3. Linguistic Essentials
... • Nouns – refers to people, animals and things – Dog, tree, person, hat, speech, idea, philosophy – Inflection is a process by which stem of a word can be modified to create new word – English the only form of inflection is one indicating whether a noun is singular or plural – Ex. Dogs, trees, hats, ...
... • Nouns – refers to people, animals and things – Dog, tree, person, hat, speech, idea, philosophy – Inflection is a process by which stem of a word can be modified to create new word – English the only form of inflection is one indicating whether a noun is singular or plural – Ex. Dogs, trees, hats, ...
Repaso: C4G2 Verbs with reflexive pronouns and direct objects 1.
... 3. Irregular: romper -> ____________: broke abrir -> _______________: open ...
... 3. Irregular: romper -> ____________: broke abrir -> _______________: open ...
Grammar Basics - HCC Learning Web
... Interjections Interjections are forceful expressions, usually written with an exclamation point. (examples: Yo! Damn! Gadzooks! Eureka! Oh no!) Note: In formal writing (like the writing you do in college), use interjections (and exclamation points, for that matter) very sparingly. In fact, if you m ...
... Interjections Interjections are forceful expressions, usually written with an exclamation point. (examples: Yo! Damn! Gadzooks! Eureka! Oh no!) Note: In formal writing (like the writing you do in college), use interjections (and exclamation points, for that matter) very sparingly. In fact, if you m ...
Present Tense of Latin Verbs
... • Third person verbs denote action performed by parties other than the speaker or listener. ...
... • Third person verbs denote action performed by parties other than the speaker or listener. ...
Parts of Speech
... (and therefore must be followed by subject and verb) –Most common are: after, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, as if, etc. –Ex: I have known Susan since I was 11. ...
... (and therefore must be followed by subject and verb) –Most common are: after, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, as if, etc. –Ex: I have known Susan since I was 11. ...
Subject – Verb Agreement
... At times you might want to use words like “along with” or “as well” to add something to a sentence’s subject. Unlike “and,” these phrases don’t pluralize the subject. “Paul, along with his friend Greg, is leaving to play racquetball.” “Jane, as well as seventeen other people, is running for student ...
... At times you might want to use words like “along with” or “as well” to add something to a sentence’s subject. Unlike “and,” these phrases don’t pluralize the subject. “Paul, along with his friend Greg, is leaving to play racquetball.” “Jane, as well as seventeen other people, is running for student ...
The FOUR LEVELS OF ANALYSIS
... • PRONOUNS ARE VAGUE AND TAKE THE PLACE OF A NOUN. THEY ARE LAZY: • HE, US, SHE, IT, WE, THEY, THEM, THAT…. • THEY CAN ONLY BE USED AFTER THE ANTECEDENT IS SET. ...
... • PRONOUNS ARE VAGUE AND TAKE THE PLACE OF A NOUN. THEY ARE LAZY: • HE, US, SHE, IT, WE, THEY, THEM, THAT…. • THEY CAN ONLY BE USED AFTER THE ANTECEDENT IS SET. ...
Grammar for Grown-ups
... words that begins with a preposition (on, in, over, under, against, with, among…) and ends with a noun or pronoun. It gives extra information about another word in the sentence. The student in the front row is smart. ...
... words that begins with a preposition (on, in, over, under, against, with, among…) and ends with a noun or pronoun. It gives extra information about another word in the sentence. The student in the front row is smart. ...
Verb Tense Exercises
... second independent clause. • The sopranos sang well. So first prize was awarded to them. “Them” is third-person plural and the object of a preposition. ...
... second independent clause. • The sopranos sang well. So first prize was awarded to them. “Them” is third-person plural and the object of a preposition. ...
PARTS OF SPEECH NOTES • NOUN – person, place, thing, or idea
... An object noun is used as the direct object, indirect object, or object of the preposition. We would often eat our lunch there. ...
... An object noun is used as the direct object, indirect object, or object of the preposition. We would often eat our lunch there. ...
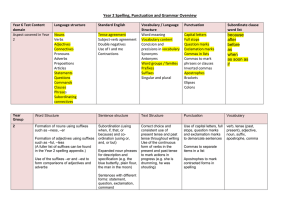
Year 1: Terminology Taught • Letter • Capital letter • Word • Singular
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
Final_Review_Grammar_07_grovesite
... Noun- person, place, thing, or idea Pronoun- replaces a noun Verb- indicates action or state of being Verbal-a verb that acts like another part ...
