An Introductory to Statistical Models of Neural Data - Math
... models inappropriate, it is necessary to define probability models that account for history dependence. ...
... models inappropriate, it is necessary to define probability models that account for history dependence. ...
Neurons
... A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but all action potentials are of the ...
... A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but all action potentials are of the ...
100 - Bloomfield Central School
... balance and muscle movements, such as when you are playing a sport of instrument. ...
... balance and muscle movements, such as when you are playing a sport of instrument. ...
Do Now: Review the Human Spark
... – brain and spinal cord 3. To send information or RESPOND – to muscles, glands and other organs ...
... – brain and spinal cord 3. To send information or RESPOND – to muscles, glands and other organs ...
Nervous System
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by the axon of another neuron or by the environment. Na+ pores open and the flood of Na+ ions makes the inside positive. This reversal of charges, from negative to positive is called a nerve impulse, or an action potential. ...
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by the axon of another neuron or by the environment. Na+ pores open and the flood of Na+ ions makes the inside positive. This reversal of charges, from negative to positive is called a nerve impulse, or an action potential. ...
Slide 1
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
Crossing the Synaptic Gap
... determine how many incoming signals excite the neuron to fire. The second roll will determine how many signals inhibit firing (or have students use two different colored die and roll them together). During each trial, students should subtract the second number from the first. If the outcome is zero ...
... determine how many incoming signals excite the neuron to fire. The second roll will determine how many signals inhibit firing (or have students use two different colored die and roll them together). During each trial, students should subtract the second number from the first. If the outcome is zero ...
Peripheral nervous system
... • Saltatory connection - action potentials jumping from node to node in myelinated axons ...
... • Saltatory connection - action potentials jumping from node to node in myelinated axons ...
The nervous system - Sonoma Valley High School
... by another neuron or the environment Action potential - When an impulse is sent the charge reverses inside the cell – it becomes positive Threshold – the amount of stimulus required to activate the neuron ...
... by another neuron or the environment Action potential - When an impulse is sent the charge reverses inside the cell – it becomes positive Threshold – the amount of stimulus required to activate the neuron ...
Biology 3201 - Corner Brook Regional High
... • Neurons - nerve cells that transmit signals to/from the brain at up to 200 mph. – consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a long projection called an axon, which conducts the signal. The signal terminates at the axon terminals which transmits an electro-c ...
... • Neurons - nerve cells that transmit signals to/from the brain at up to 200 mph. – consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a long projection called an axon, which conducts the signal. The signal terminates at the axon terminals which transmits an electro-c ...
The Nervous System
... • Sensory neurons send messages about your body or environment to the spinal cord up to the brain for interpretation. ...
... • Sensory neurons send messages about your body or environment to the spinal cord up to the brain for interpretation. ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... All neurons connected to inputs not connected to each other Often uses a MLP as an output layer Neurons are self-organising Trained using “winner-takes all” ...
... All neurons connected to inputs not connected to each other Often uses a MLP as an output layer Neurons are self-organising Trained using “winner-takes all” ...
Chapter 48 Worksheet
... 3. Depolarization: influx of Na+ in. 4. Repolarization Outline the main steps taking place in this picture: ...
... 3. Depolarization: influx of Na+ in. 4. Repolarization Outline the main steps taking place in this picture: ...
Slide ()
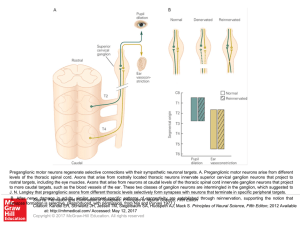
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
nervous system
... • Neurotransmitters diffuse to postsynaptic cell • Postsynaptic membrane has gated channels that open when neurotransmitters bond to specific receptors ...
... • Neurotransmitters diffuse to postsynaptic cell • Postsynaptic membrane has gated channels that open when neurotransmitters bond to specific receptors ...
PPT Guide Brain Development
... There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ____________ and ____________ ...
... There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ____________ and ____________ ...
Slide 1 - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... 4. Recurrent networks of spiking neurons. This is a field that is advancing rapidly! There were two absolutely seminal papers about a decade ago: van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Science, 1996) van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Neural Comp., 1998) We now understand very well randomly connected networks ...
... 4. Recurrent networks of spiking neurons. This is a field that is advancing rapidly! There were two absolutely seminal papers about a decade ago: van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Science, 1996) van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Neural Comp., 1998) We now understand very well randomly connected networks ...
The Nervous System
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
The Emerging Nervous System
... Neurons • Neural Plate: A group of cells that form a flat structure three weeks after conception • At four weeks the neural plate folds to form a tube that than becomes the brain and spinal cord • Neurons begin to produce ten weeks after conception ...
... Neurons • Neural Plate: A group of cells that form a flat structure three weeks after conception • At four weeks the neural plate folds to form a tube that than becomes the brain and spinal cord • Neurons begin to produce ten weeks after conception ...
Inside the brain
... The parietal lobe processes information from the body and senses, and integrates it to help orient the body and carry out movement in space. The occipital lobe is the part of the brain that manages vision, containing dozens of areas that are specialised for processing inputs from the eyes. The tempo ...
... The parietal lobe processes information from the body and senses, and integrates it to help orient the body and carry out movement in space. The occipital lobe is the part of the brain that manages vision, containing dozens of areas that are specialised for processing inputs from the eyes. The tempo ...
1 - Kvalley Computers and Internet
... Karen Ann Quinlan was a woman who, as a result of mixing tranquilizers and alcohol, became what is called "brain dead". Describe the parts of her brain that were most likely damaged. Be specific. Provide a plausible explanation of why she continued to live even after life supports were ...
... Karen Ann Quinlan was a woman who, as a result of mixing tranquilizers and alcohol, became what is called "brain dead". Describe the parts of her brain that were most likely damaged. Be specific. Provide a plausible explanation of why she continued to live even after life supports were ...
Chapter 2 - bobcat
... MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not use xrays. The process involves passing a strong magnetic field through the head. The magnetic field used is 30,000 + times that of the earth's magnetic field. It's effect on the body, however, is harmless and temporary. The MRI scanner can detect ...
... MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not use xrays. The process involves passing a strong magnetic field through the head. The magnetic field used is 30,000 + times that of the earth's magnetic field. It's effect on the body, however, is harmless and temporary. The MRI scanner can detect ...