The Molecular Biology of Memory Storage: A Dialog
... ganglia, each of which contains about 2000 cells (Fig. 2). An individual ganglion, such as the abdominal ganglion, mediates not one but a family of behaviors. Thus, the simplest behaviors that can be modified by learning may involve less than 100 cells. This numerical simplification made it possible ...
... ganglia, each of which contains about 2000 cells (Fig. 2). An individual ganglion, such as the abdominal ganglion, mediates not one but a family of behaviors. Thus, the simplest behaviors that can be modified by learning may involve less than 100 cells. This numerical simplification made it possible ...
posterior pituitary
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) TSH (also known as thyrotropin) – glycoportein consisting of: a b chain of 112 amino acids and an a chain of 89 amino acids. The a chain is identical to that found in two other pituitary hormones, FSH and LH as well as in the hormone chorionic ...
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) TSH (also known as thyrotropin) – glycoportein consisting of: a b chain of 112 amino acids and an a chain of 89 amino acids. The a chain is identical to that found in two other pituitary hormones, FSH and LH as well as in the hormone chorionic ...
USC Brain Project Specific Aims
... Gabor filters. Laurent Itti: CS599 – Computational Architectures in Biological Vision, USC 2004. Lecture 5: Introduction to Vision 2 ...
... Gabor filters. Laurent Itti: CS599 – Computational Architectures in Biological Vision, USC 2004. Lecture 5: Introduction to Vision 2 ...
Pupilllary Light Reflex Pathways
... orbit). Innervation to the dilator mm. of the iris enters the globe via long ciliary nerve (recall the difference between the cat vs. dog), and travel through the suprachoroidal space to anterior segment. Additionally, some fibers pass through the maxillary division of CNV to infraorbital/zygomatic ...
... orbit). Innervation to the dilator mm. of the iris enters the globe via long ciliary nerve (recall the difference between the cat vs. dog), and travel through the suprachoroidal space to anterior segment. Additionally, some fibers pass through the maxillary division of CNV to infraorbital/zygomatic ...
A Role of Central NELL2 in the Regulation of Feeding Behavior in
... of daily body weight gain (–1.8 ± 1.3 g/day, p<0.001 compared to ACSF or SCR; Figs. 2A and 2D). This attenuation of body weight gain appeared in NELL2 AS ODN group is due to an attenuation of food consumption, as rats in this group ate significantly less than that of the control groups (average of d ...
... of daily body weight gain (–1.8 ± 1.3 g/day, p<0.001 compared to ACSF or SCR; Figs. 2A and 2D). This attenuation of body weight gain appeared in NELL2 AS ODN group is due to an attenuation of food consumption, as rats in this group ate significantly less than that of the control groups (average of d ...
Neuronal networks for induced `40 Hz` rhythms
... occur in brief bursts with a considerable jitter in the frequency”, so any correlation could conceivably be smudgedout when measurementsare averagedduring 0.5s runs of an EEG, or 20 cycles at 40 Hz; Ref. 28). However,the reasons for these discrepanciesremain unresolved. Coherent rhythms might have o ...
... occur in brief bursts with a considerable jitter in the frequency”, so any correlation could conceivably be smudgedout when measurementsare averagedduring 0.5s runs of an EEG, or 20 cycles at 40 Hz; Ref. 28). However,the reasons for these discrepanciesremain unresolved. Coherent rhythms might have o ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... olfactory stimuli or visual stimuli such as the sight of food(17) Neurons in the primary taste cortex do not represent the reward value of taste, that is, the appetite for a food, in that their firing is not decreased to zero by feeding the taste to satiety(18,19). The secondary taste cortex A secon ...
... olfactory stimuli or visual stimuli such as the sight of food(17) Neurons in the primary taste cortex do not represent the reward value of taste, that is, the appetite for a food, in that their firing is not decreased to zero by feeding the taste to satiety(18,19). The secondary taste cortex A secon ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology I
... Spinal nerves branch after pass through intervertebral foramina Some join with branches from neighboring nerves to form plexuses Nerve names relate to region innervated Spinal nerves T2-T12 do not form plexuses ...
