ventricles & central canal Some regions ciliated Some specialized to produce CSF ...
Vision
... Cortical cells have receptive fields too Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
... Cortical cells have receptive fields too Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
Vision - Dave Brodbeck
... • Cortical cells have receptive fields too • Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells • Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
... • Cortical cells have receptive fields too • Receptive field in cortex relates to much bigger area that receptive field in retina, so , many ganglion cells • Only adjacent areas of visual field in centre have colossal connections ...
The Primary Visual C..
... • Note that the central region is oblong and not circular as was the case for the center-surround receptive field of the retinal ganglion cells. • Also, the surround region is now located only on the sides. In this particular cell, the inhibitory region is located in the center, not on the sides ...
... • Note that the central region is oblong and not circular as was the case for the center-surround receptive field of the retinal ganglion cells. • Also, the surround region is now located only on the sides. In this particular cell, the inhibitory region is located in the center, not on the sides ...
Slide ()
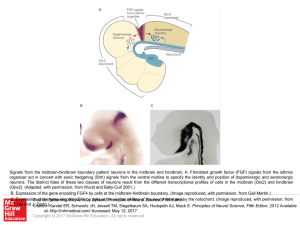
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
awl review q answers
... integrates these sources of information to determine appropriate behavioural strategies. When there is a deviation from homeostatic norms of, for example, body fluid-level, behaviour is biased in favour of seeking and ingesting water. This is the negative feedback mode of control, where, with the he ...
... integrates these sources of information to determine appropriate behavioural strategies. When there is a deviation from homeostatic norms of, for example, body fluid-level, behaviour is biased in favour of seeking and ingesting water. This is the negative feedback mode of control, where, with the he ...
Topology - UCSB Physics
... topology of the wiring is more important than physical location. The exact wiring in the cortex is not known, because there are far too many connections (thousands per neuron) and the connections themselves are small, but may follow a convoluted path over long distance. Fortunately, it may be unnece ...
... topology of the wiring is more important than physical location. The exact wiring in the cortex is not known, because there are far too many connections (thousands per neuron) and the connections themselves are small, but may follow a convoluted path over long distance. Fortunately, it may be unnece ...
Visual Processing - West Virginia University
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
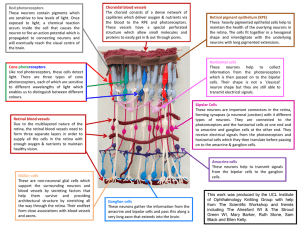
Click here to view a labelled image of the Knitted Retina
... These heavily pigmented epithelial cells help to maintain the health of the overlying neurons in the retina. The cells fit together in a hexagonal shape and interdigitate with the underlying neurons with long pigmented extensions. ...
... These heavily pigmented epithelial cells help to maintain the health of the overlying neurons in the retina. The cells fit together in a hexagonal shape and interdigitate with the underlying neurons with long pigmented extensions. ...
013368718X_CH31_483
... information about the body’s environment G. Chemical that transmits an impulse across a synapse to another cell H. Tough, transparent layer of cells through which light enters the eye I. Fluid-filled inner ear structure lined with hair cells J. Quick, automatic response to a stimulus ...
... information about the body’s environment G. Chemical that transmits an impulse across a synapse to another cell H. Tough, transparent layer of cells through which light enters the eye I. Fluid-filled inner ear structure lined with hair cells J. Quick, automatic response to a stimulus ...
File
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensions or processes (nerve “fibers”) which conduct impulses. There are two types of processes: 1. Dendrites – shorter, more numerous. These, along with the cell body, form the receptive surfaces of neurons. 2. Axons – single, long “ ...
... C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensions or processes (nerve “fibers”) which conduct impulses. There are two types of processes: 1. Dendrites – shorter, more numerous. These, along with the cell body, form the receptive surfaces of neurons. 2. Axons – single, long “ ...
2015 Midterm Exam
... 56. In contrast to the thalamic relay nuclei, the neurons of the reticular nucleus (RTN) release the neurotransmitter [GABA / Glutamate]. 57. Axons collaterals of the [L5 pyramidal tract / L6 corticothalamic] neurons synapse onto the RTN for disynaptic inhibition of the thalamocortical neurons. 58-6 ...
... 56. In contrast to the thalamic relay nuclei, the neurons of the reticular nucleus (RTN) release the neurotransmitter [GABA / Glutamate]. 57. Axons collaterals of the [L5 pyramidal tract / L6 corticothalamic] neurons synapse onto the RTN for disynaptic inhibition of the thalamocortical neurons. 58-6 ...
MS Word - GEOCITIES.ws
... Coding – conversion of an item’s physical features into specific pattern of _________ activity, which represents those features in the brain ...
... Coding – conversion of an item’s physical features into specific pattern of _________ activity, which represents those features in the brain ...
1-nervous_system
... Predictable, automatic response to stimuli 5 parts--Sensory receptor--->sensory neuron---> integrating center (processing center)---> motor neuron--->effector (completes action) ...
... Predictable, automatic response to stimuli 5 parts--Sensory receptor--->sensory neuron---> integrating center (processing center)---> motor neuron--->effector (completes action) ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... sense the missing limb. Originally thought to be caused by signals coming from the spinal cord from scar tissue. Now thought to originate from representation areas as they are remapped (other functions expand into the area for the lost limb). ...
... sense the missing limb. Originally thought to be caused by signals coming from the spinal cord from scar tissue. Now thought to originate from representation areas as they are remapped (other functions expand into the area for the lost limb). ...
04/09 PPT
... -- Depth Perception for near objects (<100 ft). binocular disparity The difference between the images of an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for ...
... -- Depth Perception for near objects (<100 ft). binocular disparity The difference between the images of an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for ...
E.2 - Perception of Stimuli
... react by slamming on the breaks. But, this “reaction time” process has taken up a certain amount of time. What nervous system processes needed to happen? Describe it, including what your motor neurons, sensory neurons, and relay neurons did during that process. ...
... react by slamming on the breaks. But, this “reaction time” process has taken up a certain amount of time. What nervous system processes needed to happen? Describe it, including what your motor neurons, sensory neurons, and relay neurons did during that process. ...
Automatic unconscious knowledge
... Automatic unconscious knowledge - Tsushima, Sasaki, & Watanabe (2006). Science, 314. ...
... Automatic unconscious knowledge - Tsushima, Sasaki, & Watanabe (2006). Science, 314. ...
graded potentials
... hyperpolarize and produce graded potentials • Photoreceptors use glutamate as transmitter • Bipolar cells can both hyperpolarize and depolarize producing both ON and OFF responses • ON bipolar – glutamate is inhibitory • OFF bipolar – glutamate is excitatory ...
... hyperpolarize and produce graded potentials • Photoreceptors use glutamate as transmitter • Bipolar cells can both hyperpolarize and depolarize producing both ON and OFF responses • ON bipolar – glutamate is inhibitory • OFF bipolar – glutamate is excitatory ...
The Nervous System
... •These are the suport cells in the peripheral nervous system. •Schwann cells provide the myelin sheath for peripheral axons. •Satellite cells serve a slightly similar function to astrocytes, supporting the cell bodies of peripheral neurons. ...
... •These are the suport cells in the peripheral nervous system. •Schwann cells provide the myelin sheath for peripheral axons. •Satellite cells serve a slightly similar function to astrocytes, supporting the cell bodies of peripheral neurons. ...