W7 Lecture
... Contraction of the extensor muscle on the thigh tenses the Golgi tendon organ and activates it to fire action potentials. Responses include: Inhibition of the motor neurons that innervate this muscle (A), and excitation in the opposing flexor’s motor neurons (B). ...
... Contraction of the extensor muscle on the thigh tenses the Golgi tendon organ and activates it to fire action potentials. Responses include: Inhibition of the motor neurons that innervate this muscle (A), and excitation in the opposing flexor’s motor neurons (B). ...
intraoperative motor evoked potential monitoring
... wave EPSP summation and most do not fire. Thus, each successive response represents a varying subpopulation of the recorded muscle’s motor units. Barker et al. developed transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) in the mid-1980’s, introducing diagnostic MEP testing without the scalp discomfort of TES ...
... wave EPSP summation and most do not fire. Thus, each successive response represents a varying subpopulation of the recorded muscle’s motor units. Barker et al. developed transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) in the mid-1980’s, introducing diagnostic MEP testing without the scalp discomfort of TES ...
Ch.11
... Cerebral Cortex – thin layer of gray matter that constitutes the outermost portion of cerebrum; contains 75% of all neurons. ...
... Cerebral Cortex – thin layer of gray matter that constitutes the outermost portion of cerebrum; contains 75% of all neurons. ...
Lecture notes
... • As we ascend within a processing hierarchy, we tend to see RFs that are selective for increasingly behaviorally relevant stimulus features. • We also tend to see RFs that are increasingly invariant (or at least tolerant) to less behaviorally relevant stimulus features. ...
... • As we ascend within a processing hierarchy, we tend to see RFs that are selective for increasingly behaviorally relevant stimulus features. • We also tend to see RFs that are increasingly invariant (or at least tolerant) to less behaviorally relevant stimulus features. ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s own track to the cerebral cortex • Audition has it own tra ...
... brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s own track to the cerebral cortex • Audition has it own tra ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
Sensory Motor Approaches with People with Mental Illness Week 5
... • Speech and Language: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these • Eye-hand Coordination: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these with the visual system directing the hand • Visual Perception: intimately related to tactile and vestibular systems and is belie ...
... • Speech and Language: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these • Eye-hand Coordination: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these with the visual system directing the hand • Visual Perception: intimately related to tactile and vestibular systems and is belie ...
Text S2: Conflicting demands of localization and pattern
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
The dual nature of time preparation: neural
... The trial events are schematically represented in Fig. 1. After the blue LED was lit, the subject initiated the trial by exerting an isometric press on both sensors. The trial began when the correct force was attained, then the subject was to maintain this force during 3 s. This period of time corre ...
... The trial events are schematically represented in Fig. 1. After the blue LED was lit, the subject initiated the trial by exerting an isometric press on both sensors. The trial began when the correct force was attained, then the subject was to maintain this force during 3 s. This period of time corre ...
Unit 2 PowerPoint 2.1 and 2.2
... sensory nerves bypass brain and go up to CNS only in the case of reflex. ...
... sensory nerves bypass brain and go up to CNS only in the case of reflex. ...
Study materials CNS
... cerebellum, the basal ganglia realize programmes for slow extensive movements. Programs input via thalamus the motoric cortical regions as a starting point from which a movement realization is controlled. Informations conducted in pyramidal tracts are modified by situation in effectors and by a syst ...
... cerebellum, the basal ganglia realize programmes for slow extensive movements. Programs input via thalamus the motoric cortical regions as a starting point from which a movement realization is controlled. Informations conducted in pyramidal tracts are modified by situation in effectors and by a syst ...
CNS
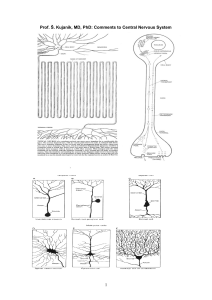
... from one side of the organ brain with the other side form synapses on a second common d. Locus a ii. sense Defines the location to the CNS of the ii.from Share a common function ii. Commonly referred to as the iii. Fissure: a deep grooveoccipital lobe limbic lobe caudally located occipital lobes i. ...
... from one side of the organ brain with the other side form synapses on a second common d. Locus a ii. sense Defines the location to the CNS of the ii.from Share a common function ii. Commonly referred to as the iii. Fissure: a deep grooveoccipital lobe limbic lobe caudally located occipital lobes i. ...
