Chlorine
... titanium anodes ( formerly graphite ones ) are placed in a sodium ( or potassium ) chloride solution flowing over a liquid mercury cathode. When a potential difference is applied and current flows, chlorine is released at the titanium anode and sodium ( or potassium ) dissolves in the mercury cathod ...
... titanium anodes ( formerly graphite ones ) are placed in a sodium ( or potassium ) chloride solution flowing over a liquid mercury cathode. When a potential difference is applied and current flows, chlorine is released at the titanium anode and sodium ( or potassium ) dissolves in the mercury cathod ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction between carbon monoxide and molecular chlorine to form COCl2 (g) at 740C are [CO] = 0.012 M, [Cl2] = 0.054 M, and [COCl2] = 0.14 M. Calculate the equilibrium constants Kc and Kp. ...
... The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction between carbon monoxide and molecular chlorine to form COCl2 (g) at 740C are [CO] = 0.012 M, [Cl2] = 0.054 M, and [COCl2] = 0.14 M. Calculate the equilibrium constants Kc and Kp. ...
Gr. 11 Chemistry Student Workbook (Spring 2016)
... The most basic piece of personal protective equipment is a pair of goggles, and these will always be made available to students. Like a calculator for mathematics, and running shoes for physical education goggles are personal pieces of equipment best owned by students. When students own their own go ...
... The most basic piece of personal protective equipment is a pair of goggles, and these will always be made available to students. Like a calculator for mathematics, and running shoes for physical education goggles are personal pieces of equipment best owned by students. When students own their own go ...
ksp - lozon.ca
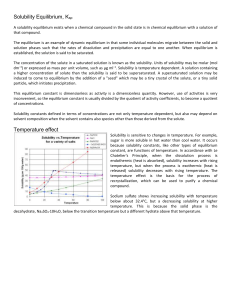
... The solubility of a sparingly soluble salt is reduced in a solution that contains an ion in common with that salt. For instance, the solubility of silver chloride in water is reduced if a solution of sodium chloride is added to a suspension of silver chloride in water. A practical example used very ...
... The solubility of a sparingly soluble salt is reduced in a solution that contains an ion in common with that salt. For instance, the solubility of silver chloride in water is reduced if a solution of sodium chloride is added to a suspension of silver chloride in water. A practical example used very ...
Lab Manual Yr 1 organic
... existence of elements other than carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Elements such as nitrogen, sulphur, iodine, chlorine and bromine in organic compounds can easily be detected by means of straightforward chemical tests. J.L. Lassaigne has developed a method used for the quantitative determination of elem ...
... existence of elements other than carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Elements such as nitrogen, sulphur, iodine, chlorine and bromine in organic compounds can easily be detected by means of straightforward chemical tests. J.L. Lassaigne has developed a method used for the quantitative determination of elem ...
Unit 6 Study Guide - Dorman High School
... the value of K A) increases because when A is added, more products are made, increasing the product-to-reactant ratio B) decreases because A is a reactant, so the product-toreactant ratio decreases C) does not change because A does not figure into the product-to-reactant ratio D) does not change as ...
... the value of K A) increases because when A is added, more products are made, increasing the product-to-reactant ratio B) decreases because A is a reactant, so the product-toreactant ratio decreases C) does not change because A does not figure into the product-to-reactant ratio D) does not change as ...
PDF w
... or soft (polarizable). Furthermore we can now examine equilibrium data for other Lewis acids than metal ions and classify them as (a) or (b) in type. Finally, the interesting question of why two contrasting kinds of behavior should exist will be examined. Classification of Lewis Acids as Class (a) o ...
... or soft (polarizable). Furthermore we can now examine equilibrium data for other Lewis acids than metal ions and classify them as (a) or (b) in type. Finally, the interesting question of why two contrasting kinds of behavior should exist will be examined. Classification of Lewis Acids as Class (a) o ...
CH4 Student Revision Guides pdf | GCE AS/A
... magnetic resonance is concerned with the spin properties of the nucleus. If the number of protons and the number of neutrons are both even then the nucleus has no overall ...
... magnetic resonance is concerned with the spin properties of the nucleus. If the number of protons and the number of neutrons are both even then the nucleus has no overall ...
First Semester Final Review
... 76. Of the following compounds, which is the most ionic? a. SiCl4 b. BrCl c. PCl3 d. Cl2O e. CaCl2 77. The best explanation for the fact that diamond is extremely hard is that diamond crystals ...
... 76. Of the following compounds, which is the most ionic? a. SiCl4 b. BrCl c. PCl3 d. Cl2O e. CaCl2 77. The best explanation for the fact that diamond is extremely hard is that diamond crystals ...
