Zmysły chemiczne
... A, B. The anatomical location of the three divisions of the somatic sensory cortex; SI, SII and posterior parietal cortex. C. S-I is subdivided into four distinct cytoarchitectonic regions (Brodmann's areas): 1, 2, 3a, 3b . Areas 3b and 1 receive information from receptors in the skin, whereas areas ...
... A, B. The anatomical location of the three divisions of the somatic sensory cortex; SI, SII and posterior parietal cortex. C. S-I is subdivided into four distinct cytoarchitectonic regions (Brodmann's areas): 1, 2, 3a, 3b . Areas 3b and 1 receive information from receptors in the skin, whereas areas ...
unit1sup - University of Kentucky
... first case the later tonal group sounds as one stream due to time proximity. In the second case flanking the lower tones with a sequence at same frequency, separates the lower tone from the upper tones creating 2 separate streams. ...
... first case the later tonal group sounds as one stream due to time proximity. In the second case flanking the lower tones with a sequence at same frequency, separates the lower tone from the upper tones creating 2 separate streams. ...
Lecture #6 Notes
... BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 6. Sensory and Motor Pathways Terms you should understand: somatosensory pathways, somatosensory cortex, somatotopic organization, cortical receptive field, dorsal columns, anterolateral tracts, thalamus, medial lemniscus, tonic, phasic, basal ganglia, c ...
... BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 6. Sensory and Motor Pathways Terms you should understand: somatosensory pathways, somatosensory cortex, somatotopic organization, cortical receptive field, dorsal columns, anterolateral tracts, thalamus, medial lemniscus, tonic, phasic, basal ganglia, c ...
1 Introduction to the Nervous System. Code: HMP 100/ UPC 103
... we need to have a surgical procedure we are given an anesthetic chemical that blocks pain nerve signals reaching our brain. So though our pain receptors are producing signals, these do not reach our brain so we do not feel the sensation of pain. So thought there is nociceptive activity, there is ...
... we need to have a surgical procedure we are given an anesthetic chemical that blocks pain nerve signals reaching our brain. So though our pain receptors are producing signals, these do not reach our brain so we do not feel the sensation of pain. So thought there is nociceptive activity, there is ...
Understanding trigeminal pain pathways: lessons from teeth
... The predominant, and possible sole, sensation that can be evoked by stimulation of the cornea is one of pain. There is some evidence that cold stimuli can be differentiated from mechanical/heat stimuli on the basis of the quality of the sensation, but this is always described in terms of pain rather ...
... The predominant, and possible sole, sensation that can be evoked by stimulation of the cornea is one of pain. There is some evidence that cold stimuli can be differentiated from mechanical/heat stimuli on the basis of the quality of the sensation, but this is always described in terms of pain rather ...
Motor neuron
... • when neuron receives stimulus of sufficient strength an electrical impulse travels along the dendrite and axon to the neurotransmitter swellings • electrical impulse involves movement of ions • the neuron will only carry messages once there is a stimulus of sufficient strength at the dendrites. If ...
... • when neuron receives stimulus of sufficient strength an electrical impulse travels along the dendrite and axon to the neurotransmitter swellings • electrical impulse involves movement of ions • the neuron will only carry messages once there is a stimulus of sufficient strength at the dendrites. If ...
Danczi Csaba László - 2nd WORLD CONGRESS OF ARTS
... others. Two different sensory stimuli that originate from the same location in space (e.g. derived from the same event) will effect a pronounced enhancement of the neuron's response beyond that predicted by the sum of its activation when the two cues are presented individually. When one of the two c ...
... others. Two different sensory stimuli that originate from the same location in space (e.g. derived from the same event) will effect a pronounced enhancement of the neuron's response beyond that predicted by the sum of its activation when the two cues are presented individually. When one of the two c ...
