Latin I Final Exam Study Guide (Final Exam is 20% of Course Grade
... o You will be given one verb to conjugate in all 6 tenses for only one person & number e.g. "Conjugate mitto, mittere, misī, missus in the 1st person singular" You must also write the positive and negative imperatives for this verb, in the singular and in the plural with their corresponding Engl ...
... o You will be given one verb to conjugate in all 6 tenses for only one person & number e.g. "Conjugate mitto, mittere, misī, missus in the 1st person singular" You must also write the positive and negative imperatives for this verb, in the singular and in the plural with their corresponding Engl ...
WOW Day 2 corrected
... 1. Suffixes – when adding a suffix that begins with a vowel we must drop the e on the root word - Example: ignore + ance = ignorance 2. Comma – used to separate what is being said from who said it (identifier) - Use a comma at the end of speech when it is followed by the identifier 3. Subject-verb a ...
... 1. Suffixes – when adding a suffix that begins with a vowel we must drop the e on the root word - Example: ignore + ance = ignorance 2. Comma – used to separate what is being said from who said it (identifier) - Use a comma at the end of speech when it is followed by the identifier 3. Subject-verb a ...
Latin 101: How to Identify Grammatical Forms in Context
... Or, “What is the case of horā? Why is it in that case? horā is ablative of time pronouns, including relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: Quintus, quī ingeniosus erat, ludum in Venusiā nōn amabatt. quī: nom. sing. masc. referring to Quintus adjectives: case, ...
... Or, “What is the case of horā? Why is it in that case? horā is ablative of time pronouns, including relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: Quintus, quī ingeniosus erat, ludum in Venusiā nōn amabatt. quī: nom. sing. masc. referring to Quintus adjectives: case, ...
Spanish - SFX Community
... Spanish Lower Intermediate Framework These are the grammar points we will be covering over the next three terms. Depending on the students’ interests and needs, the tutor will adapt and vary the program, topic-wise. There might be some variations depending on the general level of the class and what ...
... Spanish Lower Intermediate Framework These are the grammar points we will be covering over the next three terms. Depending on the students’ interests and needs, the tutor will adapt and vary the program, topic-wise. There might be some variations depending on the general level of the class and what ...
Yoruba Language
... Ó rá (He disappears) antidisestablishmentarianism "against-ending-institutionalize-condition-advocate-ideology" "the movement to prevent revoking the Church of England's status as the official church" ...
... Ó rá (He disappears) antidisestablishmentarianism "against-ending-institutionalize-condition-advocate-ideology" "the movement to prevent revoking the Church of England's status as the official church" ...
Latin 101: How to Identify Grammatical Forms in Context
... relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: ...
... relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: ...
Nothing but Nouns
... They come in different forms… Personal (I, you, he, she, it) Reflexive/Intensive (they end in -self) Demonstrative (this, that, these, those) Interrogative? (which, who, whom, whose) Relative (that, which, who, whose, whom) Indefinite (anyone, most, anybody…) ...
... They come in different forms… Personal (I, you, he, she, it) Reflexive/Intensive (they end in -self) Demonstrative (this, that, these, those) Interrogative? (which, who, whom, whose) Relative (that, which, who, whose, whom) Indefinite (anyone, most, anybody…) ...
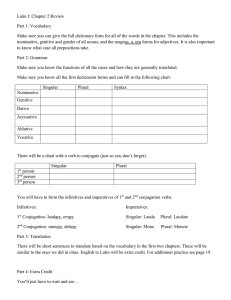
Chapter 2 Review - OCPS TeacherPress
... Make sure you can give the full dictionary form for all of the words in the chapter. This includes the nominative, genitive and gender of all nouns; and the magnus, a, um forms for adjectives. It is also important to know what case all prepositions take. Part 2: Grammar Make sure you know the functi ...
... Make sure you can give the full dictionary form for all of the words in the chapter. This includes the nominative, genitive and gender of all nouns; and the magnus, a, um forms for adjectives. It is also important to know what case all prepositions take. Part 2: Grammar Make sure you know the functi ...
1. Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing
... Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing receiving the action of the verb. ...
... Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing receiving the action of the verb. ...
Introduction to Old Persian Morphology
... can have “middle” forms but still have “active” meaning, that is, take a direct object (transitive). Passive morphology is more innovative, which the following attested: (i) forms built from the passive stem in –ya- (e.g., imperfect a-thanh-ya “it has been said”), common to Indo-Iranian for ...
... can have “middle” forms but still have “active” meaning, that is, take a direct object (transitive). Passive morphology is more innovative, which the following attested: (i) forms built from the passive stem in –ya- (e.g., imperfect a-thanh-ya “it has been said”), common to Indo-Iranian for ...
REV Grammar Handout
... Misplaced Modifier: a modifier that is placed far from the word it modifies, a modifier whose placement changes the meaning of a sentence, or a split infinitive (437-38) Dangling Modifier: a phrase or clause (often using “-ed” or “-ing”) that is not correctly attached to the object it describes (438 ...
... Misplaced Modifier: a modifier that is placed far from the word it modifies, a modifier whose placement changes the meaning of a sentence, or a split infinitive (437-38) Dangling Modifier: a phrase or clause (often using “-ed” or “-ing”) that is not correctly attached to the object it describes (438 ...
Guide to Parsing
... Throughout this grammar and the accompanying workbook, we emphasize the importance of being able to parse word forms. Parsing is the exercise by which one identifies the particular form of a given word. In learning Greek, it is important not simply to learn how to give a rough translation of a sente ...
... Throughout this grammar and the accompanying workbook, we emphasize the importance of being able to parse word forms. Parsing is the exercise by which one identifies the particular form of a given word. In learning Greek, it is important not simply to learn how to give a rough translation of a sente ...
Irregular endings for negative commands
... Sacar: to take out Tocar: to play musical instruments Practicar: to practice Buscar: to search, to look for ...
... Sacar: to take out Tocar: to play musical instruments Practicar: to practice Buscar: to search, to look for ...
THE QUESTIONS FOR FINAL EXAMINATION AT ROMANIAN
... 1. Impersonal Moods (Infinitive, Participle, Gerund and Supine); 2. Personal Moods (Indicative, Conjunctive, Conditional); 3. The Indicative Mood (Present, Past, Future Tense); 4. The Conjunctive Mood (Present, Past Tense); 5. The Conditional Mood (Present, Past); 6. Active Voice, Pasive Voice and R ...
... 1. Impersonal Moods (Infinitive, Participle, Gerund and Supine); 2. Personal Moods (Indicative, Conjunctive, Conditional); 3. The Indicative Mood (Present, Past, Future Tense); 4. The Conjunctive Mood (Present, Past Tense); 5. The Conditional Mood (Present, Past); 6. Active Voice, Pasive Voice and R ...
Parts of speech
... [e.g., he {hablado} (I have {spoken}), habríamos {spoken} (we would have {studied})]. There are three conjugations of verbs: -ar [e.g., hablar, to speak], -er [e.g., comer, to eat], and -ir [e.g., vivir], each with typical sets of endings. The endings in Spanish indicate mood, for example indicative ...
... [e.g., he {hablado} (I have {spoken}), habríamos {spoken} (we would have {studied})]. There are three conjugations of verbs: -ar [e.g., hablar, to speak], -er [e.g., comer, to eat], and -ir [e.g., vivir], each with typical sets of endings. The endings in Spanish indicate mood, for example indicative ...
conventions - Indo-European Genesis: Before Babel
... putrefy, *gh.r.bh = grab or groove) but each branch made its own choices. There may also have been subtle aspectual distinctions among the various Aorist formations, but they are now obscure, so one must lean on attested forms. Voice -- There were Active and Middle voices in Greek and Sanskrit; but ...
