Unit 11 acids and bases part 1
... Acidic Salts are formed from a strong acid and a weak base. Neutral salts are formed from a strong acid and strong base. Basic salts are formed from a strong base and a weak acid. Give the acid and base the following salts were formed from and label the salts as acidic, basic, or neutral. ...
... Acidic Salts are formed from a strong acid and a weak base. Neutral salts are formed from a strong acid and strong base. Basic salts are formed from a strong base and a weak acid. Give the acid and base the following salts were formed from and label the salts as acidic, basic, or neutral. ...
Reduction
... The difference in values of Eo for half-reactions 8.29 and 8.31 indicates that it is less easy to reduce Ag(I) in the form of solid AgCl than as hydrated Ag+. Silver iodide ( Ksp = 8.51x10 17) is less soluble than AgCl in aqueous solution, and so reduction of Ag(I) in the form of solid AgI is therm ...
... The difference in values of Eo for half-reactions 8.29 and 8.31 indicates that it is less easy to reduce Ag(I) in the form of solid AgCl than as hydrated Ag+. Silver iodide ( Ksp = 8.51x10 17) is less soluble than AgCl in aqueous solution, and so reduction of Ag(I) in the form of solid AgI is therm ...
Topic 4
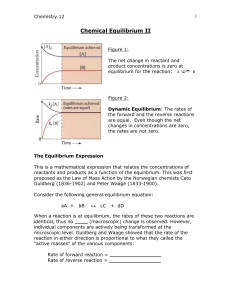
... An total ionic equation represents strong electrolytes as separate independent ions. This is a more accurate representation of the way electrolytes behave in solution. – A total ionic equation is a chemical equation in which strong electrolytes (such as soluble ionic compounds, strong acids/bases) a ...
... An total ionic equation represents strong electrolytes as separate independent ions. This is a more accurate representation of the way electrolytes behave in solution. – A total ionic equation is a chemical equation in which strong electrolytes (such as soluble ionic compounds, strong acids/bases) a ...
Thin-Layer Chromatography: Applying TLC as a
... interactions of the salicylic molecules with each other in the reaction mixture. This may be because the hydrogen on the phenolic substituent of salicylic acid interacts with the double bonded oxygen of the other substituent, carboxylic acid, through hydrogen bonding thus decreasing its polarity sig ...
... interactions of the salicylic molecules with each other in the reaction mixture. This may be because the hydrogen on the phenolic substituent of salicylic acid interacts with the double bonded oxygen of the other substituent, carboxylic acid, through hydrogen bonding thus decreasing its polarity sig ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... sample of the acid with standardized aqueous NaOH. Which of the following could explain why the student obtained a molar mass that was too large? I. Failure to rinse all acid from the weighing paper into the titration vessel II. Addition of more water than was needed to dissolve the acid III. Additi ...
... sample of the acid with standardized aqueous NaOH. Which of the following could explain why the student obtained a molar mass that was too large? I. Failure to rinse all acid from the weighing paper into the titration vessel II. Addition of more water than was needed to dissolve the acid III. Additi ...
Re-typed from The Ultimate Chemical Equations Handbook by
... 1. A binary molecule is formed when two nonmetals or metalloids combine. Electrons are shared so the bonding involved is known as _________________________ bonding. 2. Sometimes these compounds have generic or common names (water) and they also have systemic names (dihydrogen monoxide). The common n ...
... 1. A binary molecule is formed when two nonmetals or metalloids combine. Electrons are shared so the bonding involved is known as _________________________ bonding. 2. Sometimes these compounds have generic or common names (water) and they also have systemic names (dihydrogen monoxide). The common n ...
MC94 - Southchemistry.com
... 14. Which of the following is lower for a 1.0-molar aqueous solution of any solute than it is for pure water? (A) pH (B) Vapor pressure (C) Freezing point (D) Electrical conductivity (E) Absorption of visible light 15. In a molecule in which the central atom exhibits sp3d2 hybrid orbitals, the elect ...
... 14. Which of the following is lower for a 1.0-molar aqueous solution of any solute than it is for pure water? (A) pH (B) Vapor pressure (C) Freezing point (D) Electrical conductivity (E) Absorption of visible light 15. In a molecule in which the central atom exhibits sp3d2 hybrid orbitals, the elect ...
Ch 4 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Strong electrolytes completely dissociate (ex. strong acids, strong bases, soluble salts) Common strong acids: HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4 Common strong bases: oxides and hydroxides of group 1A and 2A metals (2A metal salts tend to be less soluble than 1A metal salts) ...
... Strong electrolytes completely dissociate (ex. strong acids, strong bases, soluble salts) Common strong acids: HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4 Common strong bases: oxides and hydroxides of group 1A and 2A metals (2A metal salts tend to be less soluble than 1A metal salts) ...
Conductometric and Potentiometric Determination of the Solubility
... Results and Discussion Determination of the Solubility-Product Constants of the Ion-Associates Ion-associates formation is the mean controlling factors in many chemical reactions, such as precipitation reactions, where the degree of feasibility of titration depends on the degree of completeness of ...
