The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth`s
... - sound waves produce movement of basilar membrane; - movement of basilar membrane induce movement of cilia of hair cells; - cilia movement increase or decrease polarization of hair cells, ...
... - sound waves produce movement of basilar membrane; - movement of basilar membrane induce movement of cilia of hair cells; - cilia movement increase or decrease polarization of hair cells, ...
Reading Part 5: The Nervous System
... causes a ligand or mechanically gated channel to open or close. Depending on the type of ion channel opened, the membrane can become more negative (hyperpolarized) or more positive (depolarized). ...
... causes a ligand or mechanically gated channel to open or close. Depending on the type of ion channel opened, the membrane can become more negative (hyperpolarized) or more positive (depolarized). ...
Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and
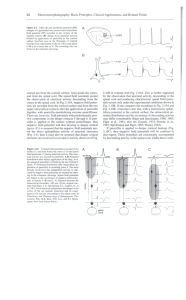
... In addition to the field potentials of the cortical surface and the membrane potentials of the pyramidal tract cells, field potentials were also recorded in the fifth lamina. Under these conditions, it can be shown that every PDS is associated with a negative monophasic field potential in the depth ...
... In addition to the field potentials of the cortical surface and the membrane potentials of the pyramidal tract cells, field potentials were also recorded in the fifth lamina. Under these conditions, it can be shown that every PDS is associated with a negative monophasic field potential in the depth ...
Today`s Objectives Describe the basic structure of a nerve. Identify
... 3. Explain the organization of the spinal nerves, the dorsal and ventral rami, and the plexuses. 4. Describe the location, structure, and function of ganglions. 5. Differentiate between the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Lesson 4: Functional Anatomy of the Peripher ...
... 3. Explain the organization of the spinal nerves, the dorsal and ventral rami, and the plexuses. 4. Describe the location, structure, and function of ganglions. 5. Differentiate between the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Lesson 4: Functional Anatomy of the Peripher ...
Nervous System Worksheets
... exit the spinal cord through openings between the vertebrae. The part of the nerve that exits the spinal cord is called the nerve root. It then branches into smaller nerves that control different parts of the body called the peripheral nerves. ...
... exit the spinal cord through openings between the vertebrae. The part of the nerve that exits the spinal cord is called the nerve root. It then branches into smaller nerves that control different parts of the body called the peripheral nerves. ...
exteroreceptive sensory systems
... About seven areas of secondary auditory cortex Functional columns (cells of a column respond to the same frequency) Tonotopic organization Secondary areas do not respond well to pure tones and have not been wellresearched Copyright © 2009 Allyn & Bacon ...
... About seven areas of secondary auditory cortex Functional columns (cells of a column respond to the same frequency) Tonotopic organization Secondary areas do not respond well to pure tones and have not been wellresearched Copyright © 2009 Allyn & Bacon ...
in the central nervous system
... Neurons can send electrical and chemical impulses (electrochemical impulses) The sending of impulses is the property of the neuron’s cell membrane Transmission not through the cytoplasm, but along the cell membrane ...
... Neurons can send electrical and chemical impulses (electrochemical impulses) The sending of impulses is the property of the neuron’s cell membrane Transmission not through the cytoplasm, but along the cell membrane ...
Cortical Control of Motor Function-L18
... closely associated area controls appropriate respiratory function for speech eye fixation and head rotation area for coordinated head and eye movements hand skills area damage causes motor apraxia the inability to perform fine hand movements University of Jordan ...
... closely associated area controls appropriate respiratory function for speech eye fixation and head rotation area for coordinated head and eye movements hand skills area damage causes motor apraxia the inability to perform fine hand movements University of Jordan ...
MOTOR NEURON DISEASE
... Clinical features 1-4 weeks after respiratory infection or diarrhoea (particularly Campylobacter) in 70% of Patients. Distal paraesthesia and numbness (often severe) precede a rapidly ascending muscle weakness, from lower to upper limbs, more marked proximally than distally. Facial and bulbar weakn ...
... Clinical features 1-4 weeks after respiratory infection or diarrhoea (particularly Campylobacter) in 70% of Patients. Distal paraesthesia and numbness (often severe) precede a rapidly ascending muscle weakness, from lower to upper limbs, more marked proximally than distally. Facial and bulbar weakn ...
Reflex arc ppt - bananateachersworld
... AIM: To investigate the sensitivity of different areas of the skin. Method: 1. Working in pairs, one student looks in a different direction, while another student touches them on the back of the hand with either one or two pieces of blunt pencil about 1 cm apart. 2. The blindfolded student has to sa ...
... AIM: To investigate the sensitivity of different areas of the skin. Method: 1. Working in pairs, one student looks in a different direction, while another student touches them on the back of the hand with either one or two pieces of blunt pencil about 1 cm apart. 2. The blindfolded student has to sa ...
Chapter 15
... • Specific sensory info sent from specific receptor in specific part of body to specific area of cortex! • Neuronal pathway from receptor to cortex is the “labeled line”! Cortex interprets:! 1. Type of stimulus based upon labeled line! 2. Location of stimulus based upon where in cortex labeled lin ...
... • Specific sensory info sent from specific receptor in specific part of body to specific area of cortex! • Neuronal pathway from receptor to cortex is the “labeled line”! Cortex interprets:! 1. Type of stimulus based upon labeled line! 2. Location of stimulus based upon where in cortex labeled lin ...
中樞神經系統
... Sensory pathways to the cerebral cortex are crossed pathways. Impulses are conducted to its sensory areas by way of relays of neurons referred to as sensory pathways. Each side of the brain registers sensations from the opposite side of the body. General sensations of the right side of the b ...
