Movement
... Figure 8.9 Map of body areas in the primary motor cortex. Stimulation at any point in the primary motor cortex is most likely to evoke movements in the body areas shown. However, actual results are usually messier than this figure implies: For example, individual cells controlling one finger may be ...
... Figure 8.9 Map of body areas in the primary motor cortex. Stimulation at any point in the primary motor cortex is most likely to evoke movements in the body areas shown. However, actual results are usually messier than this figure implies: For example, individual cells controlling one finger may be ...
Myotatic Reflex
... 2) locations of source synapses on the target neuron. • for an individual synapse, effectiveness is related to synaptic location on the target neuron most effective {axon hillock >> soma >> proximal dendrite >> distal dendrite} least effective • a given amount of synaptic input will have more effect ...
... 2) locations of source synapses on the target neuron. • for an individual synapse, effectiveness is related to synaptic location on the target neuron most effective {axon hillock >> soma >> proximal dendrite >> distal dendrite} least effective • a given amount of synaptic input will have more effect ...
chapter review questions
... During the events involved in information transfer across a chemical synapse, which of the following steps would be directly interrupted by exposing a neuron to a ...
... During the events involved in information transfer across a chemical synapse, which of the following steps would be directly interrupted by exposing a neuron to a ...
Impact on Perception, Attention, and Memory
... cortical responses to emotionally salient stimuli. One possible means by which the amygdala may modulate sensory cortical regions is through reciprocal connections. The amygdala receives input from the sensory cortex that allows the detection of an emotionally salient event and then, in turn, it mod ...
... cortical responses to emotionally salient stimuli. One possible means by which the amygdala may modulate sensory cortical regions is through reciprocal connections. The amygdala receives input from the sensory cortex that allows the detection of an emotionally salient event and then, in turn, it mod ...
Stereotyped responses of Drosophila peptidergic neuronal
... At the end of larval life, Drosophila enters the prepupal stage, then ecdyses to a pupa to initiate the transformation to the adult that occurs during metamorphosis. Pupal ecdysis consists of a sequence of behavioral subroutines, which starts with the preparatory behavior of pre-ecdysis, during whic ...
... At the end of larval life, Drosophila enters the prepupal stage, then ecdyses to a pupa to initiate the transformation to the adult that occurs during metamorphosis. Pupal ecdysis consists of a sequence of behavioral subroutines, which starts with the preparatory behavior of pre-ecdysis, during whic ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... attach to the skeleton, and intrafusal fibers, which attach to the extrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers produce the force that acts on bones and other structures. Intrafusal fibers also produce force, but they are much smaller than extrafusal fibers and the level of force that they produce is neglig ...
... attach to the skeleton, and intrafusal fibers, which attach to the extrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers produce the force that acts on bones and other structures. Intrafusal fibers also produce force, but they are much smaller than extrafusal fibers and the level of force that they produce is neglig ...
Hypothalamic Regulation of Sleep
... sleep (summarized in Shiromani et al. 1987). A disturbance in biological rhythms has been implicated in this disorder (Shiromani et al. 1987). Seasonal affective disorder, or “winter depression” is one example of how changes in external light cues affects mood. Light therapy has proven to be effecti ...
... sleep (summarized in Shiromani et al. 1987). A disturbance in biological rhythms has been implicated in this disorder (Shiromani et al. 1987). Seasonal affective disorder, or “winter depression” is one example of how changes in external light cues affects mood. Light therapy has proven to be effecti ...
Nervous Tissue
... Unequal distribution of ions in the ECF and cytosol. Inability of most anions to leave the cell. Electrogenic nature of the Na+/K+ ATPases. ...
... Unequal distribution of ions in the ECF and cytosol. Inability of most anions to leave the cell. Electrogenic nature of the Na+/K+ ATPases. ...
hormones
... 4. Compare and contrast the nervous and endocrine system. • They BOTH regulate the body. • They BOTH send messages to different parts of the body. • The endocrine system releases HORMONES. The nervous system transmit IMPULSES. • Endocrine system messages are chemical. Nervous system messages are el ...
