Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activat ...
... a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activat ...
Chapter 02_Quiz - Biloxi Public Schools
... B) projection areas C) association areas D) temporal lobes ...
... B) projection areas C) association areas D) temporal lobes ...
sensory1
... lips, palm, fingertip, calf). For touch discrimination, small receptive fields allow greater accuracy in “two point discrimination” test (upcoming lab!) ...
... lips, palm, fingertip, calf). For touch discrimination, small receptive fields allow greater accuracy in “two point discrimination” test (upcoming lab!) ...
Unit M - Notes #1 Neurons - Mr. Lesiuk
... 1. Motor Neurons -Efferent Neuron: Carries the nerve impulse from the Central Nervous System (Exiting the CNS) and heading toward an effector (organ/gland). -Relays messages from the brain or spinal cord to the muscles and organs. *Short Dendrites – Long Axon ...
... 1. Motor Neurons -Efferent Neuron: Carries the nerve impulse from the Central Nervous System (Exiting the CNS) and heading toward an effector (organ/gland). -Relays messages from the brain or spinal cord to the muscles and organs. *Short Dendrites – Long Axon ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system does what it does by virtue of its connections to other components ...
... The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system does what it does by virtue of its connections to other components ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... Young infants can be classically conditioned most easily when a. a conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with an unconditioned stimulus. b. the conditioned response is fear. c. the association between two stimuli has survival value. d. a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned response. ...
... Young infants can be classically conditioned most easily when a. a conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with an unconditioned stimulus. b. the conditioned response is fear. c. the association between two stimuli has survival value. d. a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned response. ...
PNS/Reflexes
... IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things can happen to produce this effect A. Peripheral adaptation- some sensory neurons can adapt to constant stimuli; that is, they begin to requ ...
... IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things can happen to produce this effect A. Peripheral adaptation- some sensory neurons can adapt to constant stimuli; that is, they begin to requ ...
Neurophysiology: Sensing and categorizing
... In early sensory areas of the cerebral cortex, stimulus representation appears to depend almost exclusively on elementary physical attributes, such as the orientation of visual edges, the frequency of an auditory tone, or the pressure of a somatosensory stimulus applied to the skin. Neural responses ...
... In early sensory areas of the cerebral cortex, stimulus representation appears to depend almost exclusively on elementary physical attributes, such as the orientation of visual edges, the frequency of an auditory tone, or the pressure of a somatosensory stimulus applied to the skin. Neural responses ...
L6. Thalamus (László Acsády) All cortical areas receive thalamic
... cerebral cortex, but thalamic nuclei have strong reciprocal connections with the cerebral cortex, forming thalamo-cortico-thalamic circuits that are believed to be involved with consciousness. The thalamus plays a major role in regulating arousal, the level of awareness, and activity. The thalamic m ...
... cerebral cortex, but thalamic nuclei have strong reciprocal connections with the cerebral cortex, forming thalamo-cortico-thalamic circuits that are believed to be involved with consciousness. The thalamus plays a major role in regulating arousal, the level of awareness, and activity. The thalamic m ...
Dopamine axons of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
Answers
... Return to “BRAIN BASICS,” scroll down and click on “Compare the Brains of 9 Species.” Take the test to see how many brains you can identify. 1. How many did you answer correctly? _____________ 2. Which animal has the smallest brain of those pictured? ___LEAST WEASEL___________ 3. Which animal has th ...
... Return to “BRAIN BASICS,” scroll down and click on “Compare the Brains of 9 Species.” Take the test to see how many brains you can identify. 1. How many did you answer correctly? _____________ 2. Which animal has the smallest brain of those pictured? ___LEAST WEASEL___________ 3. Which animal has th ...
Biology 360: Motor Behaviors and Review 1) What is a central
... 3) You are at an aquarium admiring the red belly of the red-bellied stickleback fish when an employee tells you it is their mating season. You notice the males are swimming around normally in the tank, but as soon as they see another red-bellied stickleback fish, they immediately attack the other ma ...
... 3) You are at an aquarium admiring the red belly of the red-bellied stickleback fish when an employee tells you it is their mating season. You notice the males are swimming around normally in the tank, but as soon as they see another red-bellied stickleback fish, they immediately attack the other ma ...
CHANGES OF THE CELL BODY OF NEURONS IN CENTRAL
... structural changes (staining of histological specimens of toluidine blue) and behavioral reactions (open field test). In morphological investigations we observed structurally modified neurons in the gray matter of the cerebrum, cerebellum and the spinal cord of all experimental groups of mice, but i ...
... structural changes (staining of histological specimens of toluidine blue) and behavioral reactions (open field test). In morphological investigations we observed structurally modified neurons in the gray matter of the cerebrum, cerebellum and the spinal cord of all experimental groups of mice, but i ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems
... receive messages from other cells Soma – cell body; contains nucleus and keeps cell healthy Axon – passes messages away from cell body to other neurons, muscles, glands Myelin Sheath – covers axon of neurons Axon Terminals – points of departure; onto next neurons dendrites ...