... Spinal nerves branch after pass through intervertebral foramina Some join with branches from neighboring nerves to form plexuses Nerve names relate to region innervated Spinal nerves T2-T12 do not form plexuses ...
Study Guide
... 1. Know the differences and similarities between SNS, ANS, and ENS. 2. What part of the nervous system are the SNS, ANS, and ENS a subdivision of? 3. Know the functions of SNS, ANS, and ENS are they voluntarily controlled or involuntarily. III. Histology of Nervous Tissue 1. Know the structures of n ...
... 1. Know the differences and similarities between SNS, ANS, and ENS. 2. What part of the nervous system are the SNS, ANS, and ENS a subdivision of? 3. Know the functions of SNS, ANS, and ENS are they voluntarily controlled or involuntarily. III. Histology of Nervous Tissue 1. Know the structures of n ...
Document
... with those of Barth-organ, MC2 and CP2. For the crayfish, Potamobius torrentium, Barth (1934) has described a similar arrangement of the innervation of 'Sinneskegel " but externally these 22-23 sensilla do not appear to be distinct, though they are located in the same general area as the 'slit sensi ...
... with those of Barth-organ, MC2 and CP2. For the crayfish, Potamobius torrentium, Barth (1934) has described a similar arrangement of the innervation of 'Sinneskegel " but externally these 22-23 sensilla do not appear to be distinct, though they are located in the same general area as the 'slit sensi ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... Following injury, distal portion of axon and myelin sheath degenerates Macrophages remove the debris Remaining neurilemma and endoneurium form a tunnel from the point of injury to the effector New Schwann cells grow in the tunnel to maintain a path for regrowth of the axon Cell body reorganizes its ...
... Following injury, distal portion of axon and myelin sheath degenerates Macrophages remove the debris Remaining neurilemma and endoneurium form a tunnel from the point of injury to the effector New Schwann cells grow in the tunnel to maintain a path for regrowth of the axon Cell body reorganizes its ...
in Primate STT Cells Differentially Modulate Brief
... 1996; Miller 1998; Neugebauer et al. 1997, 2000; Schoepp et al. 1999; Schoppa and Westbrook 1997; Schrader and Tasker 1997). An emerging field of research implicates mGluRs in nociception and hyperalgesia. Whereas the first reports on the involvement of mGluRs in spinal nociceptive processing relied ...
... 1996; Miller 1998; Neugebauer et al. 1997, 2000; Schoepp et al. 1999; Schoppa and Westbrook 1997; Schrader and Tasker 1997). An emerging field of research implicates mGluRs in nociception and hyperalgesia. Whereas the first reports on the involvement of mGluRs in spinal nociceptive processing relied ...
1 1 2 3 Efficient Generation of Reciprocal Signals by Inhibition 4 5 6
... linearity of the data, we calculated the Pearson’s correlation coefficient (R). P values ...
... linearity of the data, we calculated the Pearson’s correlation coefficient (R). P values ...
Ch 12
... the skull and is encircled by the bones of the vertebral column. – Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord, each serving a specific region of the body. • Ganglia, located outside the brain and spinal cord, are small masses of nervous tissue, containing primarily cell bodies of ...
... the skull and is encircled by the bones of the vertebral column. – Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord, each serving a specific region of the body. • Ganglia, located outside the brain and spinal cord, are small masses of nervous tissue, containing primarily cell bodies of ...
Chapter 3
... the skull and is encircled by the bones of the vertebral column. – Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord, each serving a specific region of the body. • Ganglia, located outside the brain and spinal cord, are small masses of nervous tissue, containing primarily cell bodies of ...
... the skull and is encircled by the bones of the vertebral column. – Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord, each serving a specific region of the body. • Ganglia, located outside the brain and spinal cord, are small masses of nervous tissue, containing primarily cell bodies of ...
AHD The Telencephalon R. Altman 4-03
... Vasculature of the Basal Nuclei and Related Structures • The blood supply to the caudate and putamen is provided by branches of the medial striate artery, lenticulostriate branches of the M1 segment, and the anterior choroidal artery. – The medial striate artery, usually a branch of A2, serves mu ...
