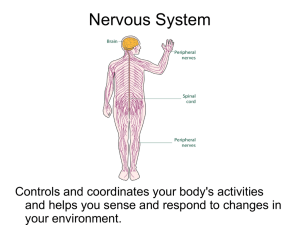
The Nervous System
... system. This can cause paralysis, sensory disturbances, or blindness. There are a couple of tests that can help diagnose multiple sclerosis, such as a MRI and spinal tap. Unfortunately there is no cure for this and only limited treatment of medications and physical therapy. ...
... system. This can cause paralysis, sensory disturbances, or blindness. There are a couple of tests that can help diagnose multiple sclerosis, such as a MRI and spinal tap. Unfortunately there is no cure for this and only limited treatment of medications and physical therapy. ...
Chapter 13
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
Focusing on connections and signaling mechanisms to
... mammals is perhaps the most dramatic form of activity-dependent plasticity in a circuit that is already fully formed and functional, and in those respects resembles learning. Monocular visual deprivation produces a series of changes in responses to the two eyes as well as a substantial rewiring of c ...
... mammals is perhaps the most dramatic form of activity-dependent plasticity in a circuit that is already fully formed and functional, and in those respects resembles learning. Monocular visual deprivation produces a series of changes in responses to the two eyes as well as a substantial rewiring of c ...
A new method to generate neurons effectively from cultured SH
... We found that the neuronal proportion of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells was significantly iicreased after 3 and 7 day treatment of CM-hNSCs and RA compared to that with only RA treatment, in which about 90% of differentiated cells showing positive beta-III tubulin staining, a well-accepted neuronal ma ...
... We found that the neuronal proportion of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells was significantly iicreased after 3 and 7 day treatment of CM-hNSCs and RA compared to that with only RA treatment, in which about 90% of differentiated cells showing positive beta-III tubulin staining, a well-accepted neuronal ma ...
Pt2Localization - MemoryAndCognition
... specific person – how could that happen? Hypothesis 1: specificity tuning – a particular neuron could selectively fire when you see that person ...
... specific person – how could that happen? Hypothesis 1: specificity tuning – a particular neuron could selectively fire when you see that person ...
vikram_slides1
... 2) Total # of spikes is duration dependent Voting: Which (1 or 2) would you guess to be correct? 2) was actually found to be true!, if one of the stimulus duration was reduced by 50% ...
... 2) Total # of spikes is duration dependent Voting: Which (1 or 2) would you guess to be correct? 2) was actually found to be true!, if one of the stimulus duration was reduced by 50% ...
Nervous System
... (electrochemical changes) which are transmitted along peripheral nerves to the CNS ...
... (electrochemical changes) which are transmitted along peripheral nerves to the CNS ...
File
... carrying information from one part of the body to another • Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibres or nerve cells. Source: HSL3 (2006) pp 191 ...
... carrying information from one part of the body to another • Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibres or nerve cells. Source: HSL3 (2006) pp 191 ...
Slide 1
... nerve cells, or neurons, which usually show numerous long processes are responsible for the reception, transmission, processing of stimuli; the triggering of certain cell activities; the release of neurotransmitters and other informational molecules. ...
... nerve cells, or neurons, which usually show numerous long processes are responsible for the reception, transmission, processing of stimuli; the triggering of certain cell activities; the release of neurotransmitters and other informational molecules. ...
Neurons
... Nervous systems have two categories of cells: • Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable— they generate and transmit electrical signals, called action potentials. • Afferent neurons carry sensory information into the nervous ...
... Nervous systems have two categories of cells: • Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable— they generate and transmit electrical signals, called action potentials. • Afferent neurons carry sensory information into the nervous ...
X- and Y-Cells in the Dorsal Lateral Geniculate
... (Fig. 2A), poor activation by fast visual stimuli (Fig. 2B), and no activation by fast targets of appropriate contrast to excite the cell through the surround. The difference between X- and Y-cells based on the tonic-phasic distinction was particularly dramatic in the owl monkey. All ...