... Noun- person, place, thing, or idea Pronoun- replaces a noun Verb- indicates action or state of being Verbal-a verb that acts like another part ...
Indefinite Pronouns
... preposition) with some other word or expression in the sentence. Example: The cow jumped over the moon. The preposition "over" links its object, "the moon," to the verb "jump." The river below the bridge is rising. The object of the preposition, "the bridge," is linked to the noun "river" through th ...
... preposition) with some other word or expression in the sentence. Example: The cow jumped over the moon. The preposition "over" links its object, "the moon," to the verb "jump." The river below the bridge is rising. The object of the preposition, "the bridge," is linked to the noun "river" through th ...
collective noun
... Test: substitute am, are, or is for the verb; if the sentence with the new verb still makes sense, then the original verb is a linking verb I smelled the rain. (action) The rain smelled fresh. (linking) ...
... Test: substitute am, are, or is for the verb; if the sentence with the new verb still makes sense, then the original verb is a linking verb I smelled the rain. (action) The rain smelled fresh. (linking) ...
IAAO Style and Usage Guidelines
... first mention of the name or expression, e.g., Private entities need to download the parcel geographic information system (GIS) data into their own mapping systems to satisfy their business requirements [note that in this instance the initialism is capitalized even though the name is not]. Note also ...
... first mention of the name or expression, e.g., Private entities need to download the parcel geographic information system (GIS) data into their own mapping systems to satisfy their business requirements [note that in this instance the initialism is capitalized even though the name is not]. Note also ...
Grammar Unit
... Third person is a person or thing other than the speaker or the person spoken to: He (she, it, they_ will do. ...
... Third person is a person or thing other than the speaker or the person spoken to: He (she, it, they_ will do. ...
Parts of Speech
... (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is a noun. The –ism ending on “patriotism” shows that the word is a noun. Subjects in sentences can be difficult to locate under certain conditions. The following link may provide some helpful tips to understand and locate ...
... (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is a noun. The –ism ending on “patriotism” shows that the word is a noun. Subjects in sentences can be difficult to locate under certain conditions. The following link may provide some helpful tips to understand and locate ...
Year 3 - Crossley Fields
... Concrete nouns name items we can see and touch, while abstract nouns name things that exist only in our minds, such as ‘beauty’, ‘truth’ and ‘justice’. Nouns are an important element in a clause, because they are used to name the subject or object of the verb. For example, in the phrase ‘Max ate chi ...
... Concrete nouns name items we can see and touch, while abstract nouns name things that exist only in our minds, such as ‘beauty’, ‘truth’ and ‘justice’. Nouns are an important element in a clause, because they are used to name the subject or object of the verb. For example, in the phrase ‘Max ate chi ...
Verbs Action Verbs Linking Verbs Verb Tenses: Past (usually end in
... A noun names something you cannot experience with your senses. Sometimes abstract nouns are called "idea nouns." Sandra's courage and curiosity made her a good explorer. It's important to have respect in a friendship. Honesty is usually the best policy. ...
... A noun names something you cannot experience with your senses. Sometimes abstract nouns are called "idea nouns." Sandra's courage and curiosity made her a good explorer. It's important to have respect in a friendship. Honesty is usually the best policy. ...
Parts of Speech Notes
... Word that is used in place of one mor more nouns or pronouns. Example: he, them, several, they Antecedents are words that a pronoun stands for or refers to Personal pronouns refer to the one speaking (first person), the one spoken to (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). Exa ...
... Word that is used in place of one mor more nouns or pronouns. Example: he, them, several, they Antecedents are words that a pronoun stands for or refers to Personal pronouns refer to the one speaking (first person), the one spoken to (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). Exa ...
ENGLISH LANGUAGE – 2° YEAR A HISTORY OF THE ENGLISH
... • All new coinages and foreign borrowings were treated as weak (e.g. daunce(n) – daunced – daunced). • Gradually, formerly strong verbs started to develop weak forms. In such a transitory phase, boh variants may be found. • In Chaucer’s language, both strong and weak past participles can occur in tw ...
... • All new coinages and foreign borrowings were treated as weak (e.g. daunce(n) – daunced – daunced). • Gradually, formerly strong verbs started to develop weak forms. In such a transitory phase, boh variants may be found. • In Chaucer’s language, both strong and weak past participles can occur in tw ...