Parts of Speech Review
... Adverbs – modify verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. They tell how, when, where and how much. Prepositions – show a relationship between its object and another word in the sentence. Conjunctions – join words, phrases and clauses. Interjections – exclamatory word that shows feeling/emotion ...
... Adverbs – modify verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. They tell how, when, where and how much. Prepositions – show a relationship between its object and another word in the sentence. Conjunctions – join words, phrases and clauses. Interjections – exclamatory word that shows feeling/emotion ...
ppt
... ‘my father is looking for the cows’ • Here, the meaning of the phrase “look for cows” is expressed in a single word (they can express it with a separate noun as well). • This is similar in many ways to what happens in compounding in English; remember truck driver. In English, though we can’t use thi ...
... ‘my father is looking for the cows’ • Here, the meaning of the phrase “look for cows” is expressed in a single word (they can express it with a separate noun as well). • This is similar in many ways to what happens in compounding in English; remember truck driver. In English, though we can’t use thi ...
Ling 001, Week 4
... ‘my father is looking for the cows’ • Here, the meaning of the phrase “look for cows” is expressed in a single word (they can express it with a separate noun as well). • This is similar in many ways to what happens in compounding in English; remember truck driver. In English, though we can’t use thi ...
... ‘my father is looking for the cows’ • Here, the meaning of the phrase “look for cows” is expressed in a single word (they can express it with a separate noun as well). • This is similar in many ways to what happens in compounding in English; remember truck driver. In English, though we can’t use thi ...
Morphology review
... If the language is at all agglutinative, is it dominantly prefixing, suffixing or neither? Illustrate the major and secondary patterns (including examples from all morphological processes if possible). If the language is at all polysynthetic, is it dominantly “head-marking” or “dependentmarking”, or ...
... If the language is at all agglutinative, is it dominantly prefixing, suffixing or neither? Illustrate the major and secondary patterns (including examples from all morphological processes if possible). If the language is at all polysynthetic, is it dominantly “head-marking” or “dependentmarking”, or ...
Latin is an inflected language, that is, a language
... _______________ – Used for indirect objects, that is, secondary objects of verbs. Usually translated with “to” or “for.” _______________ – Direct object of verbs; the person or object directly affected by the verb. Also, used with certain prepositions. _______________ – This is the adverbial c ...
... _______________ – Used for indirect objects, that is, secondary objects of verbs. Usually translated with “to” or “for.” _______________ – Direct object of verbs; the person or object directly affected by the verb. Also, used with certain prepositions. _______________ – This is the adverbial c ...
Adverbs
... where, how often, and how much. Adverbs frequently end in “ly” and modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. ...
... where, how often, and how much. Adverbs frequently end in “ly” and modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. ...
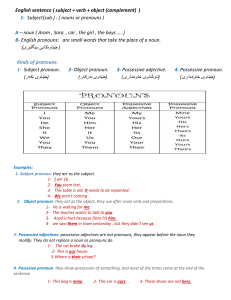
Subject(sub.) : ( nouns or pronouns )
... 1- Subject pronoun: they act as the subject. 1- I am 16. 2- You seem lost. 3- This table is old. It needs to be repainted. 4- We aren't coming. 2- Object pronoun: they act as the object, they use after main verb and prepositions. 1- He is waiting for me. 2- The teacher wants to talk to you. 3- Azad ...
... 1- Subject pronoun: they act as the subject. 1- I am 16. 2- You seem lost. 3- This table is old. It needs to be repainted. 4- We aren't coming. 2- Object pronoun: they act as the object, they use after main verb and prepositions. 1- He is waiting for me. 2- The teacher wants to talk to you. 3- Azad ...
Syntax- The description of how words, phrases, and clauses are
... Morphology- The part of grammar explaining how morphemes are put together to construct words. Grammar- The analysis of the structure of phrases and sentences. Morphemes- Parts of words, i.e. stems, prefixes, and suffixes. For example, un + friend + ly contains three morphemes: a prefix un, a stem fr ...
... Morphology- The part of grammar explaining how morphemes are put together to construct words. Grammar- The analysis of the structure of phrases and sentences. Morphemes- Parts of words, i.e. stems, prefixes, and suffixes. For example, un + friend + ly contains three morphemes: a prefix un, a stem fr ...
Irregular endings for negative commands
... Sacar: to take out Tocar: to play musical instruments Practicar: to practice Buscar: to search, to look for ...
... Sacar: to take out Tocar: to play musical instruments Practicar: to practice Buscar: to search, to look for ...
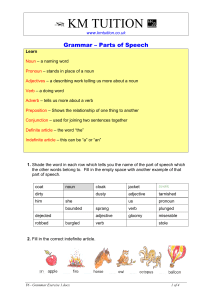
English Grammar
... and spoken formats. The student a. Identifies and uses the eight basic parts of speech and demonstrates that words can be different parts of speech within a ...