Chapter 7 -Nervous System - Austin Community College
... dorsal root carries sensory information into the spinal cord ventral root carries motor information from the spinal cord dorsal and ventral roots join just inside vertebrae to form spinal nerves spinal nerves leave through intervertebral foramina ...
... dorsal root carries sensory information into the spinal cord ventral root carries motor information from the spinal cord dorsal and ventral roots join just inside vertebrae to form spinal nerves spinal nerves leave through intervertebral foramina ...
49-1-2 Nervouse systems ppt
... • The brainstem and cerebrum control arousal and sleep • The core of the brainstem has a diffuse network of neurons called the reticular formation • regulates the amount and type of information that reaches the cerebral cortex and affects alertness • The hormone melatonin is released by the pineal g ...
... • The brainstem and cerebrum control arousal and sleep • The core of the brainstem has a diffuse network of neurons called the reticular formation • regulates the amount and type of information that reaches the cerebral cortex and affects alertness • The hormone melatonin is released by the pineal g ...
chapter 11 the somatosensory system and topographic organization
... and inhibitory neurons with receptive fields in another area, the target cell’s activity will be increased by activity in the excitatory inputs and decreased by activity in the inhibitory inputs. 11.3.1.1. Cutaneous receptive fields and sensory maps of the body. Information from the cutaneous recep ...
... and inhibitory neurons with receptive fields in another area, the target cell’s activity will be increased by activity in the excitatory inputs and decreased by activity in the inhibitory inputs. 11.3.1.1. Cutaneous receptive fields and sensory maps of the body. Information from the cutaneous recep ...
laboratory one
... In all animals, mechanical information (touch, pressure, pain) is converted into neural signals by a vast array of mechanosensory neurons whose dendritic endings respond to mechanical forces via stretch sensitive ion channels. Many of these channels provide a passage for positive ions, depolarizing ...
... In all animals, mechanical information (touch, pressure, pain) is converted into neural signals by a vast array of mechanosensory neurons whose dendritic endings respond to mechanical forces via stretch sensitive ion channels. Many of these channels provide a passage for positive ions, depolarizing ...
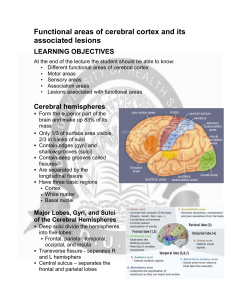
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... Composed of pyramidal cells Large neurons whose axons make up the corticospinal tracts Allows conscious control of precise, skilled, voluntary movements i.e., controls skeletal muscle Motor homunculus – caricature of relative amounts of cortical tissue devoted to each motor function Premot ...
... Composed of pyramidal cells Large neurons whose axons make up the corticospinal tracts Allows conscious control of precise, skilled, voluntary movements i.e., controls skeletal muscle Motor homunculus – caricature of relative amounts of cortical tissue devoted to each motor function Premot ...
Basic Structure and Function of Neurons
... connected in series with extrafusal muscle fibers and inserted between the muscles and their tendon(see figure6.12).Each Golgi tendon organ is responsive to contraction of about 10 to 20 single muscle fibers, each belong to a separate motor unit. When stimulated, the afferent nerve fibers from. Golg ...
... connected in series with extrafusal muscle fibers and inserted between the muscles and their tendon(see figure6.12).Each Golgi tendon organ is responsive to contraction of about 10 to 20 single muscle fibers, each belong to a separate motor unit. When stimulated, the afferent nerve fibers from. Golg ...
Annotated Bibliography Ferdinando A. Mussa
... The authors give a general summary of the breakthroughs in BMI technology up to date. The first breakthrough in using neural activity to control prosthetic devices was made by Chapin and researchers. They recorded the neural activity of multiple brain areas of rats, which controlled the one dimensio ...
... The authors give a general summary of the breakthroughs in BMI technology up to date. The first breakthrough in using neural activity to control prosthetic devices was made by Chapin and researchers. They recorded the neural activity of multiple brain areas of rats, which controlled the one dimensio ...
test1 - Scioly.org
... sensory receptors and keeps the CNS constantly informed of the activities going on inside and outside the body. ...
