Nervous System
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
Slide 1
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
Slide ()
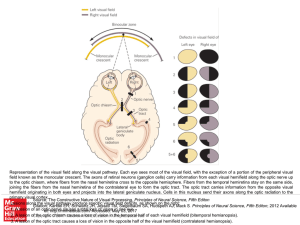
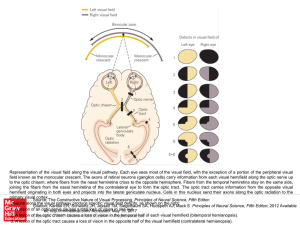
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
Slide ()
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
Visual Field - Warren`s Science Page
... Makes mistake because of nervous system construction Sensory inputs of ...
... Makes mistake because of nervous system construction Sensory inputs of ...
Development of the central nervous system
... A. Motor horn cell with naked rootlet. B. In the spinal cordoligodendroglia cells surround the ventral rootlet; outside the spinal cord, Schwann cells begin to surround the rootlet. C. In the spinal cord the myelin sheath is formed by oligodendroglia cells; outside the spinal cord the sheath is for ...
... A. Motor horn cell with naked rootlet. B. In the spinal cordoligodendroglia cells surround the ventral rootlet; outside the spinal cord, Schwann cells begin to surround the rootlet. C. In the spinal cord the myelin sheath is formed by oligodendroglia cells; outside the spinal cord the sheath is for ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... a. am individual reflexively withdraws from a pain stimulus. b. an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. c. a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. d. dendrites transmit more electrical signals to axons. e. positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membran ...
... a. am individual reflexively withdraws from a pain stimulus. b. an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. c. a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. d. dendrites transmit more electrical signals to axons. e. positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membran ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... responses to changes. 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolar ...
... responses to changes. 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolar ...
Part 1 - Kirkwood Community College
... • Is the same as other cells in that it… – Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus – Is the major biosynthetic center – Has well-developed RER (Nissle bodies) • Is different from other cells in that it… – Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes – Has no centrioles • (hence its amitot ...
... • Is the same as other cells in that it… – Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus – Is the major biosynthetic center – Has well-developed RER (Nissle bodies) • Is different from other cells in that it… – Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes – Has no centrioles • (hence its amitot ...
Brainfunction - Oakton Community College
... networks occurs throughout life but does require more time and effort during adulthood. ...
... networks occurs throughout life but does require more time and effort during adulthood. ...
Nervous System - Westminster College
... Voltage changes from -70 mV to +40 mV. At +40 mV sodium channels close – negative feedback loop ...
... Voltage changes from -70 mV to +40 mV. At +40 mV sodium channels close – negative feedback loop ...
Neurotransmission
... Peripheral Nervous System – Composed of nerve branches arising from the brain and spinal cord ...
... Peripheral Nervous System – Composed of nerve branches arising from the brain and spinal cord ...
Sensation
... Thus, our sense organs are really just change detectors. Example – Feed lots in Greeley. ...
... Thus, our sense organs are really just change detectors. Example – Feed lots in Greeley. ...
Paper
... In order to investigate whether and how medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of the rat is involved in processing of information related to fear conditioning, we recorded from single units in the prelimbic and infralimbic cortex of fear-conditioned rats in response to an explicit conditional stimulus (CS ...
... In order to investigate whether and how medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of the rat is involved in processing of information related to fear conditioning, we recorded from single units in the prelimbic and infralimbic cortex of fear-conditioned rats in response to an explicit conditional stimulus (CS ...
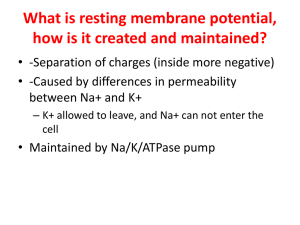
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... • Occurs because myelin insulates the current and does not allow it to leak out ...
... • Occurs because myelin insulates the current and does not allow it to leak out ...
Spatial Working Memory
... world, closely related to consciousness. Working memory contents, under some circumstances, may be converted into long-term memory stores. One early but still influential model of working memory (Baddeley and Hitch) entails a central executive (for top-down attention, manipulation etc.) over several ...
... world, closely related to consciousness. Working memory contents, under some circumstances, may be converted into long-term memory stores. One early but still influential model of working memory (Baddeley and Hitch) entails a central executive (for top-down attention, manipulation etc.) over several ...
Overview of the Day
... terminal branches of axon (forms junctions with other cells) myelin sheath (insulates axons and helps speed their impulses) ...
... terminal branches of axon (forms junctions with other cells) myelin sheath (insulates axons and helps speed their impulses) ...
Frog Vision
... • The four tectal sheets of neurons essentially provide a recoding of the retinal image. • The retinal image is specified in terms of luminance at each receptor - this description is redundant and not useful to frog. • Tectal neurons recode each small region on retina in terms of 4 basic features or ...
... • The four tectal sheets of neurons essentially provide a recoding of the retinal image. • The retinal image is specified in terms of luminance at each receptor - this description is redundant and not useful to frog. • Tectal neurons recode each small region on retina in terms of 4 basic features or ...
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... ANN, the landscape artist, is standing at her easel, painting with her right hand as she looks out the window at her garden. She is listening to classical music as she paints. Brain ...
... ANN, the landscape artist, is standing at her easel, painting with her right hand as she looks out the window at her garden. She is listening to classical music as she paints. Brain ...
poster - Stanford University
... neuromodulation by acetylcholine is a potential mechanism for evoking synchrony during bottom-up stimulus selection. ...
... neuromodulation by acetylcholine is a potential mechanism for evoking synchrony during bottom-up stimulus selection. ...
Nervous System Vocab1 - Everglades High School
... 25. Synaptic Cleft: The separation between neurons 26. Myelin: whitish, fatty material that protects and insulates the fibers 27. Myelin Sheath: A tight coil of wrapped membranes encloses the axon 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or i ...
... 25. Synaptic Cleft: The separation between neurons 26. Myelin: whitish, fatty material that protects and insulates the fibers 27. Myelin Sheath: A tight coil of wrapped membranes encloses the axon 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or i ...
multiple choice
... 6) Aggressive behaviors A) need not be an actual attack. B) include actual attacks against another organism. C) include those involved in predation. D) are often associated with reproduction. E) All of the above are correct. 7) According to Darwin, the expressions of emotion in humans A) involve mus ...
... 6) Aggressive behaviors A) need not be an actual attack. B) include actual attacks against another organism. C) include those involved in predation. D) are often associated with reproduction. E) All of the above are correct. 7) According to Darwin, the expressions of emotion in humans A) involve mus ...