... Sensory pathways to the cerebral cortex are crossed pathways. Impulses are conducted to its sensory areas by way of relays of neurons referred to as sensory pathways. Each side of the brain registers sensations from the opposite side of the body. General sensations of the right side of the b ...
Movement
... Disorders of the Motor Neurons. a) Myasthenia Gravis: The immune system progressively attacks acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. This leads to progressive muscle weakness and rapid fatigue apparent after short periods of exercise. Drugs such as Physostigmine (an acetylcholine agonis ...
... Disorders of the Motor Neurons. a) Myasthenia Gravis: The immune system progressively attacks acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. This leads to progressive muscle weakness and rapid fatigue apparent after short periods of exercise. Drugs such as Physostigmine (an acetylcholine agonis ...
Notes Chapter 50 Nervous and Sensory Systems
... Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves each consist of a dorsal root containing sensory neurons and a ventral root containing motor neurons. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) links the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The PNS is composed of a sensory division and a motor division. ...
... Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves each consist of a dorsal root containing sensory neurons and a ventral root containing motor neurons. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) links the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The PNS is composed of a sensory division and a motor division. ...
Neuroglia - wsscience
... •Treatment and Research Although there is no cure for Parkinson's disease, medicines and surgery can often provide help with dealing with it. However, these treatments are not very effected sometimes and scientist are trying to find better ways to treat it. Recent advances in areas such as genetics ...
... •Treatment and Research Although there is no cure for Parkinson's disease, medicines and surgery can often provide help with dealing with it. However, these treatments are not very effected sometimes and scientist are trying to find better ways to treat it. Recent advances in areas such as genetics ...
somatic sensory system
... lie lateral to the fibers of the medial lemniscus make synapses in the reticular formation have arisen from cells in the dorsal column nuclei have arisen from cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord decussate (cross the midline) ...
... lie lateral to the fibers of the medial lemniscus make synapses in the reticular formation have arisen from cells in the dorsal column nuclei have arisen from cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord decussate (cross the midline) ...
Slide 1
... morphology reflects early ventral differentiation of the mantle layer (2), which is accompanied by an early ventral thinning of the neuroepithelial or ventricular layer of the neural tube (it remains as the ependymal lining of the adult ventricular system). The mantle layer develops into adult gray ...
... morphology reflects early ventral differentiation of the mantle layer (2), which is accompanied by an early ventral thinning of the neuroepithelial or ventricular layer of the neural tube (it remains as the ependymal lining of the adult ventricular system). The mantle layer develops into adult gray ...
Jackson Rancheria Casino Shooting
... ____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS. ____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and motor neurons ____ 6. Gaps in a myelin sheath ____ 7. Collection of nerve cell bodies found outside the CNS ____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscl ...
... ____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS. ____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and motor neurons ____ 6. Gaps in a myelin sheath ____ 7. Collection of nerve cell bodies found outside the CNS ____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscl ...
Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
... The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases because the myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing ion loss f ...
... The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases because the myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing ion loss f ...
Diencephalon - People Server at UNCW
... includes three main symptoms: simultanagnosia (the inability to see more than one object at a time); optic ataxia (the fixation of gaze with severe problems in voluntarily moving fixation); and optic apraxia (the inability to reach towards the correct location of perceived objects)78 ...
... includes three main symptoms: simultanagnosia (the inability to see more than one object at a time); optic ataxia (the fixation of gaze with severe problems in voluntarily moving fixation); and optic apraxia (the inability to reach towards the correct location of perceived objects)78 ...
cranial nerve ix: glossopharyngeal nerve
... 1. In this role, the Vagus is "stealing" some of the innervation from the Spinal Accessory (XI). Hence in this case the Vagus is actually innervating striated rather than smooth muscle. 2. VISCERAL MOTOR (GVE): Parasympathetics to the Thoracic and Abdominal viscera. 1. The Vagus serves no Parasympat ...
... 1. In this role, the Vagus is "stealing" some of the innervation from the Spinal Accessory (XI). Hence in this case the Vagus is actually innervating striated rather than smooth muscle. 2. VISCERAL MOTOR (GVE): Parasympathetics to the Thoracic and Abdominal viscera. 1. The Vagus serves no Parasympat ...
Primary motor cortex
... To Basal ganglia (postural contractions) To Red nucleus (→rubrospinal tract) To Reticular system (→ reticulocerebellar tracts) To Vestibular system (→ vestibulocerebellar tracts) To Pons nuclei (→ pontocerebellar tracts) To Nuc. olivarius inferior (→ olivocerebellar tracts) ...
... To Basal ganglia (postural contractions) To Red nucleus (→rubrospinal tract) To Reticular system (→ reticulocerebellar tracts) To Vestibular system (→ vestibulocerebellar tracts) To Pons nuclei (→ pontocerebellar tracts) To Nuc. olivarius inferior (→ olivocerebellar tracts) ...
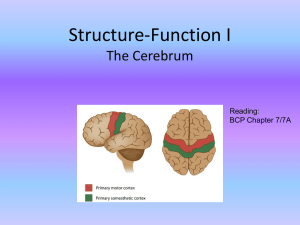
Structure-Function I
... century but remain the most widely known and frequently cited map of human cortex. Brodmann postulated that these areas with different structures performed different functions. ...
... century but remain the most widely known and frequently cited map of human cortex. Brodmann postulated that these areas with different structures performed different functions. ...