1aUnit Two Handouts - Dunmore High School
... ANSWER: Potassium changes from 0 to +1 by losing electrons 5. A solution of acidified sodium dichromate has a solution of iron (II) ions added to it. ...
... ANSWER: Potassium changes from 0 to +1 by losing electrons 5. A solution of acidified sodium dichromate has a solution of iron (II) ions added to it. ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... The forward and reverse reactions are balanced The concentrations of all species (reactants and products) become stable The equilibrium position is not the same for all reactions ...
... The forward and reverse reactions are balanced The concentrations of all species (reactants and products) become stable The equilibrium position is not the same for all reactions ...
Related concepts Concentration cells without transport
... the activities a of the participating substances into account. As in the law of mass action, the substance on the right appears in the numerator, the substance on the left in the denominator. In this case, we have: ...
... the activities a of the participating substances into account. As in the law of mass action, the substance on the right appears in the numerator, the substance on the left in the denominator. In this case, we have: ...
Chemistry Lab 2010
... Assuming that seawater is an aqueous solution of NaCl, what is its molarity? The density of seawater is 1.025 g/mL at 20 °C, and the NaCl concentration is 3.50 mass %. 3.50 mass % = 3.50 grams of salt in 100.00 grams of solution Assuming 100.00 g of solution, calculate the volume: 1 mL solution ...
... Assuming that seawater is an aqueous solution of NaCl, what is its molarity? The density of seawater is 1.025 g/mL at 20 °C, and the NaCl concentration is 3.50 mass %. 3.50 mass % = 3.50 grams of salt in 100.00 grams of solution Assuming 100.00 g of solution, calculate the volume: 1 mL solution ...
Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Notice that in Interactive Figure 4.2.1 the water molecules orient themselves so that the oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Se ...
... Notice that in Interactive Figure 4.2.1 the water molecules orient themselves so that the oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Se ...
Chapter 6
... constant expressions. Because the solvent, H2O, is not pure, you might wonder why we have not included it in acetic acid’s Ka expression. Recall that we divide each term in the equilibrium constant expres‑ sion by its standard state value. Because the concentration of H2O is so large—it is approxima ...
... constant expressions. Because the solvent, H2O, is not pure, you might wonder why we have not included it in acetic acid’s Ka expression. Recall that we divide each term in the equilibrium constant expres‑ sion by its standard state value. Because the concentration of H2O is so large—it is approxima ...
Chemistry 120
... In an ionic solution, there are therefore charged particles – the ions – and as the compound is electrically neutral, then the solution is neutral. When a voltage is applied to the solution, the ions can move and a current flows through the solution. ...
... In an ionic solution, there are therefore charged particles – the ions – and as the compound is electrically neutral, then the solution is neutral. When a voltage is applied to the solution, the ions can move and a current flows through the solution. ...
Chapter 2 Geochemical Reactions
... implied in the term geochemistry. These processes include dissolution of air-borne material and gases, weathering at the Earth’s surface, biodegradation and nutrient cycling in the soil, mineral dissolution in the subsurface, and mixing with seawater or deep crustal water. Human activity also plays ...
... implied in the term geochemistry. These processes include dissolution of air-borne material and gases, weathering at the Earth’s surface, biodegradation and nutrient cycling in the soil, mineral dissolution in the subsurface, and mixing with seawater or deep crustal water. Human activity also plays ...
Solution-Solubility-Equilibrium
... Since most solutes have a limited solubility in a given amount of solvent at a fixed temperature (i.e. are not miscible), the temperature of the solvent generally has a marked effect on the amount of solute that will dissolve. For most solids dissolved in liquids, the dissolving process is endotherm ...
... Since most solutes have a limited solubility in a given amount of solvent at a fixed temperature (i.e. are not miscible), the temperature of the solvent generally has a marked effect on the amount of solute that will dissolve. For most solids dissolved in liquids, the dissolving process is endotherm ...