... putrefy, *gh.r.bh = grab or groove) but each branch made its own choices. There may also have been subtle aspectual distinctions among the various Aorist formations, but they are now obscure, so one must lean on attested forms. Voice -- There were Active and Middle voices in Greek and Sanskrit; but ...
english to sanskrit machine translation semantic mapper
... singular number denotes one, the dual two and the plural three or more. The English language has two numbers: singular and plural, where singular denotes one and plural denotes two or more. There exist eight classifications in each number (grammar cases): nominative, vocative, accusative, instrument ...
... singular number denotes one, the dual two and the plural three or more. The English language has two numbers: singular and plural, where singular denotes one and plural denotes two or more. There exist eight classifications in each number (grammar cases): nominative, vocative, accusative, instrument ...
SANSKRIT LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE. The most important
... central Asia where now is Chinese Turkestan; and as vehicles of Buddhism they have influenced through translation the whole of central and eastern Asia; Hindu civilization carried their vocabulary into the East Indies and the Malay peninsula. The oldest documents of Indo-Aryan are composed in Sanskr ...
... central Asia where now is Chinese Turkestan; and as vehicles of Buddhism they have influenced through translation the whole of central and eastern Asia; Hindu civilization carried their vocabulary into the East Indies and the Malay peninsula. The oldest documents of Indo-Aryan are composed in Sanskr ...
Grammar I-II
... Nouns: declensions I, II, and III Case usage: nominative: subject, predicate nominative, predicate adjective genitive: possession, objective dative: indirect object accusative: direct object, place to which and into which and after certain prepositions ablative: means, place where, place from which, ...
... Nouns: declensions I, II, and III Case usage: nominative: subject, predicate nominative, predicate adjective genitive: possession, objective dative: indirect object accusative: direct object, place to which and into which and after certain prepositions ablative: means, place where, place from which, ...
Parts of Speech
... 6) PREPOSITIONS show relation between a noun or pronoun and some other word or words in the same sentence. 7) CONJUNCTIONS connect words, groups of words, without affecting their grammatical relations. 8) INTERJECTIONS are simply exclamations (e.g. oh! vae!); they are often not strictly classified a ...
... 6) PREPOSITIONS show relation between a noun or pronoun and some other word or words in the same sentence. 7) CONJUNCTIONS connect words, groups of words, without affecting their grammatical relations. 8) INTERJECTIONS are simply exclamations (e.g. oh! vae!); they are often not strictly classified a ...
Latin I Review - Dover High School
... ▫ Introduces a phrase which gives more information about the sentence (in tablinō—in the study) ...
... ▫ Introduces a phrase which gives more information about the sentence (in tablinō—in the study) ...
Unpacked L3.1a
... Standard English (nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, simple verb tenses, subject/verb agreement). Students must be able to explain the proper functions of different parts of speech. Standards that are related to conventions are appropriate to formal spoken English as they are to formal ...
... Standard English (nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, simple verb tenses, subject/verb agreement). Students must be able to explain the proper functions of different parts of speech. Standards that are related to conventions are appropriate to formal spoken English as they are to formal ...
Chapter 8
... • Extension of be- forms with present participles: I am working; they are dancing • Largely due to loss of on as a preposition before the participle used as gerund from phonological leveling • Happens in 16th c. • By 18th c. has extended to passive voice: The house is being built. Earliest example o ...
... • Extension of be- forms with present participles: I am working; they are dancing • Largely due to loss of on as a preposition before the participle used as gerund from phonological leveling • Happens in 16th c. • By 18th c. has extended to passive voice: The house is being built. Earliest example o ...
The Old English Alphabet
... possessive pronouns were derived from the genitive case of the personal pronouns. Demonstrative Pronouns could also act as a noun determiner (the definite article) indicating its gender, number, and case: Þes (this) and sē (that). Interrogative Pronouns hwā (who) and hwæt (what) had a four-case ...
... possessive pronouns were derived from the genitive case of the personal pronouns. Demonstrative Pronouns could also act as a noun determiner (the definite article) indicating its gender, number, and case: Þes (this) and sē (that). Interrogative Pronouns hwā (who) and hwæt (what) had a four-case ...