Brain 1
... (a) A particular experience causes a neuron to fire and transmitter to be released. The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the syna ...
... (a) A particular experience causes a neuron to fire and transmitter to be released. The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the syna ...
Neurons
... membrane will open allowing positively charged sodium ions to rush in At that moment, the charge becomes less negative/even positive, creating an action potential ACTION POTENTIAL- a very brief shift in a neuron’s electrical charge that travels along an axon Voltage change will race down the a ...
... membrane will open allowing positively charged sodium ions to rush in At that moment, the charge becomes less negative/even positive, creating an action potential ACTION POTENTIAL- a very brief shift in a neuron’s electrical charge that travels along an axon Voltage change will race down the a ...
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling
... packages in synaptic vesicles. The arrival of action potential at axon/synaptic terminal depolarizes plasma membrane, opening voltage-gated channels, which allow Ca2+ to diffuse into the synaptic terminal, which forces vesicles to fuse with membrane causing the release of neurotransmitter into the s ...
... packages in synaptic vesicles. The arrival of action potential at axon/synaptic terminal depolarizes plasma membrane, opening voltage-gated channels, which allow Ca2+ to diffuse into the synaptic terminal, which forces vesicles to fuse with membrane causing the release of neurotransmitter into the s ...
here
... 22. Draw a graph and label the following: polarization, stimulus, full depolarization, action potential, repolarization, refractory period. Use units on your y axis. ...
... 22. Draw a graph and label the following: polarization, stimulus, full depolarization, action potential, repolarization, refractory period. Use units on your y axis. ...
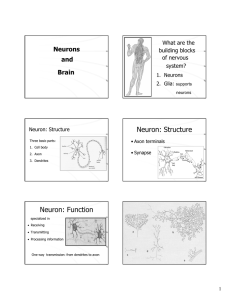
Neuron: Structure Neuron: Function
... How Neurons Communicate One way transmission: from dendrites to axon. 1. Electrical 2. Chemical ...
... How Neurons Communicate One way transmission: from dendrites to axon. 1. Electrical 2. Chemical ...
48 Nervous System PowerPoint
... >Speed of Transmission: Larger axons & Myelin sheath (Saltatory conduction) ...
... >Speed of Transmission: Larger axons & Myelin sheath (Saltatory conduction) ...
Biology Notes: The Nervous System and Neurons
... ReView (at the end of the PowerPoint you should be able to answer these questions) 1. What is the function of the nervous system? 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they incl ...
... ReView (at the end of the PowerPoint you should be able to answer these questions) 1. What is the function of the nervous system? 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they incl ...
Slide ()
... Mechanisms of persistent neuronal activity that may contribute to working memory. When a monkey performs a working memory task neurons in prefrontal cortex fire persistently during the delay period of the task. A. Intrinsic mechanisms of graded persistent activity. A brief depolarizing stimulus to a ...
... Mechanisms of persistent neuronal activity that may contribute to working memory. When a monkey performs a working memory task neurons in prefrontal cortex fire persistently during the delay period of the task. A. Intrinsic mechanisms of graded persistent activity. A brief depolarizing stimulus to a ...
A2.2.2.SecretSignals - jj-sct
... no wonder that you are able to react to stimuli very quickly. Neurons work together to send messages in a hurry, allowing a race car driver to react while driving at intense speeds or a tennis player to return the lightning-fast serve of an opponent. We have looked at the structure of a neuron and w ...
... no wonder that you are able to react to stimuli very quickly. Neurons work together to send messages in a hurry, allowing a race car driver to react while driving at intense speeds or a tennis player to return the lightning-fast serve of an opponent. We have looked at the structure of a neuron and w ...
The Nervous System
... • 2. beating of cilia moves cerebrospinal fluid • 3. fluid nourishes and cushions CNS • 4. creates CSF in the choroid plexi of the brain’s ventricles ...