Enthalpy Change of Hydrogen Bond Formation between
... in the solution state: In the gas phase the only important consideration in the stability of the anion radical is the electron affinity of the neutral specie^,^ which is 12.7 kcal/mol for anthracenee6 If this gas-phase anion radical is generated from the transfer of an electron from sodium metal, wh ...
... in the solution state: In the gas phase the only important consideration in the stability of the anion radical is the electron affinity of the neutral specie^,^ which is 12.7 kcal/mol for anthracenee6 If this gas-phase anion radical is generated from the transfer of an electron from sodium metal, wh ...
National 5 - Deans Community High School
... On Andy's first day in chemistry his teacher demonstrated an experiment to the class. Here is the report that Andy wrote in his notebook. Mr. Murray took this really thin kind of copper and put it in a jar of gas. The gas was chlorine. We had to keep clear of the ...
... On Andy's first day in chemistry his teacher demonstrated an experiment to the class. Here is the report that Andy wrote in his notebook. Mr. Murray took this really thin kind of copper and put it in a jar of gas. The gas was chlorine. We had to keep clear of the ...
Solutions
... solubility. Solution____________. When a solution contains more than the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve at a specific temperature it is____________. In this case the amount dissolved will be ________the line of solubility. Made from a saturated solution at a _______temperature and then ...
... solubility. Solution____________. When a solution contains more than the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve at a specific temperature it is____________. In this case the amount dissolved will be ________the line of solubility. Made from a saturated solution at a _______temperature and then ...
chemistry sp.indd
... hydrogen compounds of Group 16 elements are gases at room temperature and pressure except for that of oxygen. Explain this observation, referring to the intermolecular forces in hydrogen sulfide and in the hydrogen compound of oxygen. ...
... hydrogen compounds of Group 16 elements are gases at room temperature and pressure except for that of oxygen. Explain this observation, referring to the intermolecular forces in hydrogen sulfide and in the hydrogen compound of oxygen. ...
Chem 1B Fa2015 FinalExam Review
... [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] is a tetrahedral complex, which is a weak-field complex, and with 3d8 electron configuration for Ni2+, the complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] would be paramagnetic. In addition, a tetrahedral complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] will not exhibit isomerism. (Show d8 configuration in tetrahedral crystal field diagr ...
... [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] is a tetrahedral complex, which is a weak-field complex, and with 3d8 electron configuration for Ni2+, the complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] would be paramagnetic. In addition, a tetrahedral complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] will not exhibit isomerism. (Show d8 configuration in tetrahedral crystal field diagr ...
Chapter 15
... Most gases become less soluble in liquids as the temperature increases. Why? At a constant temperature, the solubility (S) of a gas is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas (Pgas) in equilibrium with the solution. S = k Pgas ...
... Most gases become less soluble in liquids as the temperature increases. Why? At a constant temperature, the solubility (S) of a gas is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas (Pgas) in equilibrium with the solution. S = k Pgas ...
Combining the Benefits of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous
... the intermediate complex of the Rh with the branched product is converted back into the starting material at higher temperatures. The reaction rates and selectivities of styrene hydroformylation in OATS show at least an order of magnitude improvement over heterogeneously reported systems using solid ...
... the intermediate complex of the Rh with the branched product is converted back into the starting material at higher temperatures. The reaction rates and selectivities of styrene hydroformylation in OATS show at least an order of magnitude improvement over heterogeneously reported systems using solid ...
Skill Practice 1
... 3. A certain ion has an atomic number of 16, a mass number of 33, and 18 electrons. a) What is the charge on the ion? b) What is the identity of this ion? c) How many neutrons does the nucleus of this ion have? 4. Tritium (an isotope of hydrogen) has 2 neutrons. How many protons does it have? What i ...
... 3. A certain ion has an atomic number of 16, a mass number of 33, and 18 electrons. a) What is the charge on the ion? b) What is the identity of this ion? c) How many neutrons does the nucleus of this ion have? 4. Tritium (an isotope of hydrogen) has 2 neutrons. How many protons does it have? What i ...
2010
... 11. Hydrogen sulphide is a highly toxic and flammable gas. It is normally prepared in a fume chamber. a) Name two reagents that can be used to prepare hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory. b) One of the uses of hydrogen sulphide is to produce sulphur as shown in the following equation; 2H2S(g) + SO2( ...
... 11. Hydrogen sulphide is a highly toxic and flammable gas. It is normally prepared in a fume chamber. a) Name two reagents that can be used to prepare hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory. b) One of the uses of hydrogen sulphide is to produce sulphur as shown in the following equation; 2H2S(g) + SO2( ...