... and spoken formats. The student a. Identifies and uses the eight basic parts of speech and demonstrates that words can be different parts of speech within a ...
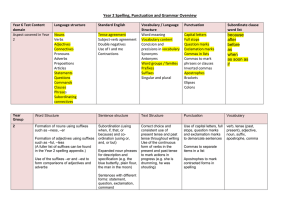
Year 1: Terminology Taught • Letter • Capital letter • Word • Singular
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
Word Classes - Elstow School
... Pronoun Sometimes you refer to a person or thing without using its actual name. The word you use instead of the noun is called a pronoun. I ...
... Pronoun Sometimes you refer to a person or thing without using its actual name. The word you use instead of the noun is called a pronoun. I ...
Grammatical terminology Terminologia gramatyczna
... The ball rolled down the road and stopped under a car. Przyimek We got up early because it was a special day. We Czasownik (co have never been so nervous. I remember this day. I robi?) will never forget it. ...
... The ball rolled down the road and stopped under a car. Przyimek We got up early because it was a special day. We Czasownik (co have never been so nervous. I remember this day. I robi?) will never forget it. ...
HNL GYMNASIUM BRUGKLAS NEW HEADWAY ELEMENTARY
... Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. Adjective /noun: The grey elephant Adjective/pronoun: The grey one ...
... Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. Adjective /noun: The grey elephant Adjective/pronoun: The grey one ...
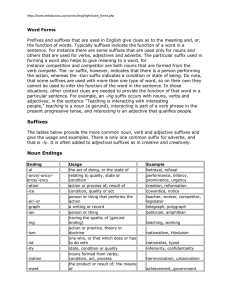
Word Forms - Professor Catherine Hatzakos
... Prefixes and suffixes that are used in English give clues as to the meaning and, or, the function of words. Typically suffixes indicate the function of a word in a sentence. For instance there are some suffixes that are used only for nouns and others that are used for verbs, adjectives and adverbs. ...
... Prefixes and suffixes that are used in English give clues as to the meaning and, or, the function of words. Typically suffixes indicate the function of a word in a sentence. For instance there are some suffixes that are used only for nouns and others that are used for verbs, adjectives and adverbs. ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... ours, yours, theirs), Reflexive (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves), demonstrative (this, that, these, those), indefinite (someone, something, anything, anyone, nothing, everyone), and relative (who, that, which, when, where, why). ...
... ours, yours, theirs), Reflexive (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves), demonstrative (this, that, these, those), indefinite (someone, something, anything, anyone, nothing, everyone), and relative (who, that, which, when, where, why). ...
Parts of Speech – Verbs
... Verb: A verb is a word used to express an action or a state of being. A verb may be more than one word (when it includes helping verbs or auxiliaries). This is called a verb phrase. Example: The woman painted a picture. In this example, the word “painted” is a verb because it expresses action. Examp ...
... Verb: A verb is a word used to express an action or a state of being. A verb may be more than one word (when it includes helping verbs or auxiliaries). This is called a verb phrase. Example: The woman painted a picture. In this example, the word “painted” is a verb because it expresses action. Examp ...
Verb - Plain Local Schools
... Verb: A verb is a word used to express an action or a state of being. A verb may be more than one word (when it includes helping verbs or auxiliaries). This is called a verb phrase. Example: The woman painted a picture. In this example, the word “painted” is a verb because it expresses action. Examp ...
... Verb: A verb is a word used to express an action or a state of being. A verb may be more than one word (when it includes helping verbs or auxiliaries). This is called a verb phrase. Example: The woman painted a picture. In this example, the word “painted” is a verb because it expresses action. Examp ...
English Grammar - HCC Learning Web
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
Parts of Speech Table
... Determiners (a, the, every, this, that) modify and determine the kind of reference a noun or noun group has. ...
... Determiners (a, the, every, this, that) modify and determine the kind of reference a noun or noun group has. ...
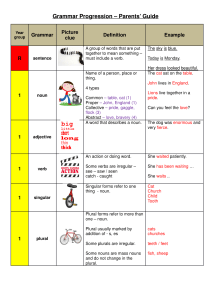
Parents` Guide to Grammar: Progression
... There are two types of clauses She can leave the office now 1) Independent- this can stand alone. Dependent clause 2) dependent-works only as a whole sentence. It could begin because she finished work with after, although, because, early. if, when, while. A small group of closely If you can related ...
... There are two types of clauses She can leave the office now 1) Independent- this can stand alone. Dependent clause 2) dependent-works only as a whole sentence. It could begin because she finished work with after, although, because, early. if, when, while. A small group of closely If you can related ...
Grammar Review
... a word usually preceding (coming before) a noun or pronoun and expressing a relation to another word or element in the clause, as in “the man on the platform” and “she arrived after dinner.” ...
... a word usually preceding (coming before) a noun or pronoun and expressing a relation to another word or element in the clause, as in “the man on the platform” and “she arrived after dinner.” ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.