... receive messages from other cells Soma – cell body; contains nucleus and keeps cell healthy Axon – passes messages away from cell body to other neurons, muscles, glands Myelin Sheath – covers axon of neurons Axon Terminals – points of departure; onto next neurons dendrites ...
Introductory Assignment to the Nervous System
... do we call the tiny space between neurons over which signals must pass from neuron to neuron? What do we call the electrical signals that have reached the end of an axon and have become chemical signals? What special nerve cells allow us to see, hear, feel, taste, and smell the world around us? ...
... do we call the tiny space between neurons over which signals must pass from neuron to neuron? What do we call the electrical signals that have reached the end of an axon and have become chemical signals? What special nerve cells allow us to see, hear, feel, taste, and smell the world around us? ...
Slide 1
... Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must find compromises between two seemingly mut ...
... Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must find compromises between two seemingly mut ...
Neural Decoding www.AssignmentPoint.com Neural decoding is a
... we find to be the most salient aspects of the input stimulus. As these images hit the back of our retina, these stimuli are converted from varying wavelengths to a series of neural spikes called action potentials. These pattern of action potentials are different for different objects and different c ...
... we find to be the most salient aspects of the input stimulus. As these images hit the back of our retina, these stimuli are converted from varying wavelengths to a series of neural spikes called action potentials. These pattern of action potentials are different for different objects and different c ...
Lecture 13A
... “Even before the evolution of a central brain, nervous systems took advantage of a simple computing trick: competition. Neurons act like candidates in an election, each one shouting and trying to suppress its fellows. At any moment only a few neurons win that intense competition, their signals risin ...
... “Even before the evolution of a central brain, nervous systems took advantage of a simple computing trick: competition. Neurons act like candidates in an election, each one shouting and trying to suppress its fellows. At any moment only a few neurons win that intense competition, their signals risin ...
Pattern Vision and Natural Scenes
... sensitivity of many cortical neurons, each tuned to a particular range of frequencies. Similarly (but not shown), behavioral contrast sensitivity as a function of orientation reflects the combined neural contrast sensitivity of many cortical neurons each tuned to a particular range of orientations. ...
... sensitivity of many cortical neurons, each tuned to a particular range of frequencies. Similarly (but not shown), behavioral contrast sensitivity as a function of orientation reflects the combined neural contrast sensitivity of many cortical neurons each tuned to a particular range of orientations. ...
Endocrine System PowerPoint
... Only cells that have receptors that are complementary to a specific hormone will respond to that hormone Some receptors are on most cells e.g. Insulin receptor Some receptors are on only a relatively small number of cells e.g. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone receptors Cells can have receptors for more t ...
... Only cells that have receptors that are complementary to a specific hormone will respond to that hormone Some receptors are on most cells e.g. Insulin receptor Some receptors are on only a relatively small number of cells e.g. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone receptors Cells can have receptors for more t ...
The Nervous System funtions and neuron
... a. Large and surrounded by myelin sheath (made of lipids) b. Contains Schwann Cells i. Myelinated nerve fibers/ produce the myelin ii. Between each Schwann cell is a space called Nodes of ...
... a. Large and surrounded by myelin sheath (made of lipids) b. Contains Schwann Cells i. Myelinated nerve fibers/ produce the myelin ii. Between each Schwann cell is a space called Nodes of ...
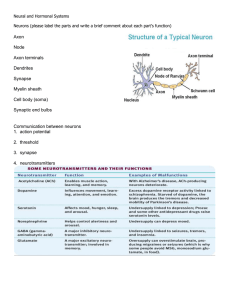
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
file - Athens Academy
... A. if the membrane potential reaches a threshold value. B. when negative proteins and ions rapidly enter the cell. C. when the inside of the cell becomes negative compared to the outside. D. when there is repolarization. E. All of these are correct. ...
... A. if the membrane potential reaches a threshold value. B. when negative proteins and ions rapidly enter the cell. C. when the inside of the cell becomes negative compared to the outside. D. when there is repolarization. E. All of these are correct. ...
Sparse but not `Grandmother-cell` coding in the medial temporal lobe
... neurons. This is clearly not the case for our human data and it is plausible that the additional delay of !100– 200 ms is due to high-level processing needed to transform visual percepts into memories to be stored. It is common to remember abstract concepts and not details, unless attention is expli ...
... neurons. This is clearly not the case for our human data and it is plausible that the additional delay of !100– 200 ms is due to high-level processing needed to transform visual percepts into memories to be stored. It is common to remember abstract concepts and not details, unless attention is expli ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Module 4 – Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - division of the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the ______________________ muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. ...
... Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - division of the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the ______________________ muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. ...