Somatic Sensation - PROFESSOR AC BROWN
... 1. When stimulated, an afferent nerve ending (sensory receptor) generates one or more action potentials (1st order or primary afferent neuron) 2. These action potentials are conducted into the Central Nervous System (spinal cord and brain), where they excite adjacent nerve cells (2nd order, 3rd orde ...
... 1. When stimulated, an afferent nerve ending (sensory receptor) generates one or more action potentials (1st order or primary afferent neuron) 2. These action potentials are conducted into the Central Nervous System (spinal cord and brain), where they excite adjacent nerve cells (2nd order, 3rd orde ...
Lecture 7
... o __________________ – all neurons have the ability to respond to environmental changes o Conductivity – Neurons produce traveling electrical signals that quickly reach other cells at _________________ locations o Secretion – when the electrical signal reaches the end of a nerve fiber, the neuron us ...
... o __________________ – all neurons have the ability to respond to environmental changes o Conductivity – Neurons produce traveling electrical signals that quickly reach other cells at _________________ locations o Secretion – when the electrical signal reaches the end of a nerve fiber, the neuron us ...
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
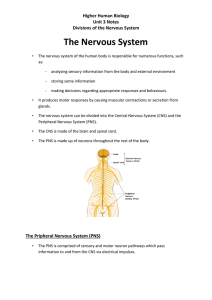
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
unit 3 study sheet - El Camino College
... 2. Know the function of each region and subregion of the brain: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum 3. Review the cranial nerves, their point of origin, where they end, the types of signals they carry 4. Review the assending and descending spinal tracts (more information in anatomy lab o ...
... 2. Know the function of each region and subregion of the brain: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum 3. Review the cranial nerves, their point of origin, where they end, the types of signals they carry 4. Review the assending and descending spinal tracts (more information in anatomy lab o ...
Evidence of Basal Temporo-occipital Cortex
... based on small positional differences, known as retinal disparities. Neurophysiological studies in monkeys showed that there is a widespread distribution of retinal disparity sensitive cells throughout many cortical areas of nonhuman primates. Sensitivity to retinal disparity has been recently found ...
... based on small positional differences, known as retinal disparities. Neurophysiological studies in monkeys showed that there is a widespread distribution of retinal disparity sensitive cells throughout many cortical areas of nonhuman primates. Sensitivity to retinal disparity has been recently found ...
Nervous System - Alamo Colleges
... The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla The effect of ACh binding to nicotinic receptors is ...
... The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla The effect of ACh binding to nicotinic receptors is ...
Nervous System 1
... • The nervous system control your actions. It coordinates different parts of your body so that they work together and are able to bring about the correct responses • Your nervous system coordinates your muscles, so that you can walk, run, write, read etc • When you smile the nervous system coordinat ...
... • The nervous system control your actions. It coordinates different parts of your body so that they work together and are able to bring about the correct responses • Your nervous system coordinates your muscles, so that you can walk, run, write, read etc • When you smile the nervous system coordinat ...
ppt file
... the pyramids, they decussate, which means that the axons within this fiber bundle cross from the left side of the brain to the right side of the brain. The cortex on the right side of the brain send and receives information from the left side of the body. I do not know why this is the case but it me ...
... the pyramids, they decussate, which means that the axons within this fiber bundle cross from the left side of the brain to the right side of the brain. The cortex on the right side of the brain send and receives information from the left side of the body. I do not know why this is the case but it me ...
Treatment of Thalamic Pain by Chronic Motor Cortex Stimulation
... moved to the correct position by using this response. After checking that the stimulating electrode had been placed on the motor cortex by recording the V-iu of the somatosensory evoked potentials, the electrode was connected to a transmitter which was implanted in the subcutaneous area of the anter ...
... moved to the correct position by using this response. After checking that the stimulating electrode had been placed on the motor cortex by recording the V-iu of the somatosensory evoked potentials, the electrode was connected to a transmitter which was implanted in the subcutaneous area of the anter ...
The Nervous System - Florida International University
... A heat receptor (free nerve ending) located in the L3 dermatome on the anterior thigh is stimulated by the heating pad you have put on the quadriceps muscle group of your sore right thigh The impulse travels along the peripheral nerve through the sensory neuron in the dorsal root ganglion and on ...
... A heat receptor (free nerve ending) located in the L3 dermatome on the anterior thigh is stimulated by the heating pad you have put on the quadriceps muscle group of your sore right thigh The impulse travels along the peripheral nerve through the sensory neuron in the dorsal root ganglion and on ...