AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ______-______-________________ response. (2 pts) ...
... ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ______-______-________________ response. (2 pts) ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
File
... Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
... Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTERS 48 and 50 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... ACTION POTENTIALS ARE THE SIGNALS CONDUCTED BY AXONS D. Read this section and take notes about the new concepts and bold-faced words. E. Figure 48.11 The role of voltage-gated ion channels in the generation of an action potential. This picture tells everything about the action potential. 1. Draw the ...
... ACTION POTENTIALS ARE THE SIGNALS CONDUCTED BY AXONS D. Read this section and take notes about the new concepts and bold-faced words. E. Figure 48.11 The role of voltage-gated ion channels in the generation of an action potential. This picture tells everything about the action potential. 1. Draw the ...
neurology1ned2013 31.5 KB - d
... A neuron is the fundamental cell type that mediates input and output of stimulus information. A stimulus is an electric potential or difference in ion concentration across a membrane due to a change in environment. (like a charged battery). A potential is a change in charge (chemical or physical) th ...
... A neuron is the fundamental cell type that mediates input and output of stimulus information. A stimulus is an electric potential or difference in ion concentration across a membrane due to a change in environment. (like a charged battery). A potential is a change in charge (chemical or physical) th ...
Check Yourself
... ACROSS 3. Space between two neurons 5. Cause for tobacco dependence 7. Brain part for integration of information, planning 8. Chemical signal carried through the blood 9. Amount of drug given 11. Fastest way to get a drug to the brain 12. Agency responsible for regulating pharmaceuticals 15. Where m ...
... ACROSS 3. Space between two neurons 5. Cause for tobacco dependence 7. Brain part for integration of information, planning 8. Chemical signal carried through the blood 9. Amount of drug given 11. Fastest way to get a drug to the brain 12. Agency responsible for regulating pharmaceuticals 15. Where m ...
Nervous System
... change across the cell wall as a nerve impulse is transmitted. Each neuron has a different charge. Gated channels for calcium ions span the presynaptic cell's membrane, and they open once action potential occurs. ...
... change across the cell wall as a nerve impulse is transmitted. Each neuron has a different charge. Gated channels for calcium ions span the presynaptic cell's membrane, and they open once action potential occurs. ...
Nervous system lecture 1
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
6th Study Guide D1w:ans
... 2. A neuron is a nerve cell. 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that ...
... 2. A neuron is a nerve cell. 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that ...
CENTENNIAL HONORS COLLEGE Western Illinois University Undergraduate Research Day 2015
... of a central pattern generator. This can let us examine how ion channels shape and alter the output of a central pattern generator. Using flies from a strain with two potassium channel mutations, eag1and Sh120, I am recording action potentials from the flight muscles, for the fact that their action ...
... of a central pattern generator. This can let us examine how ion channels shape and alter the output of a central pattern generator. Using flies from a strain with two potassium channel mutations, eag1and Sh120, I am recording action potentials from the flight muscles, for the fact that their action ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... General Info Be able to diagram how the nervous system is organized (refer to concept map). What is the fundamental unit of the nervous system? Distinguish between a neuron and a neuroglia cell. Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structu ...
... General Info Be able to diagram how the nervous system is organized (refer to concept map). What is the fundamental unit of the nervous system? Distinguish between a neuron and a neuroglia cell. Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structu ...
CS 256: Neural Computation Lecture Notes
... • Two types of electric potentials – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They add in an quasilinear manner. – Action potentials, a transient spike that can propagate alo ...
... • Two types of electric potentials – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They add in an quasilinear manner. – Action potentials, a transient spike that can propagate alo ...
Nervous System Poster
... Essential Knowledge: Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information and produce responses. A. The neuron is the basic structure of the nervous system that reflects function. 1. A typical neuron has a cell body, axon and dendrites. Many axon ...
... Essential Knowledge: Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information and produce responses. A. The neuron is the basic structure of the nervous system that reflects function. 1. A typical neuron has a cell body, axon and dendrites. Many axon ...
Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms
... Suppose that a mutation caused gated sodium channels to remain inactivated for a longer time following an action potential. How would such a mutation affect the maximum frequency at which action potentials could be generated? ...
... Suppose that a mutation caused gated sodium channels to remain inactivated for a longer time following an action potential. How would such a mutation affect the maximum frequency at which action potentials could be generated? ...
01 - Fort Bend ISD
... Fill in the blanks in the Concept Map with the names of the different types of neurons. ...
... Fill in the blanks in the Concept Map with the names of the different types of neurons. ...
Biopsychology
... Shows what behaviors(/cognitions) occur if we stimulate or damage (lesion) a particular area of the brain. Electroencephalogram (EEG) & Evoked Potentials The EEG measures the brain's electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. Indicates a person’s state of arousal. The Evoked Pot ...
... Shows what behaviors(/cognitions) occur if we stimulate or damage (lesion) a particular area of the brain. Electroencephalogram (EEG) & Evoked Potentials The EEG measures the brain's electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. Indicates a person’s state of arousal. The Evoked Pot ...
013368718X_CH31_483
... information about the body’s environment G. Chemical that transmits an impulse across a synapse to another cell H. Tough, transparent layer of cells through which light enters the eye I. Fluid-filled inner ear structure lined with hair cells J. Quick, automatic response to a stimulus ...
... information about the body’s environment G. Chemical that transmits an impulse across a synapse to another cell H. Tough, transparent layer of cells through which light enters the eye I. Fluid-filled inner ear structure lined with hair cells J. Quick, automatic response to a stimulus ...
Nervous System Quiz Answers
... Ependymal – simple epithelium that lines central cavity of brain and spinal cord. NOTE: I did not list the Schwann cells because they are part of the PNS not CNS. 2. How does a nerve send a “message” when stimulated? (8pts) -A resting neuron is polarized when more Na+ is outside the membrane the K+ ...
... Ependymal – simple epithelium that lines central cavity of brain and spinal cord. NOTE: I did not list the Schwann cells because they are part of the PNS not CNS. 2. How does a nerve send a “message” when stimulated? (8pts) -A resting neuron is polarized when more Na+ is outside the membrane the K+ ...
Slide ()
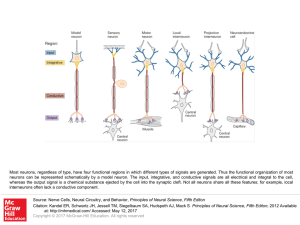
... Most neurons, regardless of type, have four functional regions in which different types of signals are generated. Thus the functional organization of most neurons can be represented schematically by a model neuron. The input, integrative, and conductive signals are all electrical and integral to the ...
... Most neurons, regardless of type, have four functional regions in which different types of signals are generated. Thus the functional organization of most neurons can be represented schematically by a model neuron. The input, integrative, and conductive signals are all electrical and integral to the ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells Electrical synapses ...
... Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells Electrical synapses ...
Slide ()
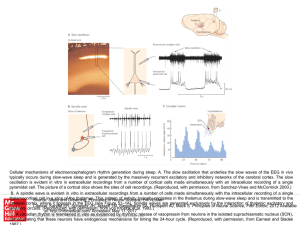
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...