... • 2. beating of cilia moves cerebrospinal fluid • 3. fluid nourishes and cushions CNS • 4. creates CSF in the choroid plexi of the brain’s ventricles ...
1 Neurons 2 Electrical activity of neurons at rest.
... Neurons are electrically active. They produce large electrical signals called “action potentials” or “spikes” or “nerve impulses” that can travel down the axon and are reliably transmitted to other neurons. Action potentials are considered to be stereotypical and are the main communication units in ...
... Neurons are electrically active. They produce large electrical signals called “action potentials” or “spikes” or “nerve impulses” that can travel down the axon and are reliably transmitted to other neurons. Action potentials are considered to be stereotypical and are the main communication units in ...
Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory period helps to ensure that stimulus only flows in one direction. ...
... back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory period helps to ensure that stimulus only flows in one direction. ...
Anikeeva
... General route for synthesis of monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles that is biocompatible and can attach directly onto the plasma membrane ...
... General route for synthesis of monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles that is biocompatible and can attach directly onto the plasma membrane ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... to K+ than Na+ , K+ moves out of the cell faster than Na+ moves in. • This results in an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane, and an overall external positive charge which is referred to as resting potential. ...
... to K+ than Na+ , K+ moves out of the cell faster than Na+ moves in. • This results in an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane, and an overall external positive charge which is referred to as resting potential. ...
How Does the Brain Work?
... The brain is a multilayered web of cells: nerve cells (neurons) and vastly more numerous glial cells that stabilize the chemical environment and regulate and protect neurons. The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most ev ...
... The brain is a multilayered web of cells: nerve cells (neurons) and vastly more numerous glial cells that stabilize the chemical environment and regulate and protect neurons. The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most ev ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... inside. Negative protein ions on inside. The neuron is said to be polarized. This is due to the Na+/K+ pump. ...
... inside. Negative protein ions on inside. The neuron is said to be polarized. This is due to the Na+/K+ pump. ...
Slide 1 - AccessPhysiotherapy
... Picture of typical neuron with parts labeled by function. A shows a projection interneuron. This is the kind of cell that sends information over a relatively long distance in the nervous system. For example, there are projection neurons with their cell bodies in the cerebral cortex that reach the sp ...
... Picture of typical neuron with parts labeled by function. A shows a projection interneuron. This is the kind of cell that sends information over a relatively long distance in the nervous system. For example, there are projection neurons with their cell bodies in the cerebral cortex that reach the sp ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... cerebrum, medulla oblongata, pons, thalamus, hypothalamus. Know the location and main function of each component. What would be the effect of damage individually to each of these components? (11.8) 36. The cerebral cortex is involved in many complex functions of the brain that require coordination o ...
... cerebrum, medulla oblongata, pons, thalamus, hypothalamus. Know the location and main function of each component. What would be the effect of damage individually to each of these components? (11.8) 36. The cerebral cortex is involved in many complex functions of the brain that require coordination o ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... cell body: contains nucleus & organelles dendrites: receive incoming messages axons: transmit messages away to other cells myelin sheath: fatty insulation covering axon, speeds up nerve impulses • synapse: junction between 2 neurons • neurotransmitter: chemical messengers sent across synapse • Glia: ...
... cell body: contains nucleus & organelles dendrites: receive incoming messages axons: transmit messages away to other cells myelin sheath: fatty insulation covering axon, speeds up nerve impulses • synapse: junction between 2 neurons • neurotransmitter: chemical messengers sent across synapse • Glia: ...
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... deteriorates, leading in extreme cases to multiple sclerosis. Your brain is vastly more complex than a computer, but slower at executing simple responses. Commit Figure 4.2 to memory; it is crucial to understanding further material in this course. ...
... deteriorates, leading in extreme cases to multiple sclerosis. Your brain is vastly more complex than a computer, but slower at executing simple responses. Commit Figure 4.2 to memory; it is crucial to understanding further material in this course. ...
PNS and Transmission
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...