Chapter 7
... • Axon – Carries electrical impulse away from cell body – May be covered by Schwann cells • Forms discontinuous myelin sheath along length of axon ...
... • Axon – Carries electrical impulse away from cell body – May be covered by Schwann cells • Forms discontinuous myelin sheath along length of axon ...
three basic functions of the nervous system
... Autonomic Nervous System - smooth muscles, glands (involuntary) ...
... Autonomic Nervous System - smooth muscles, glands (involuntary) ...
02biologya
... – A chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from the axon terminal of a sending neuron, crosses a synapse, and binds to appropriate receptor sites on the dendrites or cell body of a receiving neuron, influencing the cell either to fire or not to fire ...
... – A chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from the axon terminal of a sending neuron, crosses a synapse, and binds to appropriate receptor sites on the dendrites or cell body of a receiving neuron, influencing the cell either to fire or not to fire ...
Document
... 3 types of neurons -Sensory neurons to CNS(afferent neurons) -Motor neurons (efferent neurons) to effectors (muscles and glands) -Interneurons (association neurons) provide associative functions ...
... 3 types of neurons -Sensory neurons to CNS(afferent neurons) -Motor neurons (efferent neurons) to effectors (muscles and glands) -Interneurons (association neurons) provide associative functions ...
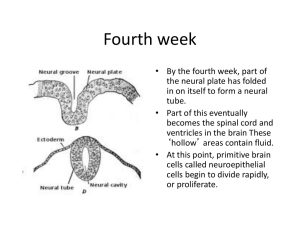
Fourth week
... The telencephalon gives rise to several parts. First comes the hippocampus, which eventually will be involved in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control moveme ...
... The telencephalon gives rise to several parts. First comes the hippocampus, which eventually will be involved in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control moveme ...
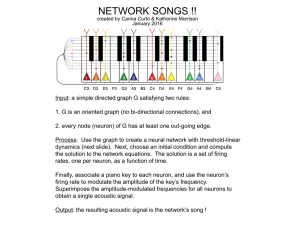
network songs - Personal.psu.edu
... Input: a simple directed graph G satisfying two rules: 1. G is an oriented graph (no bi-directional connections), and 2. every node (neuron) of G has at least one out-going edge. Process: Use the graph to create a neural network with threshold-linear dynamics (next slide). Next, choose an initial co ...
... Input: a simple directed graph G satisfying two rules: 1. G is an oriented graph (no bi-directional connections), and 2. every node (neuron) of G has at least one out-going edge. Process: Use the graph to create a neural network with threshold-linear dynamics (next slide). Next, choose an initial co ...
Project Self-Discovery
... • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • motor (efferent)—send outgoing messages from brain to move muscles • sensory (afferent)—rece ...
... • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • motor (efferent)—send outgoing messages from brain to move muscles • sensory (afferent)—rece ...
Neurons and Functional Neuroanatomy
... respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
... respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
Tayler
... Cerebral Hemispheres: Controls muscle functions along with speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, and learning o Right hemisphere o Left hemisphere ...
... Cerebral Hemispheres: Controls muscle functions along with speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, and learning o Right hemisphere o Left hemisphere ...
How Antidepressants Work - Rainsville Family Practice
... The seratonins are released normally and activate the receptor sites as usual. However, instead of being reabsorbed, they are blocked from returning to the first neuron. Think of it as “Gortex for the brain.” The particles can get out, but they cannot easily return. They are then free to activate m ...
... The seratonins are released normally and activate the receptor sites as usual. However, instead of being reabsorbed, they are blocked from returning to the first neuron. Think of it as “Gortex for the brain.” The particles can get out, but they cannot easily return. They are then free to activate m ...
Nervous tissue
... contribute to BBB and regulate composition of brain tissue fluid convert glucose to lactate to feed neurons secrete nerve growth factor promoting synapse formation electrical influence on synaptic signaling sclerosis – damaged neurons replace by hardened mass of astrocytes ...
... contribute to BBB and regulate composition of brain tissue fluid convert glucose to lactate to feed neurons secrete nerve growth factor promoting synapse formation electrical influence on synaptic signaling sclerosis – damaged neurons replace by hardened mass of astrocytes ...
Maximum entropy modeling of multi-neuron firing patterns in V1
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
Nervous System
... – Neurons only possess one – mm to m in length. Where could an axon a meter in length be found? ...
... – Neurons only possess one – mm to m in length. Where could an axon a meter in length be found? ...
Neural Coalition and Main Theorem
... • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obtained by solving for the minimum of the Gibbs/Helmholtz Fre ...
... • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obtained by solving for the minimum of the Gibbs/Helmholtz Fre ...
Slide 1
... ► The mystery begins in the womb -- only four weeks into gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connec ...
... ► The mystery begins in the womb -- only four weeks into gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connec ...
Neurons: Our Building Blocks
... -Neurons do not actually touch each other to pass on information. The gap between neurons is called the synapse. -The synapse acts as an electrical insulator, preventing an electrical charge from racing to the next cell. -To pass across the synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft, an electrical message must ...
... -Neurons do not actually touch each other to pass on information. The gap between neurons is called the synapse. -The synapse acts as an electrical insulator, preventing an electrical charge from racing to the next cell. -To pass across the synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft, an electrical message must ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These chemicals (neurotransmitters) travel across the space between the two neurons (synapse) and cause the ne ...
... At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These chemicals (neurotransmitters) travel across the space between the two neurons (synapse) and cause the ne ...
Chapter 34
... Neurotransmitter: type of signaling molecule that is synthesized in neurons only Plasma membrane has many gated channels for calcium ions In between action potentials, more calcium ions outside than inside (gate are shut) ...
... Neurotransmitter: type of signaling molecule that is synthesized in neurons only Plasma membrane has many gated channels for calcium ions In between action potentials, more calcium ions outside than inside (gate are shut) ...
Kein Folientitel - Institut für Grundlagen der Informationsverarbeitung
... • Introduction to the PCSIM simulator of biological networks of neurons (with Python-interface) • Recent research results on models for cortical micorcircuits ...
... • Introduction to the PCSIM simulator of biological networks of neurons (with Python-interface) • Recent research results on models for cortical micorcircuits ...
The Brain
... 1. Axon is filled and surrounded by fluids containing electrically charged atoms and molecules called ions- Positively charged sodium and potassium atoms flow back and forth across the cell membrane but they do not cross at the same rate- there is a slightly higher concentration of negatively charge ...
... 1. Axon is filled and surrounded by fluids containing electrically charged atoms and molecules called ions- Positively charged sodium and potassium atoms flow back and forth across the cell membrane but they do not cross at the same rate- there is a slightly higher concentration of negatively charge ...
Central Nervous System Honors Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... – Small gap between the end of the axon or one neuron and the dendrite or cell body of another – Neurotransmitters: • Chemicals that are released in the synaptic cleft • They cause electrical activity in the second neuron ...
... – Small gap between the end of the axon or one neuron and the dendrite or cell body of another – Neurotransmitters: • Chemicals that are released in the synaptic cleft • They cause electrical activity in the second neuron ...