1. (a) Write the electronic structure of a manganese atom and a Mn
... two salts produces a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq) → AgCl(s) Under these conditions all the chloride from the violet salt is precipitated but only two-thirds of the chloride from the green salt. ...
... two salts produces a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq) → AgCl(s) Under these conditions all the chloride from the violet salt is precipitated but only two-thirds of the chloride from the green salt. ...
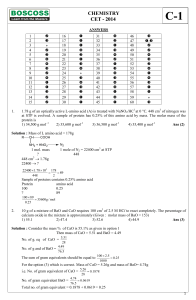
CHEMISTRY CET
... Volume of 0.03 M KMnO4 required to oxidize the same amount of H2S gas to sulphur, in acidic medium is 1) 80 cm3 2) 120 cm3 3) 60 cm3 4) 90 cm3 Solution : K2Cl2O4 KMnO4 ...
... Volume of 0.03 M KMnO4 required to oxidize the same amount of H2S gas to sulphur, in acidic medium is 1) 80 cm3 2) 120 cm3 3) 60 cm3 4) 90 cm3 Solution : K2Cl2O4 KMnO4 ...
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU THE GIFTED AND
... d) Calculate the ratio of the density of the original mixture (A+B) and the density of helium. ...
... d) Calculate the ratio of the density of the original mixture (A+B) and the density of helium. ...
Equilibrium - Clayton State University
... - Gases must be involved in the chemical reaction - The total number of moles of the gaseous state must change - Equilibrium is shifted in the direction of fewer moles - Volume and pressure are inversely related - Decrease in volume implies increase in pressure - Increase in volume implies decrease ...
... - Gases must be involved in the chemical reaction - The total number of moles of the gaseous state must change - Equilibrium is shifted in the direction of fewer moles - Volume and pressure are inversely related - Decrease in volume implies increase in pressure - Increase in volume implies decrease ...
Organic Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... With the exception of the protonated amines and alcohols just mentioned, all of the organic molecules that we have considered have no ionic charge so they are electrically neutral. A molecule is electrically neutral because the total number of its electrons (-1 charge) is equal to the number of prot ...
... With the exception of the protonated amines and alcohols just mentioned, all of the organic molecules that we have considered have no ionic charge so they are electrically neutral. A molecule is electrically neutral because the total number of its electrons (-1 charge) is equal to the number of prot ...
Complete Set
... increasing levels of CO2 will lead to increased dissolution of CaCO3 and critically affect the survival of life forms that rely on a carbonaceous skeleton. Calculate the concentrations of Ca2+ and CO32– in a saturated solution of CaCO3. (The Ksp of CaCO3 is 3.3 × 10–9.) The dissolution of CaCO3 foll ...
... increasing levels of CO2 will lead to increased dissolution of CaCO3 and critically affect the survival of life forms that rely on a carbonaceous skeleton. Calculate the concentrations of Ca2+ and CO32– in a saturated solution of CaCO3. (The Ksp of CaCO3 is 3.3 × 10–9.) The dissolution of CaCO3 foll ...
1 - msstadler
... 28. Calculate milligrams of the solute dissolved in the following aqueous solutions. (Assume that the density of the very dilute sample is equal to the density of water, 1.00 g/mL.) a) 5.50 L of a water sample having 15 ppm strontium ions. b) 9.80 L of ocean water having 65 ppm bromide ions. c) 15.0 ...
... 28. Calculate milligrams of the solute dissolved in the following aqueous solutions. (Assume that the density of the very dilute sample is equal to the density of water, 1.00 g/mL.) a) 5.50 L of a water sample having 15 ppm strontium ions. b) 9.80 L of ocean water having 65 ppm bromide ions. c) 15.0 ...
3: Haloalkanes, Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... and C-H bonds. These haloalkanes (RX), alcohols (ROH), ethers (ROR), and amines (RNH2 , R2 NH, R3 N) have different properties than alkanes and cycloalkanes because the X, O, and N atoms have valence shell unshared electron pairs and their bonds to C are polar. We will also see that amines are organ ...
... and C-H bonds. These haloalkanes (RX), alcohols (ROH), ethers (ROR), and amines (RNH2 , R2 NH, R3 N) have different properties than alkanes and cycloalkanes because the X, O, and N atoms have valence shell unshared electron pairs and their bonds to C are polar. We will also see that amines are organ ...
CHAPTER 4: CHEMICAL QUANTITIES and AQUEOUS REACTIONS
... Therefore, if the concentration of one reactant is known, we can find out the concentration another reactant required for complete neutralization. This can be measured by ‘titration’ (with the use of a chemical indicator). The point at which the indicator changes color is called ‘end point’. 3) OXID ...