... 4. Compare and contrast the nervous and endocrine system. • They BOTH regulate the body. • They BOTH send messages to different parts of the body. • The endocrine system releases HORMONES. The nervous system transmit IMPULSES. • Endocrine system messages are chemical. Nervous system messages are el ...
binding, internalization, and retrograde transport of `251
... no tissue. Background levels, grains per pm2, were constant over each individual grid; these values were used where necessary to correct for background in determining real grain counts. From each grid, one or two grid squares were analyzed. In each square, all of the cellular material was photograph ...
... no tissue. Background levels, grains per pm2, were constant over each individual grid; these values were used where necessary to correct for background in determining real grain counts. From each grid, one or two grid squares were analyzed. In each square, all of the cellular material was photograph ...
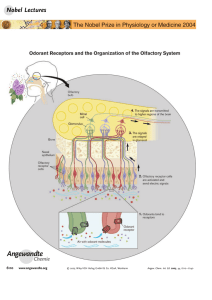
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically masterful and within a few years he devised procedures that permitted the introduction of virtually any gene into any cell in ...
... developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically masterful and within a few years he devised procedures that permitted the introduction of virtually any gene into any cell in ...
BRAIN DYNAMICS AT MULTIPLE SCALES: CAN ONE RECONCILE
... Dynamics in Brain Activity The above results are consistent with the idea that awake brain activity may be associated with high-dimensional dynamics, perhaps analogous to a stochastic system. To further investigate this aspect, we have examined data from animal experiments in which both microscopic ...
... Dynamics in Brain Activity The above results are consistent with the idea that awake brain activity may be associated with high-dimensional dynamics, perhaps analogous to a stochastic system. To further investigate this aspect, we have examined data from animal experiments in which both microscopic ...
Mechanisms of Magnetic Stimulation of Central Nervous System
... (diameter 100 mm, length 16 cm along the x-axis) was placed in a plane parallel to that of the coil (coil radius 2 cm, the axon lay 1 cm from the plane of the coil). As any change perpendicular to the axon (y-axis) is important for stimulating the axon [16,17,21], the coil was moved along the y-axis ...
... (diameter 100 mm, length 16 cm along the x-axis) was placed in a plane parallel to that of the coil (coil radius 2 cm, the axon lay 1 cm from the plane of the coil). As any change perpendicular to the axon (y-axis) is important for stimulating the axon [16,17,21], the coil was moved along the y-axis ...
Neurotransmitters
... postsynaptic cell and are therefore asymmetric in structure and function. The presynaptic terminal, or synaptic bouton, is a specialized area within the axon of the presynaptic cell that contains neurotransmitters enclosed in small membrane-bound spheres called synaptic vesicles. Synaptic vesicles a ...
... postsynaptic cell and are therefore asymmetric in structure and function. The presynaptic terminal, or synaptic bouton, is a specialized area within the axon of the presynaptic cell that contains neurotransmitters enclosed in small membrane-bound spheres called synaptic vesicles. Synaptic vesicles a ...
chapter 4 the evolution of body, brain, behavior, and mind in
... are interconnected by way of a meshwork of vertically aligned bipolar cells and horizontally oriented amacrine cells, and there is a layer of ganglion cells whose axons form the optic nerve (Dowling, 1968; Fig. 4-5B). The processing of visual input begins at the retinal level where many ganglion cel ...
... are interconnected by way of a meshwork of vertically aligned bipolar cells and horizontally oriented amacrine cells, and there is a layer of ganglion cells whose axons form the optic nerve (Dowling, 1968; Fig. 4-5B). The processing of visual input begins at the retinal level where many ganglion cel ...
Optical imaging combined with targeted electrical recordings
... E-mail address: [email protected] (A. Arieli). ...
... E-mail address: [email protected] (A. Arieli). ...
Comparative neuronal morphology of the
... to 5405 cerebral cortex neurons). In terms of digital reconstructions, the Purkinje neuron has been traced much more than other cerebellar neurons, perhaps because of its central role as the sole output neuron for the cerebellar cortex in tetrapods (Marr, 1969; Dean et al., 2010). The most complete ...
... to 5405 cerebral cortex neurons). In terms of digital reconstructions, the Purkinje neuron has been traced much more than other cerebellar neurons, perhaps because of its central role as the sole output neuron for the cerebellar cortex in tetrapods (Marr, 1969; Dean et al., 2010). The most complete ...