... sensory receptors and keeps the CNS constantly informed of the activities going on inside and outside the body. ...
Cranial Nerves
... • By age 90, frontal cortex has lost half its neurons • Number of dendritic branches decreases • Decreased levels of neurotransmitters • Fading memory • Slowed responses and reflexes • Increased risk of falling • Changes in sleep patterns that result in fewer sleeping hours ...
... • By age 90, frontal cortex has lost half its neurons • Number of dendritic branches decreases • Decreased levels of neurotransmitters • Fading memory • Slowed responses and reflexes • Increased risk of falling • Changes in sleep patterns that result in fewer sleeping hours ...
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION 1. A function
... (A) increase the resting potential by 60 mV (B) decrease the resting potential by 60 mV (C) change the equilibrium potential for K+ by 60 mV (D) increase the overshoot of the action potential by 60 mV (E) increase the magnitude of the hyperpolarizing afterpotential by 60 mV 20. The probability of a ...
... (A) increase the resting potential by 60 mV (B) decrease the resting potential by 60 mV (C) change the equilibrium potential for K+ by 60 mV (D) increase the overshoot of the action potential by 60 mV (E) increase the magnitude of the hyperpolarizing afterpotential by 60 mV 20. The probability of a ...
PDF
... the contralateral CN, in close apposition to neurons of all major cell types throughout the CN [6]. These observations are consistent with our results showing commissural inhibitory responses in most categories of cells of the PVCN and DCN. In addition to direct monosynaptic inhibitory projections, ...
... the contralateral CN, in close apposition to neurons of all major cell types throughout the CN [6]. These observations are consistent with our results showing commissural inhibitory responses in most categories of cells of the PVCN and DCN. In addition to direct monosynaptic inhibitory projections, ...
Document
... down an axon one small section at a time – In myelinated fibers, an action potential at one node causes an action potential at the next node • Saltatory (jumping) Conduction ...
... down an axon one small section at a time – In myelinated fibers, an action potential at one node causes an action potential at the next node • Saltatory (jumping) Conduction ...
Nervous System - IB BiologyMr. Van Roekel Salem High School
... • Motor neurons also have long axons and transmit nerve impulses from the central nervous system to effectors (muscles and glands) all over the body. • Interneurons (also called connector neurons or relay neurons) are usually much smaller cells, with many interconnections. • When many individual neu ...
... • Motor neurons also have long axons and transmit nerve impulses from the central nervous system to effectors (muscles and glands) all over the body. • Interneurons (also called connector neurons or relay neurons) are usually much smaller cells, with many interconnections. • When many individual neu ...
Nervous System
... The nervous system is our processing system, and the system that keeps us in contact with the outside world. It tells us that we exist, and along with the muscles allows us to move and react to stimuli. Our consciousness resides in our nervous systems, as do our thoughts and emotions. • In short, th ...
... The nervous system is our processing system, and the system that keeps us in contact with the outside world. It tells us that we exist, and along with the muscles allows us to move and react to stimuli. Our consciousness resides in our nervous systems, as do our thoughts and emotions. • In short, th ...
Endocrine and Nervous Systems
... B. The production of a hormone by an endocrine gland that works on another endocrine gland C. A series of events that monitor how hormones work in the body D. A process in which a change in the environment causes a response that returns conditions to their original status ...
... B. The production of a hormone by an endocrine gland that works on another endocrine gland C. A series of events that monitor how hormones work in the body D. A process in which a change in the environment causes a response that returns conditions to their original status ...
Nervous System Project
... These fibres are covered by fatty substance called myelin (say my-elin). Myelin helps the messages go fast through the neurons. ...
... These fibres are covered by fatty substance called myelin (say my-elin). Myelin helps the messages go fast through the neurons. ...