... Therefore, if the concentration of one reactant is known, we can find out the concentration another reactant required for complete neutralization. This can be measured by ‘titration’ (with the use of a chemical indicator). The point at which the indicator changes color is called ‘end point’. 3) OXID ...
File - Junior College Chemistry tuition
... for both adults and children, and also in veterinary medicine. OH ...
... for both adults and children, and also in veterinary medicine. OH ...
C. 3.5 g
... 51. When 10.6 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate was added to 200.0 cm3 of 1.0 M sulphuric acid at room conditions, the reaction stopped in 40 seconds. At the same time, 2400 cm3 of carbon dioxide was produced. Which of the following statements about the reaction is INCORRECT? A. ...
... 51. When 10.6 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate was added to 200.0 cm3 of 1.0 M sulphuric acid at room conditions, the reaction stopped in 40 seconds. At the same time, 2400 cm3 of carbon dioxide was produced. Which of the following statements about the reaction is INCORRECT? A. ...
2/22 Lecture Slides
... ΔG = Change in Gibbs free energy This tells us if a process is spontaneous (expected to happen) or non-spontaneous ΔG < 0 process is spontaneous (favored) ΔG = ΔH - TΔS (T is absolute temperature) processes that are exothermic (Δ H < 0) and increase disorder (Δ S > 0) are favored at all T processes ...
... ΔG = Change in Gibbs free energy This tells us if a process is spontaneous (expected to happen) or non-spontaneous ΔG < 0 process is spontaneous (favored) ΔG = ΔH - TΔS (T is absolute temperature) processes that are exothermic (Δ H < 0) and increase disorder (Δ S > 0) are favored at all T processes ...
1)A neutral atom has no overall charge, and ion is a
... 5)a)Create graph, will be gone over in class. b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attractio ...
... 5)a)Create graph, will be gone over in class. b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attractio ...
Net Ionic Equation Powerpoint Tutorial
... might occur: the formation of a weak acid. An acid is a compound that has an H+ ion bonded to some negative ion: HNO3 for example is nitric acid. HF is hydrofluoric acid. All acids fall into one of two categories: strong acids and weak acids. A strong acid is one that dissociates 100% in water. That ...
... might occur: the formation of a weak acid. An acid is a compound that has an H+ ion bonded to some negative ion: HNO3 for example is nitric acid. HF is hydrofluoric acid. All acids fall into one of two categories: strong acids and weak acids. A strong acid is one that dissociates 100% in water. That ...
Discussion Questions
... hydrogen, and oxygen. It was commonly used as a dye in the first half of the nineteenth century. It is 53.66% C and 4.09% H by mass. A titration required 18.02 mL of 0.0406 M NaOH to neutralize 0.3602 g of carminic acid. Assuming that there is only one acidic hydrogen per molecule, what is the molec ...
... hydrogen, and oxygen. It was commonly used as a dye in the first half of the nineteenth century. It is 53.66% C and 4.09% H by mass. A titration required 18.02 mL of 0.0406 M NaOH to neutralize 0.3602 g of carminic acid. Assuming that there is only one acidic hydrogen per molecule, what is the molec ...
equilibrium - eVirtualGuru
... If you continue intertransferring coloured solution between the cylinders, there will not be any further change in the levels of coloured water in two cylinders. If we take analogy of ‘level’ of coloured water with ‘concentration’ of reactants and products in the two cylinders, we can say the proces ...
... If you continue intertransferring coloured solution between the cylinders, there will not be any further change in the levels of coloured water in two cylinders. If we take analogy of ‘level’ of coloured water with ‘concentration’ of reactants and products in the two cylinders, we can say the proces ...
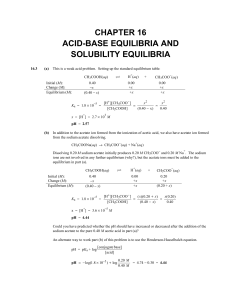
CHAPTER 16 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA AND SOLUBILITY
... Could you have predicted whether the pH should have increased or decreased after the addition of the sodium acetate to the pure 0.40 M acetic acid in part (a)? An alternate way to work part (b) of this problem is to use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. pH = pKa + log ...
... Could you have predicted whether the pH should have increased or decreased after the addition of the sodium acetate to the pure 0.40 M acetic acid in part (a)? An alternate way to work part (b) of this problem is to use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. pH = pKa + log ...