Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the nervous system 3types: 1. sensory neurons- carry impulses from sense organs to brain; 2. motor neurons- carry impulses from brain to muscles/glands. 3. Interneuron: carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons (connects them) Parts of the Neuron: ...
... Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the nervous system 3types: 1. sensory neurons- carry impulses from sense organs to brain; 2. motor neurons- carry impulses from brain to muscles/glands. 3. Interneuron: carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons (connects them) Parts of the Neuron: ...
1. Which of the following is the component of the limbic system that
... E) was controlled by both her nervous system and impulses from her endocrine system. 33. A picture of a cat is briefly flashed in the left visual field and a picture of a mouse is briefly flashed in the right visual field of a split-brain patient. The individual will be able to use her A) right hand ...
... E) was controlled by both her nervous system and impulses from her endocrine system. 33. A picture of a cat is briefly flashed in the left visual field and a picture of a mouse is briefly flashed in the right visual field of a split-brain patient. The individual will be able to use her A) right hand ...
Neural Pathways and Transmission
... This creates an overall charge that is negative within the cell at rest The internal environment is generally at –70 mV ...
... This creates an overall charge that is negative within the cell at rest The internal environment is generally at –70 mV ...
Neural Oscillators on the Edge: Harnessing Noise to Promote Stability
... discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability of an oscillator to switch off, for example prolonged pauses in automatic breathing commonly observed in preterm infants. I will present theory and experimental ...
... discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability of an oscillator to switch off, for example prolonged pauses in automatic breathing commonly observed in preterm infants. I will present theory and experimental ...
The Nervous System - Science with Mr. Enns
... Analyzes information from the receptors and decides what to do ...
... Analyzes information from the receptors and decides what to do ...
Seminar Slides
... Synapse - point where the axon of one neuron connects to a dendrite of another Electrical synapse - two cells touch and are connected by tiny holes, which lets the nerve impulse pass directly from one neuron to the other Chemical synapse - two cells do not touch and the nerve impulse needs par ...
... Synapse - point where the axon of one neuron connects to a dendrite of another Electrical synapse - two cells touch and are connected by tiny holes, which lets the nerve impulse pass directly from one neuron to the other Chemical synapse - two cells do not touch and the nerve impulse needs par ...
hebbRNN: A Reward-Modulated Hebbian Learning Rule for
... and Gerstner 2014; Carnevale et al. 2015; Laje, Buonomano, and Buonomano 2013). However, training these networks to produce meaningful behavior has proven difficult. Furthermore, the most common methods are generally not biologically-plausible and rely on information not local to the synapses of ind ...
... and Gerstner 2014; Carnevale et al. 2015; Laje, Buonomano, and Buonomano 2013). However, training these networks to produce meaningful behavior has proven difficult. Furthermore, the most common methods are generally not biologically-plausible and rely on information not local to the synapses of ind ...
Brain Neurotransmitters
... • Contributes to the control of voluntary movement, • Inhibitory (i.e., decreasing action of receiving cell) or excitatory, depending on receptor on receiving cell. • Affects areas related to body movement; emotional arousal, and "reward" systems, pleasurable emotions • Neurotransmitter looked at mo ...
... • Contributes to the control of voluntary movement, • Inhibitory (i.e., decreasing action of receiving cell) or excitatory, depending on receptor on receiving cell. • Affects areas related to body movement; emotional arousal, and "reward" systems, pleasurable emotions • Neurotransmitter looked at mo ...
Ch 48 Nervous System
... Myelin sheath- supporting, insulating layer produced by Schwann Cells Schwann cells-PNS support cells; surround axons Axon hillock-Hillock-axon extends from here Synaptic terminals~ neurotransmitter releaser ...
... Myelin sheath- supporting, insulating layer produced by Schwann Cells Schwann cells-PNS support cells; surround axons Axon hillock-Hillock-axon extends from here Synaptic terminals~ neurotransmitter releaser ...
1. Receptor cells
... The Biological Foundations of Behavior • The nervous system: the most complicated system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting ...
... The Biological Foundations of Behavior • The nervous system: the most complicated system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting ...
Unit 3- Biological Psychology Study Guide
... their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between the nervous system, endocrine system, and the brain in relation to individual development, actions, and behaviors. ...
... their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between the nervous system, endocrine system, and the brain in relation to individual development, actions, and behaviors. ...
The Nervous System
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
Microscopic Nervous System and Reflexes with answers
... lie within the brain and spinal cord; multipolar and link other neurons; transmit impulses from one part of the brain or spinal cord to another; direct incoming sensory impulses to appropriate parts for processing and interpreting; Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) – multipolar and carry impulses out ...
... lie within the brain and spinal cord; multipolar and link other neurons; transmit impulses from one part of the brain or spinal cord to another; direct incoming sensory impulses to appropriate parts for processing and interpreting; Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) – multipolar and carry impulses out ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... from randomness—to which our nervous systems are adapted. This adaptation to the statistics of our physical world is another form of learning (be it on an evolutionary time scale) expressed by today’s brains. Finally, and most miraculously of all maybe, brains self-assemble, starting with just one c ...
... from randomness—to which our nervous systems are adapted. This adaptation to the statistics of our physical world is another form of learning (be it on an evolutionary time scale) expressed by today’s brains. Finally, and most miraculously of all maybe, brains self-assemble, starting with just one c ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... • Myelinated axons have a white appearance, giving rise to white matter – Areas of the brain that do not appear white (areas rich in cell bodies) area gray and are called gray ...
... • Myelinated axons have a white appearance, giving rise to white matter – Areas of the brain that do not appear white (areas rich in cell bodies) area gray and are called gray ...
Interaural Phase Difference (degree)
... Result: ITD tuning improves as synaptic inputs get farther from soma along dendrites ...
... Result: ITD tuning improves as synaptic inputs get farther from soma along dendrites ...
DM-Lecture-10 - WordPress.com
... – Each neuron is connected to the others through 10000 synapses Properties of the brain – It can learn, reorganize itself from experience – It adapts to the environment – It is robust and fault tolerant ...
... – Each neuron is connected to the others through 10000 synapses Properties of the brain – It can learn, reorganize itself from experience – It adapts to the environment – It is robust and fault tolerant ...
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... Chapter 2 The Biology of Mind Neural Communication The body’s information system is built from billions of interconnected cells called neurons. Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. Neuron A nerve cell, or a neuron, ...
... Chapter 2 The Biology of Mind Neural Communication The body’s information system is built from billions of interconnected cells called neurons. Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. Neuron A nerve cell, or a neuron, ...
Chapter 3
... Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
... Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
Slide ()
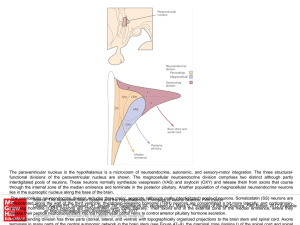
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Slide ()
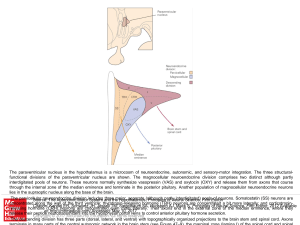
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...