Chapter 3
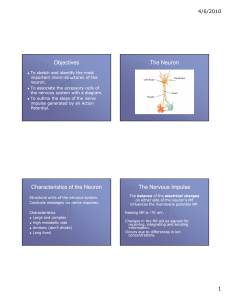
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
Mind Is Matter
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
PPT
... Decades ago, a common treatment of epilepsy was to cut the corpus callosum, which is the main connection between the hemispheres, in order to limit the spreading of epileptic activity. These split-brain patients typically behaved and felt like healthy people in everyday life situations. In laborator ...
... Decades ago, a common treatment of epilepsy was to cut the corpus callosum, which is the main connection between the hemispheres, in order to limit the spreading of epileptic activity. These split-brain patients typically behaved and felt like healthy people in everyday life situations. In laborator ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
Madison Pejsa Pd.4
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
Ch 8 Neurons and Network properties part-1
... Graded potentials decrease in strength as they spread out from the point of origin but may bring about an action potential. ...
... Graded potentials decrease in strength as they spread out from the point of origin but may bring about an action potential. ...
Neurophysiology Complete
... Excitability: the ability to respond to stimuli and convert it to nerve impulses Conductivity: the ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles or glands In a resting neuron, the outside is more positive than the inside Resting membrane potential: the difference in electrical charges th ...
... Excitability: the ability to respond to stimuli and convert it to nerve impulses Conductivity: the ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles or glands In a resting neuron, the outside is more positive than the inside Resting membrane potential: the difference in electrical charges th ...
Brain Questions
... 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripher ...
... 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripher ...
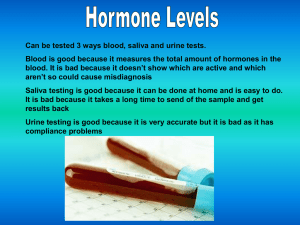
Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... The human brain consists of a large number of neurons that are interconnected with each other. On average, each neuron is connected to other neurons through about 10 000 synapses. The brain network of neurons forms a massively parallel information processing system. This contrasts with conventional ...
... The human brain consists of a large number of neurons that are interconnected with each other. On average, each neuron is connected to other neurons through about 10 000 synapses. The brain network of neurons forms a massively parallel information processing system. This contrasts with conventional ...
(friendship) of neurons
... each other to control the body A brain with only one neuron is not a brain ...
... each other to control the body A brain with only one neuron is not a brain ...
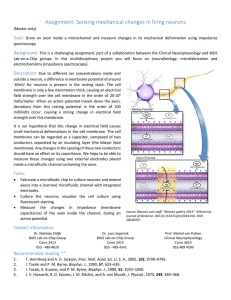
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deforma ...
... Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deforma ...
Module Worksheet - Germantown School District
... Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
... Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES Name: Section: Date: ______
... • Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
... • Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
Recording Action Potentials from Cockroach Mechanoreceptors
... to the resting level. Often, however, a neurophysiologist does not need to know the actual changes in the membrane potential, but only when an action potential occurs. In this case, an extracellular recording is usually adequate. Electrodes are placed outside a neuron to record the electrical potent ...
... to the resting level. Often, however, a neurophysiologist does not need to know the actual changes in the membrane potential, but only when an action potential occurs. In this case, an extracellular recording is usually adequate. Electrodes are placed outside a neuron to record the electrical potent ...
PsychSim 5 neural messages
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
click - Uplift Education
... 10) Describe the function(s) of each of the following PNS neuroglia: ...
... 10) Describe the function(s) of each of the following PNS neuroglia: ...
Carrie Heath
... 3. What is the function of the basal ganglia and what three nuclei constitute the basal ganglia? 4. Who invented the voltage clamp and who used it for further investigation into the movement of ions across the cell membrane? 5. What is the function of the cerebellum and the function of the cerebral ...
... 3. What is the function of the basal ganglia and what three nuclei constitute the basal ganglia? 4. Who invented the voltage clamp and who used it for further investigation into the movement of ions across the cell membrane? 5. What is the function of the cerebellum and the function of the cerebral ...
PsychSim - Stamford High School
... what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
... what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
Brain-Computer Interface
... Contracted by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) ...
... Contracted by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) ...
Learning Objectives
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
Slide ()
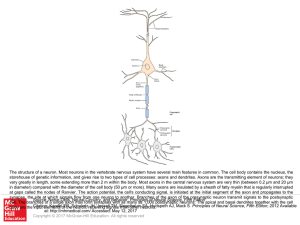
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
Nervous System - Crossword Labs
... 3. respond to efferent signals 6. Area where a neuron communicates with another cell 7. rest and digest section of the autonomic nervous system 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All ...
... 3. respond to efferent signals 6. Area where a neuron communicates with another cell 7. rest and digest section of the autonomic nervous system 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All ...