The use of Models - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... assumption in most process models that the separate stages of processing occur in a fixed sequence, with no overlap of the stages. • Independent and Nonoverlapping Stages: The assumption in the strict information processing approach that the stages of processing are independent of one another in the ...
... assumption in most process models that the separate stages of processing occur in a fixed sequence, with no overlap of the stages. • Independent and Nonoverlapping Stages: The assumption in the strict information processing approach that the stages of processing are independent of one another in the ...
Chapter 2: Brain and Behavior
... to the dendrites or cell body of the other neurons or to muscles or glands o Myelin sheath = The white, fatty coating wrapped around some axons that acts as insulation and enables impulses to travel much faster ...
... to the dendrites or cell body of the other neurons or to muscles or glands o Myelin sheath = The white, fatty coating wrapped around some axons that acts as insulation and enables impulses to travel much faster ...
Nervous System
... reversal in membrane potential (outside = - ; inside = +) = depolarization How? - controlled by gated protein channels in the membrane - stimulus small depolarization triggers opening of Na+ ion channels - if stimulus causes enough Na+ to move in = threshold: a stimulus causes minimum depolarizati ...
... reversal in membrane potential (outside = - ; inside = +) = depolarization How? - controlled by gated protein channels in the membrane - stimulus small depolarization triggers opening of Na+ ion channels - if stimulus causes enough Na+ to move in = threshold: a stimulus causes minimum depolarizati ...
Neuron communication
... level of dopamine!) • Agonists: mimic neurotransmitters when you don’t have enough (ex: Depression is caused by low levels of serotonin.) ...
... level of dopamine!) • Agonists: mimic neurotransmitters when you don’t have enough (ex: Depression is caused by low levels of serotonin.) ...
Review - TheThinkSpot
... • Neuron signaling is an all-or-nothing event. When the number of positive inputs exceeds a certain threshold, the neuron fires an action potential—an electrochemical signal that travels down the axon. In the synapse, neurotransmitters pass on information to the next neuron or gland. ...
... • Neuron signaling is an all-or-nothing event. When the number of positive inputs exceeds a certain threshold, the neuron fires an action potential—an electrochemical signal that travels down the axon. In the synapse, neurotransmitters pass on information to the next neuron or gland. ...
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
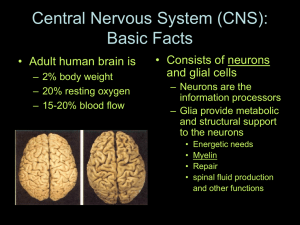
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... • Input / output vectors / patterns • Self organizing (unsupervised) / supervised • Training / testing data sets ...
... • Input / output vectors / patterns • Self organizing (unsupervised) / supervised • Training / testing data sets ...
Topic Presentation: Biopsychology
... Enables reasoning, planning, creating, problem solving Accounts for 2/3 of brain’s total mass ...
... Enables reasoning, planning, creating, problem solving Accounts for 2/3 of brain’s total mass ...
Nerve Notes
... A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
... A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
Neurons
... connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
... connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... various parts of the brain with each other Medulla = controls involuntary actions ...
... various parts of the brain with each other Medulla = controls involuntary actions ...
Stimulus space topology and geometry from neural activity
... provided by these maps, remains a mystery. I will present some work on this question in the context of hippocampal place cells – i.e., neurons in rodent hippocampus whose activity is strongly correlated to the animal’s position in space. In particular, we find that topological and geometric features ...
... provided by these maps, remains a mystery. I will present some work on this question in the context of hippocampal place cells – i.e., neurons in rodent hippocampus whose activity is strongly correlated to the animal’s position in space. In particular, we find that topological and geometric features ...
Nerve Tissue Notes
... “The secret of action is to begin.” 1. What does this mean to you? 2. How can you apply this to Biology II? ...
... “The secret of action is to begin.” 1. What does this mean to you? 2. How can you apply this to Biology II? ...
The Biological Perspective - Shannon Deets Counseling LLC
... Neurotransmitters, Messengers of the Network ...
... Neurotransmitters, Messengers of the Network ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 48 Neurons synapses and
... vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell, resulting in depolarization of the muscle cell and its contraction. ...
... vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell, resulting in depolarization of the muscle cell and its contraction. ...
Neuroscience & Behavior
... Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential. Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell. When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons. ...
... Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential. Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell. When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons. ...
JARINGAN SYARAF TIRUAN
... The Nervous System The human nervous system can be broken down into three stages that may be represented in block diagram form as: ...
... The Nervous System The human nervous system can be broken down into three stages that may be represented in block diagram form as: ...
eating spaghetti!
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
Artificial Intelligence Methods
... Neurons in a McCulloch-Pitts network are connected by directed, weighted paths A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the ...
... Neurons in a McCulloch-Pitts network are connected by directed, weighted paths A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the ...
General design of the nervous system
... Parts of the neuron: dendrite, nucleus, cytoplasm, membrane, axon, synaptic vesicle, receptor. Structure of the Neuron The synapse is the junction point from one neuron to the next and therefore an advantageous site for control of signal transmission. The Resting Potential Remember the Nernst Equat ...
... Parts of the neuron: dendrite, nucleus, cytoplasm, membrane, axon, synaptic vesicle, receptor. Structure of the Neuron The synapse is the junction point from one neuron to the next and therefore an advantageous site for control of signal transmission. The Resting Potential Remember the Nernst Equat ...
Basic Neuroscience Series: Introduction and Series Overview
... • Thus, the Nervous System includes all thoughts, perceptions, bodily actions, behaviors, and ultimately: Consciousness • Philosophical debate: • Dualism: • Mind and Body are separate; “mind” is distinct from “brain” • Rene Descartes (1596-1650): “soul” controlled muscles via the pineal gland by hyd ...
... • Thus, the Nervous System includes all thoughts, perceptions, bodily actions, behaviors, and ultimately: Consciousness • Philosophical debate: • Dualism: • Mind and Body are separate; “mind” is distinct from “brain” • Rene Descartes (1596-1650): “soul” controlled muscles via the pineal gland by hyd ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... • 1. I can describe the functions of the nervous system • 2. I can describe the parts of a neuron cell and identify how they transmit electrochemical impulses. • 3. I can compare and contrast the central and peripheral nervous systems • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and ...
... • 1. I can describe the functions of the nervous system • 2. I can describe the parts of a neuron cell and identify how they transmit electrochemical impulses. • 3. I can compare and contrast the central and peripheral nervous systems • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and ...