Inorganic Chemistry
... isomerism in coordination compounds, stability of complexes and factors contributing to the stability. Valence bond theory for coordination compounds. 5. Chemistry of Lanthanides ...
... isomerism in coordination compounds, stability of complexes and factors contributing to the stability. Valence bond theory for coordination compounds. 5. Chemistry of Lanthanides ...
Exames anteriores a 1994
... a function of the spatial coordinates. The maxima found in these maps coincide with the locations of the atoms and the values are approximately proportional to the number of electrons in the atom in question. a) Show where the maxima lie by drawing the contour curves around the maxima, connecting po ...
... a function of the spatial coordinates. The maxima found in these maps coincide with the locations of the atoms and the values are approximately proportional to the number of electrons in the atom in question. a) Show where the maxima lie by drawing the contour curves around the maxima, connecting po ...
Unit 2.7: Periodic Table Group1 Group2 Li Be Na Mg K Ca Rb Sr Cs
... These colours are caused because heat causes the compound to vapourise and produce some atoms of metals with electron in a higher orbital than the ground state. When the electrons falls back to its ground state energy is released in the form of visible light The light that is emitted is of a charact ...
... These colours are caused because heat causes the compound to vapourise and produce some atoms of metals with electron in a higher orbital than the ground state. When the electrons falls back to its ground state energy is released in the form of visible light The light that is emitted is of a charact ...
What is the pH of a 0.100 M
... Equilibrium of weak acids and weak bases (Chapter 15.5 and 15.7) What is the pH of 0.100 M CH3COOH? CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) ...
... Equilibrium of weak acids and weak bases (Chapter 15.5 and 15.7) What is the pH of 0.100 M CH3COOH? CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) ...
Chapter 16 Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium Lecture Presentation
... both of the following are true: a) The initial concentrations of acid and salt are not very dilute. b) The Ka is fairly small. ...
... both of the following are true: a) The initial concentrations of acid and salt are not very dilute. b) The Ka is fairly small. ...
File
... A) Al2O3 B) BeO C) Na2O D) K2O2 2. What is the chemical formula of iron (III) sulfate? A) FeSO4 B) FeSO3 C) Fe(SO4)3 D) Fe2(SO4)3 3 - 4. An experiment is done to determine the density of copper. A sample of copper is weighed, and has a mass of 36.10 grams. The sample is added to a graduated cylinder ...
... A) Al2O3 B) BeO C) Na2O D) K2O2 2. What is the chemical formula of iron (III) sulfate? A) FeSO4 B) FeSO3 C) Fe(SO4)3 D) Fe2(SO4)3 3 - 4. An experiment is done to determine the density of copper. A sample of copper is weighed, and has a mass of 36.10 grams. The sample is added to a graduated cylinder ...
Interaction Studies of Dilute Aqueous Oxalic Acid
... The values of apparent molar volume v were used for applicability of Masson’s equation. The plot of c0.5 versus v was not linear. The variation of v with c0.5 followed a cyclic trend having maxima and minima. This type of trend resembles with the X –ray refraction data on liquids in radial distribut ...
... The values of apparent molar volume v were used for applicability of Masson’s equation. The plot of c0.5 versus v was not linear. The variation of v with c0.5 followed a cyclic trend having maxima and minima. This type of trend resembles with the X –ray refraction data on liquids in radial distribut ...
Major 1 Term 101 - KFUPM Faculty List
... This is formation of 1 mol phosphoric acid (l) from the elements in their most stable forms 17. When the following reaction is balanced, the sum of all coefficients is C8H18(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(l) A) 26 B) 43 C) 25 D) 61 E) 52 ...
... This is formation of 1 mol phosphoric acid (l) from the elements in their most stable forms 17. When the following reaction is balanced, the sum of all coefficients is C8H18(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(l) A) 26 B) 43 C) 25 D) 61 E) 52 ...
