Seminar in Neuroscience Why Corticospinal Motor Neurons Are Important For
... Corticospinal motor neurons (CSMN) are some of the most important cortical components of motor neuron circuitry. Their unique ability to collect, integrate, translate and transmit the brain's input to the spinal cord targets allow them to function as the spokesperson for the cerebral cortex for the ...
... Corticospinal motor neurons (CSMN) are some of the most important cortical components of motor neuron circuitry. Their unique ability to collect, integrate, translate and transmit the brain's input to the spinal cord targets allow them to function as the spokesperson for the cerebral cortex for the ...
Neuron Physiology Notes
... Stages of a Nerve Impulse STAGE 1) Neuron at “resting membrane potential” is polarized with a resting potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is r ...
... Stages of a Nerve Impulse STAGE 1) Neuron at “resting membrane potential” is polarized with a resting potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is r ...
Essential Questions and Vocabulary
... What is a neuron? What are its major parts and functions? What types of neurons are found in the nervous system? How are neural messages transmitted? How is the neural system organized? What are the lobes and localizations of the brain? How is the cerebral cortex organized? What experi ...
... What is a neuron? What are its major parts and functions? What types of neurons are found in the nervous system? How are neural messages transmitted? How is the neural system organized? What are the lobes and localizations of the brain? How is the cerebral cortex organized? What experi ...
Document
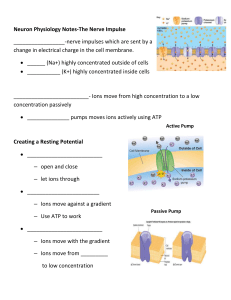
... is constantly making adjustments. It is never at rest! Part I. Nerve Control • _____________________________ – _______________- specialized for the transition of impulses from one part of the body to another. •Neurons _______________ _______________ –Cannot be replaced. If outside the brain and spin ...
... is constantly making adjustments. It is never at rest! Part I. Nerve Control • _____________________________ – _______________- specialized for the transition of impulses from one part of the body to another. •Neurons _______________ _______________ –Cannot be replaced. If outside the brain and spin ...
Chapter 48: Nervous Systems Overview: Command and Control
... • In vertebrates, axons are myelinated, which also causing the speed of an action potential to increase – Gaps between the myelination are known as ______________________________ Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses • In an electrical synapse, electrical current flows directly from one c ...
... • In vertebrates, axons are myelinated, which also causing the speed of an action potential to increase – Gaps between the myelination are known as ______________________________ Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses • In an electrical synapse, electrical current flows directly from one c ...
Frontiers in , Ph.D. Pharmacology Proudly Presents
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
Neural Tissue
... Axon terminal of presynaptic cell Synaptic cleft Dendrite or cell body of postsynaptic cell ...
... Axon terminal of presynaptic cell Synaptic cleft Dendrite or cell body of postsynaptic cell ...
The synapse.
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
THE BRAIN - Dublin City Schools
... Thinking part of the brain- most highly developed Store and process language, math and strategies Also contains the LIMBIC SYSTEM ...
... Thinking part of the brain- most highly developed Store and process language, math and strategies Also contains the LIMBIC SYSTEM ...
Receptive Fields
... Receptive Fields Introduction: Given the enormity of the sensory space through which our nervous system must guide us, it comes as intuitive that our sensory systems should parcel out sensitivity to specific sensory regions over large populations of neurons. Within these large populations, there are ...
... Receptive Fields Introduction: Given the enormity of the sensory space through which our nervous system must guide us, it comes as intuitive that our sensory systems should parcel out sensitivity to specific sensory regions over large populations of neurons. Within these large populations, there are ...
neuron
... • knobs: structure at the end of one of the axon’s branches that releases chemicals into the space between neurons, when the neuron is fired ...
... • knobs: structure at the end of one of the axon’s branches that releases chemicals into the space between neurons, when the neuron is fired ...
UNIT II: THE HUMAN BRAIN
... Reattaching Limbs • Limbs can be reattached because of something we call nerves. • In whole body except brain/spinal cord • String-like bundles of axons and dendrites • Carry messages from senses, skin, muscles, and organs ...
... Reattaching Limbs • Limbs can be reattached because of something we call nerves. • In whole body except brain/spinal cord • String-like bundles of axons and dendrites • Carry messages from senses, skin, muscles, and organs ...
Neural Networks (NN)
... Neural Networks are a different paradigm for computing: von Neumann machines are based on the processing/memory abstraction of human information processing. neural networks are based on the parallel architecture of animal brains. Neural networks are a form of multiprocessor computer system, with ...
... Neural Networks are a different paradigm for computing: von Neumann machines are based on the processing/memory abstraction of human information processing. neural networks are based on the parallel architecture of animal brains. Neural networks are a form of multiprocessor computer system, with ...
Slide ()
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...
Part 1: The Strange Tale of Phineas Gage
... For part 1, you will need to read the included link to find the answers to the questions. For part 2, you will just need to read and highlight (and play with the animations at the end- don’t skip it- it’s very important). Make sure you take care of both. Tomorrow, you will upload this file to turnit ...
... For part 1, you will need to read the included link to find the answers to the questions. For part 2, you will just need to read and highlight (and play with the animations at the end- don’t skip it- it’s very important). Make sure you take care of both. Tomorrow, you will upload this file to turnit ...
Frequently asked questions Psychology 1010.06M A Biologically-Oriented
... • output can’t get out • different levels wired to different body parts – quadraplegic vs. paraplegic ...
... • output can’t get out • different levels wired to different body parts – quadraplegic vs. paraplegic ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – _____ At end of axon a chemical is released, crosses the synapse and binds to the dendrite on the other side to begin again CNS – _____ PNS – _____ Brain coordinates all body activities except _____ 3 parts, 100 billion neurons o cerebrum – ...
... Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – _____ At end of axon a chemical is released, crosses the synapse and binds to the dendrite on the other side to begin again CNS – _____ PNS – _____ Brain coordinates all body activities except _____ 3 parts, 100 billion neurons o cerebrum – ...
Perception, learning and memory - Max-Planck
... Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in combination rather than in isolation, and experimental techniques traditionally used to study individual elements need to evolve towards this. One new approach involves light-activated genetic switches that control the activity of sp ...
... Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in combination rather than in isolation, and experimental techniques traditionally used to study individual elements need to evolve towards this. One new approach involves light-activated genetic switches that control the activity of sp ...
9.2 - 4ubiology
... of the neuron less positive (= more negative) again: this is repolarization and the neuron has become repolarized ...
... of the neuron less positive (= more negative) again: this is repolarization and the neuron has become repolarized ...