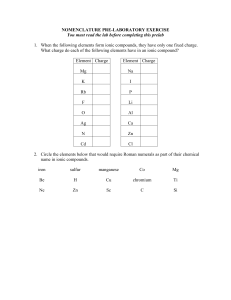
periodic table - Mesa Community College
... substances by a chemical reaction. The smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction and form a compound is called an atom. It consists of a center (nucleus) with protons and neutrons and around that nucleus are the electrons. Protons have an electrical charge of +1, neut ...
... substances by a chemical reaction. The smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction and form a compound is called an atom. It consists of a center (nucleus) with protons and neutrons and around that nucleus are the electrons. Protons have an electrical charge of +1, neut ...
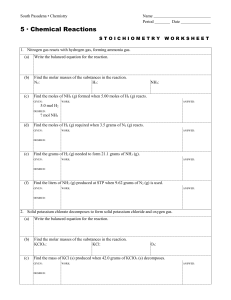
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... 3. reactions with acids : a. carbonates or bicarbonates and acids form a salt, water and CO2 • e.g. 2HCl + Na2CO3 Æ 2 NaCl + H2O + CO2 (net : H+ + CO32- Æ H2O + CO2) b. sulfites and acids form a salt, water and SO2 • e.g. 2 HCl + Na2SO3 Æ 2 NaCl + H2O + SO2 (net : H+ + SO32- Æ H2O + SO2) c. metallic ...
... 3. reactions with acids : a. carbonates or bicarbonates and acids form a salt, water and CO2 • e.g. 2HCl + Na2CO3 Æ 2 NaCl + H2O + CO2 (net : H+ + CO32- Æ H2O + CO2) b. sulfites and acids form a salt, water and SO2 • e.g. 2 HCl + Na2SO3 Æ 2 NaCl + H2O + SO2 (net : H+ + SO32- Æ H2O + SO2) c. metallic ...
Sample Paper Chemistry - Educomp Solutions Ltd.
... (a) As seen from the graph, electrolyte A is a strong electrolyte which is completely ionised in solution. With dilution, the ions are far apart from each other and hence the molar conductivity increases. (b) To determine the value of limiting molar conductivity for electrolyte B, indirect method ba ...
... (a) As seen from the graph, electrolyte A is a strong electrolyte which is completely ionised in solution. With dilution, the ions are far apart from each other and hence the molar conductivity increases. (b) To determine the value of limiting molar conductivity for electrolyte B, indirect method ba ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 151)
... 0.233 g HCl and 0.403 g of H2O. Assume all Cl and O in the original sample are converted to HCl and H2O, respectively. Determine the empirical formula of the compound. A) Cl2O7 B) ClO3 C) Cl2O5 D) Cl3O7 E) Cl3O5 ...
... 0.233 g HCl and 0.403 g of H2O. Assume all Cl and O in the original sample are converted to HCl and H2O, respectively. Determine the empirical formula of the compound. A) Cl2O7 B) ClO3 C) Cl2O5 D) Cl3O7 E) Cl3O5 ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry! AP Chemistry is
... nickel (II) carbonate copper (II) hydroxide tin (IV) sulfate ...
... nickel (II) carbonate copper (II) hydroxide tin (IV) sulfate ...
File
... Properties and Changes of Matter: 1. Physical Property: characteristics of matter, used to identify substances eg. state at room temperature, boiling and melting points, color, solubility, mass, electrical conductivity 2. Physical Change: a change in the size or form of a substance that does not cha ...
... Properties and Changes of Matter: 1. Physical Property: characteristics of matter, used to identify substances eg. state at room temperature, boiling and melting points, color, solubility, mass, electrical conductivity 2. Physical Change: a change in the size or form of a substance that does not cha ...
Chapter1 - WilsonChemWiki
... Hydrogen bond: occurs between molecules where partially positive hydrogen is attracted to the strongly electronegative atoms of O, N, or F in other molecules. Formation of Solutions: Solutions are formed by a process called hydration (ions of solute are surrounded by water molecules) Solubility and ...
... Hydrogen bond: occurs between molecules where partially positive hydrogen is attracted to the strongly electronegative atoms of O, N, or F in other molecules. Formation of Solutions: Solutions are formed by a process called hydration (ions of solute are surrounded by water molecules) Solubility and ...
Chapter 4
... Strong bases are ionic hydroxides that completely ionize in water - good conductors of electricity Weak bases are substances that act as bases but remain mostly molecular at equilibrium in water The dissociation of a weak base in solution is written using a double arrow to indicate that the dissocia ...
... Strong bases are ionic hydroxides that completely ionize in water - good conductors of electricity Weak bases are substances that act as bases but remain mostly molecular at equilibrium in water The dissociation of a weak base in solution is written using a double arrow to indicate that the dissocia ...
b) Mole
... (7) By which method copper pyrites is concentrated ? (a) Magnetic separation method (b) Froth floatation process ...
... (7) By which method copper pyrites is concentrated ? (a) Magnetic separation method (b) Froth floatation process ...
Document
... The bulb in Figure 4.6(a) is only dimly lit because acetic acid is a weak acid and therefore a weak electrolyte [recall Figure 4.3(c)]. The situation in (b) is similar because ammonia is a weak base and therefore also ionizes only slightly. When the two solutions are mixed, which is what has been do ...
... The bulb in Figure 4.6(a) is only dimly lit because acetic acid is a weak acid and therefore a weak electrolyte [recall Figure 4.3(c)]. The situation in (b) is similar because ammonia is a weak base and therefore also ionizes only slightly. When the two solutions are mixed, which is what has been do ...
ch8 - Otterville R-VI School District
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
analisis farmasi analisis farmasi anorganik -
... The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the addition of acid or base is termed the buffering capability of the solution. The ability of a natural water body to resist a decrease in pH is very important due ...
... The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the The ability of an aqueous solution to resist changes in pH upon the addition of acid or base is termed the buffering capability of the solution. The ability of a natural water body to resist a decrease in pH is very important due ...
3C95 Chemistry 12 2015-2016 (Lockwood)
... D3 analyse balanced equations representing the reaction of acids and bases with water 1. identify Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases in an equation 2. define conjugate acid-base pair 3. identify the conjugate of a given acid or base 4. show that in any Brønsted-Lowry acid-base equation there are two con ...
... D3 analyse balanced equations representing the reaction of acids and bases with water 1. identify Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases in an equation 2. define conjugate acid-base pair 3. identify the conjugate of a given acid or base 4. show that in any Brønsted-Lowry acid-base equation there are two con ...
Discussion 8
... Both diagrams and graphs are used in chemistry to help represent physical phenomena. The most common graphs show the relationship of two variables, such as distance and time, or frequency and wavelength. Diagrams, however, are a bit tricker. Diagrams can come in a number of different structures and ...
... Both diagrams and graphs are used in chemistry to help represent physical phenomena. The most common graphs show the relationship of two variables, such as distance and time, or frequency and wavelength. Diagrams, however, are a bit tricker. Diagrams can come in a number of different structures and ...