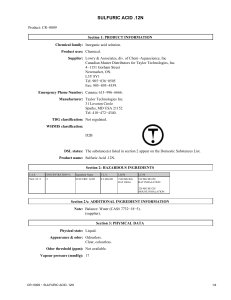
cr-0009 - sulfuric acid .12n
... If irritation occurs, consult a physician. Ingestion: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Drink a large amount of water. Do not induce vomiting, seek immediate medical attention. Additional information: The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all ...
... If irritation occurs, consult a physician. Ingestion: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Drink a large amount of water. Do not induce vomiting, seek immediate medical attention. Additional information: The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all ...
Practice Test 3
... To calculate the pH of a solution whose H3O+ concentration is given: Enter H3O+ concentration Press the LOG key Press the +/- key (The answer should always be between 0 and 14!) To calculate the H3O+ concentration of a solution whose pH is given: Enter the pH value Press the +/- key Press the 10x ke ...
... To calculate the pH of a solution whose H3O+ concentration is given: Enter H3O+ concentration Press the LOG key Press the +/- key (The answer should always be between 0 and 14!) To calculate the H3O+ concentration of a solution whose pH is given: Enter the pH value Press the +/- key Press the 10x ke ...
KEY
... to OH− . Therefore H3 O+ is acting as an acid and OH− is acting as a base. In the reverse reaction, NH+ 4 is the proton donor and thus, it is the other acid. 028 10.0 points In the two reactions represented by HCN + H2 O ⇀ ↽ CN− + H3 O+ , the two Bronsted-Lowry acids are ...
... to OH− . Therefore H3 O+ is acting as an acid and OH− is acting as a base. In the reverse reaction, NH+ 4 is the proton donor and thus, it is the other acid. 028 10.0 points In the two reactions represented by HCN + H2 O ⇀ ↽ CN− + H3 O+ , the two Bronsted-Lowry acids are ...
13. Condensed azines. Quinoline. Isoquinoline. Acridine. Diazines
... derives from the aromatic amino acid tyrosine. Isoquinoline is a colourless hygroscopic liquid at room temperature with a penetrating, unpleasant odour. Impure samples can appear brownish, as is typical for nitrogen heterocycles. It crystallizes platelets that have a low solubility in water but diss ...
... derives from the aromatic amino acid tyrosine. Isoquinoline is a colourless hygroscopic liquid at room temperature with a penetrating, unpleasant odour. Impure samples can appear brownish, as is typical for nitrogen heterocycles. It crystallizes platelets that have a low solubility in water but diss ...
1. Explain electrophile and nucleophile. 2. Explain
... 60. What are the factors on which the equilibrium constant depends? 61. Explain Dalton’s law of partial pressure. 62. Predict if the solutions of the following salts are neutaliacidic or basic NaCl, KBr,NaCN,NH4NO3,NaNO2 and KF. 63. Calculate Ka for an acid HA if degree of ionization is 0.012 in to ...
... 60. What are the factors on which the equilibrium constant depends? 61. Explain Dalton’s law of partial pressure. 62. Predict if the solutions of the following salts are neutaliacidic or basic NaCl, KBr,NaCN,NH4NO3,NaNO2 and KF. 63. Calculate Ka for an acid HA if degree of ionization is 0.012 in to ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... For those students who have just taken Chemistry 1, much of the material in the summer packet will be familiar to you. For those students who have not taken Chemistry for a while the problems will help you rebuild a foundation in chemistry and insure all students are on a relatively even plane. It w ...
... For those students who have just taken Chemistry 1, much of the material in the summer packet will be familiar to you. For those students who have not taken Chemistry for a while the problems will help you rebuild a foundation in chemistry and insure all students are on a relatively even plane. It w ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... 7. A detergent box must bear a warning label if its contents will form a solution of pH greater than 11, because a strong base degrades protein structure. Should a box bear such a label if the H3O+ concentration of a solution of its contents is 2.5 x 10-12 moles per liter? 8. A solution of ammonia h ...
... 7. A detergent box must bear a warning label if its contents will form a solution of pH greater than 11, because a strong base degrades protein structure. Should a box bear such a label if the H3O+ concentration of a solution of its contents is 2.5 x 10-12 moles per liter? 8. A solution of ammonia h ...