Symposium Poster - uospur
... glomerular level are sufficient for stereoolfactory discrimination ...
... glomerular level are sufficient for stereoolfactory discrimination ...
Chapter 4: The Central Nervous System
... identical – but they in fact have some specialised functions that are not duplicated in the other. Hemispheric Specialisation refers to the specialisation and dominance of certain functions by each hemisphere of the brain. These differences are most apparent in stroke victims and people that had suf ...
... identical – but they in fact have some specialised functions that are not duplicated in the other. Hemispheric Specialisation refers to the specialisation and dominance of certain functions by each hemisphere of the brain. These differences are most apparent in stroke victims and people that had suf ...
CNS - FIU
... dura mater (outer; L, tough mouth), arachnoid (middle; G&L, spider- (web-) like mother), and pia mater (inner; L, tender mother). The latter is adherent to the spinal cord whereas the arachnoid spans between the dura and pia mater. Within the spinal cord, gray matter (consisting chiefly of neuron ce ...
... dura mater (outer; L, tough mouth), arachnoid (middle; G&L, spider- (web-) like mother), and pia mater (inner; L, tender mother). The latter is adherent to the spinal cord whereas the arachnoid spans between the dura and pia mater. Within the spinal cord, gray matter (consisting chiefly of neuron ce ...
Specific and Nonspecific Plasticity of the Primary
... and 2, Electrode penetrations across the hippocampus (HPC) and MGBv or MGBm. ...
... and 2, Electrode penetrations across the hippocampus (HPC) and MGBv or MGBm. ...
Ascending tracts
... The first order neurone ,enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root, its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. The central process may make synaptic connections that mediate intersegmental coordination, the main fibres on the ipsilateral side terminate in synaptic contact with the second ...
... The first order neurone ,enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root, its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. The central process may make synaptic connections that mediate intersegmental coordination, the main fibres on the ipsilateral side terminate in synaptic contact with the second ...
Unit-III-The-Nervous-and-Endocrine-Systems
... Interneurons make reflexes happen. These cells in the spinal cord process motor responses quickly to protect the body from harm. ...
... Interneurons make reflexes happen. These cells in the spinal cord process motor responses quickly to protect the body from harm. ...
No Slide Title - people.vcu.edu
... FROM THE MOTOR CORTEX CORTICOSPINAL PATHWAY CORTICOBULBAR PATHWAY PYRAMIDAL TRACT LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT ...
... FROM THE MOTOR CORTEX CORTICOSPINAL PATHWAY CORTICOBULBAR PATHWAY PYRAMIDAL TRACT LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT ...
Electrical Stimulation of the Horizontal Limb of the Diagonal Band
... (n 5 8; Fig. 2), as previously reported by Zimmer et al. (1996). In contrast, component B1 of the population EPSP was increased by the preceding stimulation in the HDB (Fig. 2B). As shown in Fig. 2C, a significant effect (169 6 7.3% of the baseline response; n 5 8; P , 0.01) was observed, only for D ...
... (n 5 8; Fig. 2), as previously reported by Zimmer et al. (1996). In contrast, component B1 of the population EPSP was increased by the preceding stimulation in the HDB (Fig. 2B). As shown in Fig. 2C, a significant effect (169 6 7.3% of the baseline response; n 5 8; P , 0.01) was observed, only for D ...
2) Classical Conditioning
... 2. Neutral Stimulus (NS) ---> does not elicit the response of interest: this stimulus is a neutral stimulus since it does not elicit the Unconditioned (or reflexive) Response. 3. The Neutral Stimulus (NS) is repeatedly paired with the Unconditioned (Natural) Stimulus (US). 4. The NS is transformed i ...
... 2. Neutral Stimulus (NS) ---> does not elicit the response of interest: this stimulus is a neutral stimulus since it does not elicit the Unconditioned (or reflexive) Response. 3. The Neutral Stimulus (NS) is repeatedly paired with the Unconditioned (Natural) Stimulus (US). 4. The NS is transformed i ...
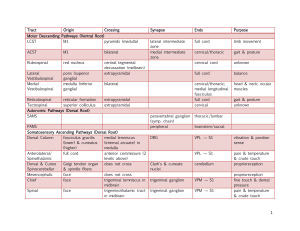
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... basis: long tracts of corticospinal & corticobulbar fibers pons: pontomesencephalic reticular formation (PRF) receives inputs from somatosensory (cord), limbic/cingulate cortex, frontoparietal association cortex, & thalamic reticular nucleus thalamic reticular nucleus: cortical input → modulate othe ...
... basis: long tracts of corticospinal & corticobulbar fibers pons: pontomesencephalic reticular formation (PRF) receives inputs from somatosensory (cord), limbic/cingulate cortex, frontoparietal association cortex, & thalamic reticular nucleus thalamic reticular nucleus: cortical input → modulate othe ...
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 1 and 10 White
... 20. If a patient performs an act with unexpected and irrelevant movements then they could likely have a: a. Cerebellar lesion b. Cerebral lesion c. Basal ganglia lesion 21. Broadman’s area 4 is the ________ area and is located _______ to the central sulcus and generates neural impulses that control ...
... 20. If a patient performs an act with unexpected and irrelevant movements then they could likely have a: a. Cerebellar lesion b. Cerebral lesion c. Basal ganglia lesion 21. Broadman’s area 4 is the ________ area and is located _______ to the central sulcus and generates neural impulses that control ...
Connecting cortex to machines: recent advances in brain interfaces
... will also be essential for normal interaction, especially when outcomes of behavior are unreliable or unpredictable. An ideal communication interface for patients lacking intact somatic sensory pathways would be able to deliver signals to the cortex that are indistinguishable from a natural stimulus ...