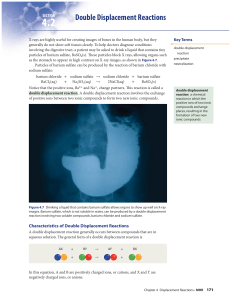
Double Displacement Reactions
... 1. The hydrogen ion, ammonium ion, and all Group 1 (alkali metal) ions form soluble compounds with nearly all anions. 2. Nitrate and acetate ions form soluble compounds with nearly all cations. 3. Chloride, bromide, and iodide ions form compounds that have low solubility with silver, lead(II), mercu ...
... 1. The hydrogen ion, ammonium ion, and all Group 1 (alkali metal) ions form soluble compounds with nearly all anions. 2. Nitrate and acetate ions form soluble compounds with nearly all cations. 3. Chloride, bromide, and iodide ions form compounds that have low solubility with silver, lead(II), mercu ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... B) Solvent – dissolving medium. This component is always in greatest amount. C) Most chemical reactions are carried out in the liquid state or in solution. This is due to the requirement that reactant molecules or ions be highly mobile so they can interact with each other. 2) Although solutions can ...
... B) Solvent – dissolving medium. This component is always in greatest amount. C) Most chemical reactions are carried out in the liquid state or in solution. This is due to the requirement that reactant molecules or ions be highly mobile so they can interact with each other. 2) Although solutions can ...
Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... Partial charge confirmed by electrical field (turning it on/off) Generally speaking: Compounds that possess dipole moments are said to be polar and compounds that do not possess dipole moments are said to be non polar. Examples: Diatomic molecules: CO, NO, HCl, HF, etc…. all have dipole moments and ...
... Partial charge confirmed by electrical field (turning it on/off) Generally speaking: Compounds that possess dipole moments are said to be polar and compounds that do not possess dipole moments are said to be non polar. Examples: Diatomic molecules: CO, NO, HCl, HF, etc…. all have dipole moments and ...
Sulphur Dioxide - School of Chemistry
... Sulphur forms two main oxides; the gas sulphur dioxide (SO2) and the liquid sulphur trioxide (SO3). Sulphur dioxide is a dense colourless gas, which is soluble in water, and has a suffocating and unpleasant smell of burnt matches. It has a melting point of -72.7 ºC, and a boiling point of -10 ºC. Su ...
... Sulphur forms two main oxides; the gas sulphur dioxide (SO2) and the liquid sulphur trioxide (SO3). Sulphur dioxide is a dense colourless gas, which is soluble in water, and has a suffocating and unpleasant smell of burnt matches. It has a melting point of -72.7 ºC, and a boiling point of -10 ºC. Su ...
Energy Matters - Perth Grammar
... Provides energy so that more molecules have successful collisions ...
... Provides energy so that more molecules have successful collisions ...
Chemistry workbook
... b. CoF2(s) c. V3N5(s) d. Cr3P2(s) e. MgS(s) Polyatomic Ions 1. groups of atoms that remain together in a chemical reaction and contain a charge 2. names usually end in ‘ate’ or ‘ite’ 3. Write the formula for the following: a. sodium nitrate b. iron (II) hydroxide c. barium sulfate d. cuprous chlora ...
... b. CoF2(s) c. V3N5(s) d. Cr3P2(s) e. MgS(s) Polyatomic Ions 1. groups of atoms that remain together in a chemical reaction and contain a charge 2. names usually end in ‘ate’ or ‘ite’ 3. Write the formula for the following: a. sodium nitrate b. iron (II) hydroxide c. barium sulfate d. cuprous chlora ...
Chlorine
... titanium anodes ( formerly graphite ones ) are placed in a sodium ( or potassium ) chloride solution flowing over a liquid mercury cathode. When a potential difference is applied and current flows, chlorine is released at the titanium anode and sodium ( or potassium ) dissolves in the mercury cathod ...
... titanium anodes ( formerly graphite ones ) are placed in a sodium ( or potassium ) chloride solution flowing over a liquid mercury cathode. When a potential difference is applied and current flows, chlorine is released at the titanium anode and sodium ( or potassium ) dissolves in the mercury cathod ...