大腦神經解剖與建置
... and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers for further processing. Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fight-or-flight response. It is also the source of posterior pituitary h ...
... and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers for further processing. Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fight-or-flight response. It is also the source of posterior pituitary h ...
Neuroscience 7b – Cortical Motor Function
... activities relating to motor acts all converge on M1 (the primary motor cortex). NB: M1 contributes to most of the fibres in the corticospinal tract. A small population of cortical neurones in M1 controls small movements. These are movements that are specific, distal (i.e. fingers) and delicate/prec ...
... activities relating to motor acts all converge on M1 (the primary motor cortex). NB: M1 contributes to most of the fibres in the corticospinal tract. A small population of cortical neurones in M1 controls small movements. These are movements that are specific, distal (i.e. fingers) and delicate/prec ...
Instructions (PDF Document)
... When we use the term direction in this exercise, we are referring to the orientation as if we were reading a magnetic compass. Now that we have defined the 0° direction, we can use the compass-like directions of 0-360° to describe the direction in which we are pushing the hair. This is different fro ...
... When we use the term direction in this exercise, we are referring to the orientation as if we were reading a magnetic compass. Now that we have defined the 0° direction, we can use the compass-like directions of 0-360° to describe the direction in which we are pushing the hair. This is different fro ...
Reduced BOLD response to periodic visual stimulation
... For Experiment 1, the average percentage BOLD increase over 10 s was calculated for each condition (seven frequencies, periodic and aperiodic), starting 10 s after the onset of stimulation. Baseline was taken as the mean signal during 30 s of rest preceding the stimulus. The results were averaged ov ...
... For Experiment 1, the average percentage BOLD increase over 10 s was calculated for each condition (seven frequencies, periodic and aperiodic), starting 10 s after the onset of stimulation. Baseline was taken as the mean signal during 30 s of rest preceding the stimulus. The results were averaged ov ...
REGULATION nervous system
... Neurons can send electrical and chemical impulses (electrochemical impulses) The sending of impulses is the property of the neuron’s cell membrane Transmission not through the cytoplasm, but along the cell membrane ...
... Neurons can send electrical and chemical impulses (electrochemical impulses) The sending of impulses is the property of the neuron’s cell membrane Transmission not through the cytoplasm, but along the cell membrane ...
The Neurological Examination
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
The Neurological Examination
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
... Graphesthesia Two-Point Discrimination Double Simultaneous Extinction ...
Spinal Cord Injuries
... reflex depression of cord function below the level of injury, with associated loss of all sensorimotor functions – (+) Increase in blood pressure (initially) due to the release of catecholamines, followed by hypotension – (+) Flaccid paralysis, including of the bowel and bladder – Symptoms last seve ...
... reflex depression of cord function below the level of injury, with associated loss of all sensorimotor functions – (+) Increase in blood pressure (initially) due to the release of catecholamines, followed by hypotension – (+) Flaccid paralysis, including of the bowel and bladder – Symptoms last seve ...
File
... • Complex ______________________ _________________ Temporal lobe association areas • Interpret complex _________________ ___________________ • Store memories of _______________ ____________, _____________, and complex patterns Parietal lobe association areas • Understanding ___________________ • Cho ...
... • Complex ______________________ _________________ Temporal lobe association areas • Interpret complex _________________ ___________________ • Store memories of _______________ ____________, _____________, and complex patterns Parietal lobe association areas • Understanding ___________________ • Cho ...
Chapter 13 - Martini
... • Sensory Pathways – Enter the cord via the dorsal roots. – Have unipolar cell bodies found in the dorsal root ganglia. – Carry sensory inputs into the CNS via the central processes of their axons. They begin at the general sensory receptors of the skin (somatic sensory) and internal organs (viscera ...
... • Sensory Pathways – Enter the cord via the dorsal roots. – Have unipolar cell bodies found in the dorsal root ganglia. – Carry sensory inputs into the CNS via the central processes of their axons. They begin at the general sensory receptors of the skin (somatic sensory) and internal organs (viscera ...
Spinal Cord Worksheet - District 196 e
... ! .! List the structures which prevent lateral and superior-inferior movement of the spinal ...
... ! .! List the structures which prevent lateral and superior-inferior movement of the spinal ...
nerve_pharmacy_(mana..
... phosphate ions) cannot leave the cell. • 3. very small amount of Na+ diffuses into the cell down its conc gradient. The mb only slightly permeable to Na+. (through Na+ leak channels). • 4. Na+-K+ pump maintain conc gradients of K+, and Na+ between the two sides of the mb. ...