View PDF - MRC BNDU - University of Oxford
... 1993; Schwaller et al., 2002; Camp & Wijesinghe, 2009). Understanding the role of neurons expressing these markers can lead to a better understanding of the functions of the PPN, but this necessitates knowledge of their numbers, distribution and expression by neurotransmitter-specific neuronal types ...
... 1993; Schwaller et al., 2002; Camp & Wijesinghe, 2009). Understanding the role of neurons expressing these markers can lead to a better understanding of the functions of the PPN, but this necessitates knowledge of their numbers, distribution and expression by neurotransmitter-specific neuronal types ...
Feedforward and feedback inhibition in neostriatal GABAergic spiny
... presynaptic convergence and divergence and the net effect of the activation of each circuit on the postsynaptic activity of the spiny neuron. These data have revealed that the feedforward inhibition is powerful and widespread, with spiking in a single interneuron being capable of significantly delay ...
... presynaptic convergence and divergence and the net effect of the activation of each circuit on the postsynaptic activity of the spiny neuron. These data have revealed that the feedforward inhibition is powerful and widespread, with spiking in a single interneuron being capable of significantly delay ...
motor neurons
... Properties of the Facilitated Area Terminate on the motor neurons that exciting antigravity muscle of the body (the muscle of vertebral column and the extensor muscle of the limbs). Have a high degree of natural (spontaneous) excitability. Receive especially strong excitatory signals from ves ...
... Properties of the Facilitated Area Terminate on the motor neurons that exciting antigravity muscle of the body (the muscle of vertebral column and the extensor muscle of the limbs). Have a high degree of natural (spontaneous) excitability. Receive especially strong excitatory signals from ves ...
Circuitry and Function of the Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus
... it is not possible to draw strong conclusions about the DCN’s role from its projection to CNIC. One intriguing hypothesis is that there are DCN-like or DCN-related subsystems of the auditory system which exist in the inferior colliculus, medial geniculate, and auditory cortex. Imig and colleagues ha ...
... it is not possible to draw strong conclusions about the DCN’s role from its projection to CNIC. One intriguing hypothesis is that there are DCN-like or DCN-related subsystems of the auditory system which exist in the inferior colliculus, medial geniculate, and auditory cortex. Imig and colleagues ha ...
The basis of the stress reaction
... established by prior learning, or deduced from circumstances, do not match the current or anticipated perceptions of the internal or external environment; this discrepancy between what is observed or sensed and what is expected or programmed elicits patterned, compensatory responses. In extreme unde ...
... established by prior learning, or deduced from circumstances, do not match the current or anticipated perceptions of the internal or external environment; this discrepancy between what is observed or sensed and what is expected or programmed elicits patterned, compensatory responses. In extreme unde ...
Does the Conventional Leaky Integrate-and
... 2- Variation of the delay between pre-synaptic spike arrival and post-synaptic channel opening, in different synapses. (Synaptic noise) 3- The noise due to spontaneous firings of the neurons, which is often treated as a Poisson process. (Spontaneous noise) Thus, if the cortical neural groups are ass ...
... 2- Variation of the delay between pre-synaptic spike arrival and post-synaptic channel opening, in different synapses. (Synaptic noise) 3- The noise due to spontaneous firings of the neurons, which is often treated as a Poisson process. (Spontaneous noise) Thus, if the cortical neural groups are ass ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 16.1 Scanning electron micrograph of a
... extending along filopodia. All of the growing ends of microtubules are pointed toward the leading edge. In contrast, actin (red) is highly concentrated in the filopodia and in the leading edges of lamellae. Within filopodia, actin fibrils are oriented with their growing tips pointed distally. The sa ...
... extending along filopodia. All of the growing ends of microtubules are pointed toward the leading edge. In contrast, actin (red) is highly concentrated in the filopodia and in the leading edges of lamellae. Within filopodia, actin fibrils are oriented with their growing tips pointed distally. The sa ...
In LHRH neurons
... More recently, studies of GT-1 cells and LHRH neurons (from mouse olfactory placode) show that GABA actually stimulates LHRH release, as well as increasing intracellular Ca2+ oscillations and membrane ...
... More recently, studies of GT-1 cells and LHRH neurons (from mouse olfactory placode) show that GABA actually stimulates LHRH release, as well as increasing intracellular Ca2+ oscillations and membrane ...