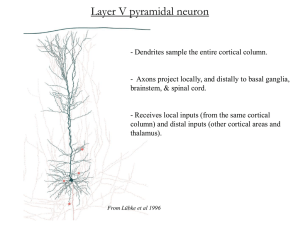
The Nervous System
... Call 911 – seek medical attention Concussions – don’t let victim fall asleep; stay away from activity which may lead to another concussion (second impact syndrome) Stroke – paralysis on one side of the body & slurred speech/facial muscles Relation to Other Systems Muscular – motor neurons he ...
... Call 911 – seek medical attention Concussions – don’t let victim fall asleep; stay away from activity which may lead to another concussion (second impact syndrome) Stroke – paralysis on one side of the body & slurred speech/facial muscles Relation to Other Systems Muscular – motor neurons he ...
module 6 - sandrablake
... a neuron always fires with the same intensity no matter what the stimulation is. It doesn’t matter if there is a strong stimulation or weak stimulation at the cell’s dendrites. As long as there is enough energy to trigger the neuron, it will fire with the same intensity. Read the comparison of a neu ...
... a neuron always fires with the same intensity no matter what the stimulation is. It doesn’t matter if there is a strong stimulation or weak stimulation at the cell’s dendrites. As long as there is enough energy to trigger the neuron, it will fire with the same intensity. Read the comparison of a neu ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... The Nervous System works with the Endocrine System to provide electrical and chemical control of ALL body processes. ...
... The Nervous System works with the Endocrine System to provide electrical and chemical control of ALL body processes. ...
The Nervous System - Needham.K12.ma.us
... within a Neuron! • The change in charge that travels from the dendrite of a neuron down the axon. • Can be represented on a graph as a nerve impluse: ...
... within a Neuron! • The change in charge that travels from the dendrite of a neuron down the axon. • Can be represented on a graph as a nerve impluse: ...
Nervous System
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory-uses receptors to gather information from all over the body 2. Interpretation-the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. Response-sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts ...
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory-uses receptors to gather information from all over the body 2. Interpretation-the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. Response-sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 03 garber edited
... – Directs metabolism – No role in neural signaling ...
... – Directs metabolism – No role in neural signaling ...
Allison Bynum Neurobiology A.1 – A.3 Allison Bynum A.1 Neural
... A.2 – The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. Nerve cells migrate to the outer edge of the neural tube and cause the walls to thicken. The neural tube develops into the brain and spinal cord. The anterior end of the tube expands to form the cerebral hemispheres of the br ...
... A.2 – The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. Nerve cells migrate to the outer edge of the neural tube and cause the walls to thicken. The neural tube develops into the brain and spinal cord. The anterior end of the tube expands to form the cerebral hemispheres of the br ...
The Nervous System
... Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicles 5. Give the role and position of three types of neuron: a. sensory neurons - carry messages from the sense organ to the CNS b. motor neurons ...
... Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicles 5. Give the role and position of three types of neuron: a. sensory neurons - carry messages from the sense organ to the CNS b. motor neurons ...
Nervous System
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
Motor Neurons
... the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a ...
... the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a ...
Differential Permeability of the Membrane
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
source1
... output. The neuron has two modes of operation; the training mode and the using mode. In the training mode, the neuron can be trained to fire (or not), for particular input patterns. In the using mode, when a taught input pattern is detected at the input, its associated output becomes the current out ...
... output. The neuron has two modes of operation; the training mode and the using mode. In the training mode, the neuron can be trained to fire (or not), for particular input patterns. In the using mode, when a taught input pattern is detected at the input, its associated output becomes the current out ...
Pt2Localization - MemoryAndCognition
... Sensory / Afferent neurons: info TOWARD CNS Motor / Efferent neurons: info AWAY from CNS Interneurons: info to other neurons in the CNS ...
... Sensory / Afferent neurons: info TOWARD CNS Motor / Efferent neurons: info AWAY from CNS Interneurons: info to other neurons in the CNS ...
Chapter 2 Notes
... Chapter 2 Brain and Behavior Neuron and Its Parts • Neuron: Individual nerve cell – Dendrites: – Soma: cell body; body of the neuron – Axon: – Axon Terminals: Branches that link the dendrites and somas of other neurons ...
... Chapter 2 Brain and Behavior Neuron and Its Parts • Neuron: Individual nerve cell – Dendrites: – Soma: cell body; body of the neuron – Axon: – Axon Terminals: Branches that link the dendrites and somas of other neurons ...
Brain Function and Organization via Imaging
... 2. Brain Macro anatomy – lobes, tissues, cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, connectivity 3. Brain Micro anatomy – Neurons 4. Dynamics of brain change over time 5. Our lab: healthy normal aging vs. dementia ...
... 2. Brain Macro anatomy – lobes, tissues, cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, connectivity 3. Brain Micro anatomy – Neurons 4. Dynamics of brain change over time 5. Our lab: healthy normal aging vs. dementia ...
Chapter 9: Nervous System guide—Please complete these notes on
... outward 6. Action potential that results causes a bioelectric current that stimulates adjacent portions of membrane 7. Wave of action potentials travels axon as nerve impulse ...
... outward 6. Action potential that results causes a bioelectric current that stimulates adjacent portions of membrane 7. Wave of action potentials travels axon as nerve impulse ...
Invariant selectivity of auditory neurons due to predictive coding
... 2 Seattle University, Department of Mathematics, Seattle, WA, USA. ...
... 2 Seattle University, Department of Mathematics, Seattle, WA, USA. ...
Slayt 1 - Department of Information Technologies
... This course gives a basic neural network architectures and learning rules. ...
... This course gives a basic neural network architectures and learning rules. ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... a. Axon An axon, also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. b. Dendrite Dendrites ar ...
... a. Axon An axon, also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. b. Dendrite Dendrites ar ...
Lectures220Week7Note..
... an example of positive feedback. How voltage gated channels generate and keep brief the action potential. The flows of major ions during resting, ...
... an example of positive feedback. How voltage gated channels generate and keep brief the action potential. The flows of major ions during resting, ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Notes
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...