... phosphate ions) cannot leave the cell. • 3. very small amount of Na+ diffuses into the cell down its conc gradient. The mb only slightly permeable to Na+. (through Na+ leak channels). • 4. Na+-K+ pump maintain conc gradients of K+, and Na+ between the two sides of the mb. ...
skeletal nervous system
... Neurotransmitters = chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse. ...
... Neurotransmitters = chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... – White matter • In areas around gray matter • Ascending and descending tracts – Ascending tract is located dorsally » Sends information to the brain – Descending tract is located ventrally » Sends information from the brain to spinal nerves » Many tracts cross over to opposite side » Left side of b ...
... – White matter • In areas around gray matter • Ascending and descending tracts – Ascending tract is located dorsally » Sends information to the brain – Descending tract is located ventrally » Sends information from the brain to spinal nerves » Many tracts cross over to opposite side » Left side of b ...
Spinal Cord - Mesa Community College
... Sensory Receptors Classified by Location and Activating Stimuli Exteroceptors – located near or at the external surface of the body Hearing, vision, smell, taste, touch, pressure, vibration, temperature, and pain Interoceptors – located in blood vessels, visceral organs and nervous system Propriocep ...
... Sensory Receptors Classified by Location and Activating Stimuli Exteroceptors – located near or at the external surface of the body Hearing, vision, smell, taste, touch, pressure, vibration, temperature, and pain Interoceptors – located in blood vessels, visceral organs and nervous system Propriocep ...
Yuste-Banbury-2006 - The Swartz Foundation
... exclusively on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, almost all of the NMDA-induced Ca2+ influx was via the NMDA ionophore itself, rather than through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Glutamate itself altered [Ca2+]i almost exclusively via the NMDA receptor. Furthermore, synaptically induced Ca2+ entry relied al ...
... exclusively on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, almost all of the NMDA-induced Ca2+ influx was via the NMDA ionophore itself, rather than through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Glutamate itself altered [Ca2+]i almost exclusively via the NMDA receptor. Furthermore, synaptically induced Ca2+ entry relied al ...
Midterm 1 with answer key
... neurons at specialized neural structures called synapses. d) Neurons influence adjacent neurons by a process called lateral inhibition. 12. If the intensity of a stimulus that is presented to a touch receptor is increased, this tends to increase the _____ in the receptor’s axon. a) rate of nerve f ...
... neurons at specialized neural structures called synapses. d) Neurons influence adjacent neurons by a process called lateral inhibition. 12. If the intensity of a stimulus that is presented to a touch receptor is increased, this tends to increase the _____ in the receptor’s axon. a) rate of nerve f ...
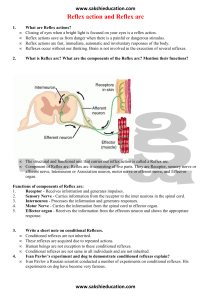
Reflex action and Reflex arc
... bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its mouth. Human beings are no exception to this. Conditional reflexes are not same in all individuals and n ...
... bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its mouth. Human beings are no exception to this. Conditional reflexes are not same in all individuals and n ...
A study on the general visceral sensory and motor systems in fish
... Afferent information from the visceral organs is carried through the general visceral sensory system while efferent information from the central nervous system is sent through the general visceral motor system. The motor system belongs to a parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous systems. ...
... Afferent information from the visceral organs is carried through the general visceral sensory system while efferent information from the central nervous system is sent through the general visceral motor system. The motor system belongs to a parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous systems. ...
MCB105 QUIZ 5 2016 wA
... visual field as juveniles exhibit neuronal plasticity as adults. a) In which neurons was this plasticity shown? [1] OT neurons with both auditory and visual responses b) How is this change measured (explain or draw)? [1] Measure the same OT neuron before and after prism fitting. Compare the visual r ...
... visual field as juveniles exhibit neuronal plasticity as adults. a) In which neurons was this plasticity shown? [1] OT neurons with both auditory and visual responses b) How is this change measured (explain or draw)? [1] Measure the same OT neuron before and after prism fitting. Compare the visual r ...
Chapt13 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... a: © Karl E. Deckart/Phototake; d: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Rebecca Gray, photographer and Don Kincaid, dissections ...
... a: © Karl E. Deckart/Phototake; d: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Rebecca Gray, photographer and Don Kincaid, dissections ...