... (Fig. 2A), poor activation by fast visual stimuli (Fig. 2B), and no activation by fast targets of appropriate contrast to excite the cell through the surround. The difference between X- and Y-cells based on the tonic-phasic distinction was particularly dramatic in the owl monkey. All ...
Small System of Neurons
... ideas from experience and to retain those ideas in memory. What changes occur in the brain when we learn and how is this information retained in the brain? ...
... ideas from experience and to retain those ideas in memory. What changes occur in the brain when we learn and how is this information retained in the brain? ...
Chapter 3: The nerve cell Multiple Choice Questions (1
... 19. Some working assumptions in the study of neurons and their connections include a. a simplified neuron to build cognitive models from artificial neural nets b. connections are either inhibitory or excitatory c. most neural connections are two-way d. all of the above 20.Finding one’s way home in t ...
... 19. Some working assumptions in the study of neurons and their connections include a. a simplified neuron to build cognitive models from artificial neural nets b. connections are either inhibitory or excitatory c. most neural connections are two-way d. all of the above 20.Finding one’s way home in t ...
AP Practice unit 3 and 4
... 50. Imagine that a softball player wears special glasses that shift her visual field upward 20 degrees. This means that when the player wears these glasses, everything appears higher than it actually is. With practice the player can hit a ball with the glasses on. What will happen when the player f ...
... 50. Imagine that a softball player wears special glasses that shift her visual field upward 20 degrees. This means that when the player wears these glasses, everything appears higher than it actually is. With practice the player can hit a ball with the glasses on. What will happen when the player f ...
Sensory receptors
... • Involuntary oscillations of the eyes, when spin is stopped. Eyes continue to move in direction opposite to spin, then jerk rapidly back to midline. • When person spins, the bending of cupula occurs in the opposite direction. • As the spin continues, the cupula straightens. • Endolymph and cupula a ...
... • Involuntary oscillations of the eyes, when spin is stopped. Eyes continue to move in direction opposite to spin, then jerk rapidly back to midline. • When person spins, the bending of cupula occurs in the opposite direction. • As the spin continues, the cupula straightens. • Endolymph and cupula a ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
Introduction
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
irons.conroeisd.net
... sensory and motor information throughout the body in the form of electrical impulses. ...
... sensory and motor information throughout the body in the form of electrical impulses. ...
File
... • Receptor detects signal, impulse passed from one neuron to the next in spinal cord, heading to brain while attach same time impulses are traveling along the motor neuron to the effector and the effector responds first ...
... • Receptor detects signal, impulse passed from one neuron to the next in spinal cord, heading to brain while attach same time impulses are traveling along the motor neuron to the effector and the effector responds first ...
Exercise 17
... Nissl bodies: elaborate type of rough ER; involved in the metabolic activity of the the cell Dendrites: are receptive regions that bear receptors for neurotransmitters released by other neurons Axons: are nerve impulse generators and transmitters Collaterals: branches of axons from neurons Axon Hill ...
... Nissl bodies: elaborate type of rough ER; involved in the metabolic activity of the the cell Dendrites: are receptive regions that bear receptors for neurotransmitters released by other neurons Axons: are nerve impulse generators and transmitters Collaterals: branches of axons from neurons Axon Hill ...
bio12_sm_11_1
... Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do not provide nerve transmission themselves. 4. Reflexes have evolved to occur without the need for t ...
... Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do not provide nerve transmission themselves. 4. Reflexes have evolved to occur without the need for t ...
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
... Integration within a modality: Integration across time. To understand the dynamic nature of the sensory world, information present at one time has to be related to and linked with information that is present earlier and later. For example, the sequential stimulation of multiple visual receptors, cor ...
... Integration within a modality: Integration across time. To understand the dynamic nature of the sensory world, information present at one time has to be related to and linked with information that is present earlier and later. For example, the sequential stimulation of multiple visual receptors, cor ...