... Vasculature of the Basal Nuclei and Related Structures • The blood supply to the caudate and putamen is provided by branches of the medial striate artery, lenticulostriate branches of the M1 segment, and the anterior choroidal artery. – The medial striate artery, usually a branch of A2, serves mu ...
Recombinant AAV-mediated gene delivery to the central nervous
... efficiency in the striatum has been improved by coinfusing heparin with the viral suspension [38,39]. The rationale was that, since transduced cells were observed only in the close vicinity of the needle tract, viral particles have presumably been trapped by receptors present at high concentrations ...
... efficiency in the striatum has been improved by coinfusing heparin with the viral suspension [38,39]. The rationale was that, since transduced cells were observed only in the close vicinity of the needle tract, viral particles have presumably been trapped by receptors present at high concentrations ...
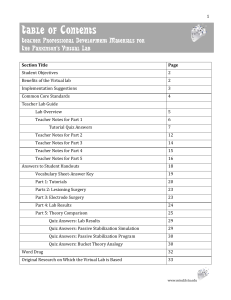
Table of Contents - The Mind Project
... additional theory is brought up later in the lab, students may get a sense of the connection between technology (instruments used to collect scientific data) and science. The Virtual Parkinson’s lab models the important combination of scientists sharing their research with the improvement of technol ...
... additional theory is brought up later in the lab, students may get a sense of the connection between technology (instruments used to collect scientific data) and science. The Virtual Parkinson’s lab models the important combination of scientists sharing their research with the improvement of technol ...
Spontaneous persistent activity in entorhinal cortex modulates
... interactions, whereby MECIII neurons produce a partial decoupling of the CA1 activity from neocortical UDS via their markedly delayed Down transitions and persistent Up states. Notably, the authors found that there was a strong correlation between a neuron’s Down-transition lag and its probability o ...
... interactions, whereby MECIII neurons produce a partial decoupling of the CA1 activity from neocortical UDS via their markedly delayed Down transitions and persistent Up states. Notably, the authors found that there was a strong correlation between a neuron’s Down-transition lag and its probability o ...
Consciousness, biology and quantum hypotheses
... A variety of brain measures converge on the conclusion that the cerebral cortex and its major input hub, the thalamus, are strongly implicated in specific conscious experiences. Damage to the thalamus and cortex impairs conscious functions, sometimes as a state (e.g., deep sleep and coma), and somet ...
... A variety of brain measures converge on the conclusion that the cerebral cortex and its major input hub, the thalamus, are strongly implicated in specific conscious experiences. Damage to the thalamus and cortex impairs conscious functions, sometimes as a state (e.g., deep sleep and coma), and somet ...
Seminar High Performance Computers
... is not a state-based system but rather a pure functional system where every input leads to an output, without any states being stored in between. This implication bares also the fact that without states, the system is free of side-effects. The static character of the neurosynaptic machine model howe ...
... is not a state-based system but rather a pure functional system where every input leads to an output, without any states being stored in between. This implication bares also the fact that without states, the system is free of side-effects. The static character of the neurosynaptic machine model howe ...
Chapter 7 | Pigments and Minerals
... red or the aluminum complex of nuclear fast red, is applied to show the tissue architecture. The reactions of formation and reduction of ...
... red or the aluminum complex of nuclear fast red, is applied to show the tissue architecture. The reactions of formation and reduction of ...
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
... sensory studies of the median, ulnar radial and sural nerves ...
... sensory studies of the median, ulnar radial and sural nerves ...
Pain
... Each taste bud contains taste cells responsive to each of the different taste categories. A given sensory neuron may be stimulated by more than 1 taste cell in # of different taste buds. One sensory fiber may not transmit information specific for only 1 category of taste. Brain interprets the patter ...
... Each taste bud contains taste cells responsive to each of the different taste categories. A given sensory neuron may be stimulated by more than 1 taste cell in # of different taste buds. One sensory fiber may not transmit information specific for only 1 category of taste. Brain interprets the patter ...