Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Behavior genetics: the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences Environment: every external influence, from prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us Chromosomes: threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain genes DNA: (deoxyribonucleic a ...
... Behavior genetics: the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences Environment: every external influence, from prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us Chromosomes: threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain genes DNA: (deoxyribonucleic a ...
Click here to get the file
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
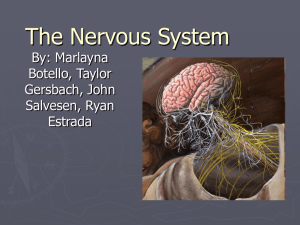
The Nervous System - Kirchner-WHS
... trough the body and up the spinal cord towards the brain, which then transmits and processes information. ...
... trough the body and up the spinal cord towards the brain, which then transmits and processes information. ...
Exam - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
Sensory Systems
... __________________: respond to movement, pressure, and tension. Photoreceptors: respond to variations of light Chemoreceptors: respond to ______________ Thermoreceptors: respond to changes in temperature Pain receptors respond to tissue ____________ ...
... __________________: respond to movement, pressure, and tension. Photoreceptors: respond to variations of light Chemoreceptors: respond to ______________ Thermoreceptors: respond to changes in temperature Pain receptors respond to tissue ____________ ...
pptx
... What brain parts are important to cognition? How do we discover the role of each brain part? ...
... What brain parts are important to cognition? How do we discover the role of each brain part? ...
Design of Intelligent Machines Heidi 2005
... They are significantly bigger than minicolumns, typically around 0.3-0.5 mm and have 4000-8000 neurons ...
... They are significantly bigger than minicolumns, typically around 0.3-0.5 mm and have 4000-8000 neurons ...
The dorsal anterior cingulate cortex ( BA32) in autism: an
... and 11 controls (28.1 ± 3.9 years) matched for age, gender and hemisphere, were obtained via the Autism Tissue Program (USA) with LREC approval. A 1-in-4 series of sections were immunolabelled to detect MAP2+ neurons (clone HM2, Sigma), and analysed using customised software (Image Pro Plus, Version ...
... and 11 controls (28.1 ± 3.9 years) matched for age, gender and hemisphere, were obtained via the Autism Tissue Program (USA) with LREC approval. A 1-in-4 series of sections were immunolabelled to detect MAP2+ neurons (clone HM2, Sigma), and analysed using customised software (Image Pro Plus, Version ...
The Nervous System
... • Fastest responses go only to the spinal cord, not all the way to the brain ...
... • Fastest responses go only to the spinal cord, not all the way to the brain ...
The Visual System: Periphery and Retina
... density in the foveal region- this is the region you use for focus. In the foveal region, ganglion cells receive input from single cones (ultra-high acuity vision) while in peripheral retina there is extensive convergence for greater sensitivity and less acuity. ...
... density in the foveal region- this is the region you use for focus. In the foveal region, ganglion cells receive input from single cones (ultra-high acuity vision) while in peripheral retina there is extensive convergence for greater sensitivity and less acuity. ...
Year 9 Biology Part B Revision Excretory System Name the organs
... Anything that causes the body to stop working normally ...
... Anything that causes the body to stop working normally ...
Anatomy of the basal ganglia - Gonda Brain Research Center
... • Essential for several types of learning ...
... • Essential for several types of learning ...
What is CDNF?
... What is CDNF? • Conserved Dopamine Neurotrophic Factor • Growth factor known as a trophic factor • Stimulates the growth of neurons ...
... What is CDNF? • Conserved Dopamine Neurotrophic Factor • Growth factor known as a trophic factor • Stimulates the growth of neurons ...
Abbreviated 11-15
... Parvocellular cells have greater spatial resolution, but lower temporal resolution, than the magnocellular cells. ...
... Parvocellular cells have greater spatial resolution, but lower temporal resolution, than the magnocellular cells. ...
Chapter 9: Nervous System guide—Please complete these notes on
... synaptic vesicles release a neurotransmitter, which reacts with receptors on the next neuron 25. 2 excitatory neurotransmitters are (increase sodium ion permeability which may trigger nerve impulses) Acetylcholine, Norepinephrine ...
... synaptic vesicles release a neurotransmitter, which reacts with receptors on the next neuron 25. 2 excitatory neurotransmitters are (increase sodium ion permeability which may trigger nerve impulses) Acetylcholine, Norepinephrine ...
Chapter 13 - Nervous Tissue
... Defined: like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust and respond to stimuli the body receives. It includes the brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, and associated peripheral nerves. ...
... Defined: like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust and respond to stimuli the body receives. It includes the brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, and associated peripheral nerves. ...
A Guided Tour of the Brain
... For many years, it was thought that the mature brain could lose neurons, but not grow new ones. But new studies showed that the hippocampus, a brain structure that plays a vital role in forming new memories, has the ability to generate new neurons throughout the lifespan. Studies since this discover ...
... For many years, it was thought that the mature brain could lose neurons, but not grow new ones. But new studies showed that the hippocampus, a brain structure that plays a vital role in forming new memories, has the ability to generate new neurons throughout the lifespan. Studies since this discover ...
CHAPTER 11 Nervous Tissue - Austin Community College
... Defined: like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust and respond to stimuli the body receives. It includes the brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, and associated peripheral nerves. ...
... Defined: like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust and respond to stimuli the body receives. It includes the brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, and associated peripheral nerves. ...
Chapter 6
... a line perpendicular to their lengths A sine-wave grating is designated by its spatial frequency, or the relative width of the bands, measured in cycles per degree of visual angle The most important visual information is that contained in low spatial frequencies ...
... a line perpendicular to their lengths A sine-wave grating is designated by its spatial frequency, or the relative width of the bands, measured in cycles per degree of visual angle The most important visual information is that contained in low spatial frequencies ...
Part 1 (nerve impulses, ppt file)
... and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by using conductors placed on the body. This is called an electrocardiogram ...
... and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by using conductors placed on the body. This is called an electrocardiogram ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... This growth is not due to new neurons, as the vast majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain ...
... This growth is not due to new neurons, as the vast majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain ...
The Nervous System
... impulse from neuron to neuron Excitatory- cause next neuron to fire Inhibitory- prevent next neuron from firing ...
... impulse from neuron to neuron Excitatory- cause next neuron to fire Inhibitory- prevent next neuron from firing ...
Nervous System
... • Allows animals to interact with their environment • Brain and spinal cord: central nervous system (CNS) • Other nerves: peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
... • Allows animals to interact with their environment • Brain and spinal cord: central nervous system (CNS) • Other nerves: peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
GBA deficiency promotes SNCA/α-synuclein accumulation through
... (A) Autophagy level and GBA protein level in two transgenic mice overexpressing HsSNCA. The SNCA level was significantly higher in cortex of transgenic mice (TG) than wild type (WT), followed by decreased LC3-II and GBA protein level. (B, C) Decreased cell viability and increased LDH release by GBA ...
... (A) Autophagy level and GBA protein level in two transgenic mice overexpressing HsSNCA. The SNCA level was significantly higher in cortex of transgenic mice (TG) than wild type (WT), followed by decreased LC3-II and GBA protein level. (B, C) Decreased cell viability and increased LDH release by GBA ...
Neural Development
... These neurons then migrate from their birthplace to a final destination in the brain. They collect together to form each of the various brain structures and acquire specific ways of transmitting nerve messages. Their processes, or axons, grow long distances to find and connect with appropriate partn ...
... These neurons then migrate from their birthplace to a final destination in the brain. They collect together to form each of the various brain structures and acquire specific ways of transmitting nerve messages. Their processes, or axons, grow long distances to find and connect with appropriate partn ...