... Results and Discussion Determination of the Solubility-Product Constants of the Ion-Associates Ion-associates formation is the mean controlling factors in many chemical reactions, such as precipitation reactions, where the degree of feasibility of titration depends on the degree of completeness of ...
Aqueous Solutions
... Aqueous Solutions: An Introduction Strong Bases, Insoluble Bases, and Weak Bases • Insoluble bases – Ionic compounds that are insoluble in water, consequently, not very basic – Cu(OH)2, Zn(OH)2, Fe(OH)2氫氧化亞鐵, Fe(OH)3 • Weak bases – are covalent compounds that ionize slightly in water. – Ammonia is ...
... Aqueous Solutions: An Introduction Strong Bases, Insoluble Bases, and Weak Bases • Insoluble bases – Ionic compounds that are insoluble in water, consequently, not very basic – Cu(OH)2, Zn(OH)2, Fe(OH)2氫氧化亞鐵, Fe(OH)3 • Weak bases – are covalent compounds that ionize slightly in water. – Ammonia is ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 23: ACID BASE BALANCE I
... Person can (unless they have a respiratory disease) always alter ventilation rates to change plasma acid-base balance. H. Respiratory system usually only returns pH 50% to 75% of normal, because as pH gets closer to normal, the less the ventilation rates are influenced. IV. Kidneys are third line of ...
... Person can (unless they have a respiratory disease) always alter ventilation rates to change plasma acid-base balance. H. Respiratory system usually only returns pH 50% to 75% of normal, because as pH gets closer to normal, the less the ventilation rates are influenced. IV. Kidneys are third line of ...
Dr David`s Chemistry Revision Themes
... (a) The concentration of the thiosulphate solution was varied and the time taken for a given amount of sulphur to be deposited was recorded. The temperature and the concentration of hydrogen ion were kept constant. A graph was plotted of rate (reciprocal of time) against concentration. Draw the best ...
... (a) The concentration of the thiosulphate solution was varied and the time taken for a given amount of sulphur to be deposited was recorded. The temperature and the concentration of hydrogen ion were kept constant. A graph was plotted of rate (reciprocal of time) against concentration. Draw the best ...
Chemistry 1: Second Semester Practice Exam Read each question
... 3. As the temperature of a sample of an ideal gas increases at constant pressure the volume occupied by the sample: B. Increases C. Remains the same A. Decreases 4. Which sample of methane contains the greatest number of molecules at standard temperature? A. 22.4 liters at 1 atmosphere C. 11.2 liter ...
... 3. As the temperature of a sample of an ideal gas increases at constant pressure the volume occupied by the sample: B. Increases C. Remains the same A. Decreases 4. Which sample of methane contains the greatest number of molecules at standard temperature? A. 22.4 liters at 1 atmosphere C. 11.2 liter ...
syllabus details - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Standard enthalpy change is heat transferred under standard conditions—pressure 101.3 kPa, temperature298 K. Only ΔH can be measured, not H for the initial or ...
... Standard enthalpy change is heat transferred under standard conditions—pressure 101.3 kPa, temperature298 K. Only ΔH can be measured, not H for the initial or ...
2011 Exam 2 Key
... g) (6 pts) A) In the first circle, a small volume of the starting material of the above reaction at the molecular level is shown. This should represent the reactants as shown in your molecular equation. Complete the picture diagram by writing enough number of NaOH. B) In the middle circle, write the ...
... g) (6 pts) A) In the first circle, a small volume of the starting material of the above reaction at the molecular level is shown. This should represent the reactants as shown in your molecular equation. Complete the picture diagram by writing enough number of NaOH. B) In the middle circle, write the ...
234, advanced chemistry ii - East Pennsboro Area School District
... Rate Constant Reaction Rate L:aw Differential Rate L:aw Integrated Rate Law Method of Initial Rates Initial Rate Overall Reaction Order First Order Reaction Integrated First-Order Rate Law Half-Life of a Reaction Integrated second-Order Rate Law Zero-Order Reaction Integrated Zero-Order Rate Law Pse ...
... Rate Constant Reaction Rate L:aw Differential Rate L:aw Integrated Rate Law Method of Initial Rates Initial Rate Overall Reaction Order First Order Reaction Integrated First-Order Rate Law Half-Life of a Reaction Integrated second-Order Rate Law Zero-Order Reaction Integrated Zero-Order Rate Law Pse ...
Unit 3
... • We repeat the experiment but this time we progressively dilute alkali. Tube 1 10 ml 0.1 mol/l sodium hydroxide ...
... • We repeat the experiment but this time we progressively dilute alkali. Tube 1 10 ml 0.1 mol/l sodium hydroxide ...
PowerPoint Lectures - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Write a balanced molecular equation. Write the ionic equation by dissociating all soluble, strong electrolytes. (Remember to use coefficients to indicate how many of each ion were in the molecular equation.) Cross out anything that remains unchanged from the left side to the right side of the equati ...
... Write a balanced molecular equation. Write the ionic equation by dissociating all soluble, strong electrolytes. (Remember to use coefficients to indicate how many of each ion were in the molecular equation.) Cross out anything that remains unchanged from the left side to the right side of the equati ...