... will also be essential for normal interaction, especially when outcomes of behavior are unreliable or unpredictable. An ideal communication interface for patients lacking intact somatic sensory pathways would be able to deliver signals to the cortex that are indistinguishable from a natural stimulus ...
Cell Body - Cloudfront.net
... sensory for balance and hearing IX Glossopharyngeal nerve – sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx X Vagus nerves – sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera ...
... sensory for balance and hearing IX Glossopharyngeal nerve – sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx X Vagus nerves – sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera ...
The Nervous System
... • Most neuron cell bodies are found in the central nervous system • Gray matter—cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers • Nuclei—clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system • Ganglia—collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system ...
... • Most neuron cell bodies are found in the central nervous system • Gray matter—cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers • Nuclei—clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system • Ganglia—collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system ...
GLOSSARY of Occupational Therapy Terminology
... Self-regulation: Nervous system’s ability to attain, maintain, and change levels of arousal or alertness. Sensory Diet: A term devised by Patricia Wilbarger in 1971 to describe a therapeutic method to maintain an optimal level of arousal (in the nervous system) by offering the right combination of s ...
... Self-regulation: Nervous system’s ability to attain, maintain, and change levels of arousal or alertness. Sensory Diet: A term devised by Patricia Wilbarger in 1971 to describe a therapeutic method to maintain an optimal level of arousal (in the nervous system) by offering the right combination of s ...
Nerve Conduction Studies - Cumbria Partnership NHS Foundation
... between the brain and all the other parts of the body. The brain can send signals, in the form of electrical impulses via the spinal cord to the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral nerves can be 'motor' nerves, which means they are attached to muscles and cause the muscles to clench (contract). Th ...
... between the brain and all the other parts of the body. The brain can send signals, in the form of electrical impulses via the spinal cord to the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral nerves can be 'motor' nerves, which means they are attached to muscles and cause the muscles to clench (contract). Th ...
CH 14 brain cranial nerves A and P 2017
... - studies from injuries, surgeries, lesions, and ablations - prefrontal seat of judgement, intent, control over expressions of our emotions - amygdala gets sensory input from general senses, vision, hearing, taste, and smell and info used to mediate a response to the sensory input - amygdala sends i ...
... - studies from injuries, surgeries, lesions, and ablations - prefrontal seat of judgement, intent, control over expressions of our emotions - amygdala gets sensory input from general senses, vision, hearing, taste, and smell and info used to mediate a response to the sensory input - amygdala sends i ...
Sensory System –L4
... Rate and Strength of the response is related to the Rate and Intensity of the stimulus important for predicting the future position or condition of the body very important for balance and movement types of rapidly adapting receptors: pacinian corpuscle, semicircular canals in the inner ear U ...
... Rate and Strength of the response is related to the Rate and Intensity of the stimulus important for predicting the future position or condition of the body very important for balance and movement types of rapidly adapting receptors: pacinian corpuscle, semicircular canals in the inner ear U ...
Optic Nerves * Jack Baesman
... impulses to neurons in olfactory bulbs Sensory impulses travel from bulbs along olfactory tracts to the cerebral centers where they are interpreted into the sensation of smell. ...
... impulses to neurons in olfactory bulbs Sensory impulses travel from bulbs along olfactory tracts to the cerebral centers where they are interpreted into the sensation of smell. ...
Motor Systems II Loops and Tracts
... the extremities and face. Huntington’s disease results from the selective loss of striatal neurons in the indirect pathway. Thus, the balance between the direct and indirect pathways becomes tipped in favor of the direct pathway. Without their normal inhibitory inputs, thalamic neurons can fire rand ...
... the extremities and face. Huntington’s disease results from the selective loss of striatal neurons in the indirect pathway. Thus, the balance between the direct and indirect pathways becomes tipped in favor of the direct pathway. Without their normal inhibitory inputs, thalamic neurons can fire rand ...
Chapt13 Lecture 13ed Pt 1
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) sensory (afferent) nerves — carry sensory information into brain and spinal cord ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) sensory (afferent) nerves — carry sensory information into brain and spinal cord ...
differentiation of brain vesicles
... 18) What is the role of the “rhombic lip” – a structure seen during the development of the rostral hindbrain? 19) Try to describe the critical roles of the hindbrain in feeding behavior. Questions on Schneider chapter 11: 1) What are the two inputs carrying information about light levels into the CN ...
... 18) What is the role of the “rhombic lip” – a structure seen during the development of the rostral hindbrain? 19) Try to describe the critical roles of the hindbrain in feeding behavior. Questions on Schneider chapter 11: 1) What are the two inputs carrying information about light levels into the CN ...
The Nervous System - Optum360Coding.com
... controls unconscious movements in skeletal muscle for coordination, posture, balance; injury/trauma characterized by lack of muscle coordination, abnormal gait, may affect speech muscles; some cognitive functions such as attention, language, emotional functions such as fear and pleasure responses; d ...
... controls unconscious movements in skeletal muscle for coordination, posture, balance; injury/trauma characterized by lack of muscle coordination, abnormal gait, may affect speech muscles; some cognitive functions such as attention, language, emotional functions such as fear and pleasure responses; d ...
Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System
... cord and supply all parts of the body except the head They are named according to their point of issue 8 cervical (C1-C8) 12 thoracic (T1-T12) 5 Lumbar (L1-L5) ...
... cord and supply all parts of the body except the head They are named according to their point of issue 8 cervical (C1-C8) 12 thoracic (T1-T12) 5 Lumbar (L1-L5) ...