Principles of Neural Science
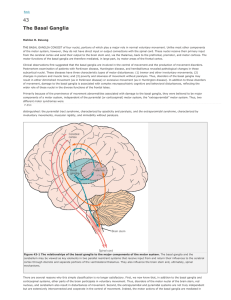
... in an excitatory glutaminergic projection (Figure 43-3). The projection from the subthalamic nucleus is the only excitatory intrinsic connection of the basal ganglia; all others are GABA-ergic and inhibitory. The neurons in the two output nuclei discharge tonically at high frequency. When phasic exc ...
... in an excitatory glutaminergic projection (Figure 43-3). The projection from the subthalamic nucleus is the only excitatory intrinsic connection of the basal ganglia; all others are GABA-ergic and inhibitory. The neurons in the two output nuclei discharge tonically at high frequency. When phasic exc ...
2016 department of medicine research day
... ~140% (0.33±0.08 to 0.79±0.19 impulses/sec, p=0.001). The neural response to LAD CAO was suppressed by SCS (0.85±0.3 to 0.11±0.4, p=0.03) or VNS (0.74±0.26 to 0.11±0.05, p=0.03). Nodose neural activity increased progressively with VNS current from 1 to 5 mA (0.2±0.1 to 0.69±0.1 impulses/sec, p=0.005 ...
... ~140% (0.33±0.08 to 0.79±0.19 impulses/sec, p=0.001). The neural response to LAD CAO was suppressed by SCS (0.85±0.3 to 0.11±0.4, p=0.03) or VNS (0.74±0.26 to 0.11±0.05, p=0.03). Nodose neural activity increased progressively with VNS current from 1 to 5 mA (0.2±0.1 to 0.69±0.1 impulses/sec, p=0.005 ...
the original powerpoint file
... sensible weights that already do well at the task. – So the initial gradients are sensible and backpropagation only needs to perform a local search. • Most of the information in the final weights comes from modeling the distribution of input vectors. – The precious information in the labels is only ...
... sensible weights that already do well at the task. – So the initial gradients are sensible and backpropagation only needs to perform a local search. • Most of the information in the final weights comes from modeling the distribution of input vectors. – The precious information in the labels is only ...
Unit 5: Nervous System
... 2. List the main divisions of the nervous system 3. List the functions of the nervous system 4. Identify and label parts of the brain and major nerves ...
... 2. List the main divisions of the nervous system 3. List the functions of the nervous system 4. Identify and label parts of the brain and major nerves ...
Biology 212: January 30, 2002
... Na+, thus K+ is nearly solely responsible for the RP of neurons. These differences are due to differences in numbers of channels (proteins allowing particular ions through) that are “open” at rest. (i) At rest, the membrane is about 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+ because there are so many ...
... Na+, thus K+ is nearly solely responsible for the RP of neurons. These differences are due to differences in numbers of channels (proteins allowing particular ions through) that are “open” at rest. (i) At rest, the membrane is about 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+ because there are so many ...
Neurotransmitter Test Assessment
... oxygen, copper, and vitamin C as co-factors. The noradrenergic system is most active when an individual is awake, which is important for focused attention. Elevated norepinephrine activity seems to be a contributor to anxiousness. Also, brain norepinephrine turnover is increased in conditions of str ...
... oxygen, copper, and vitamin C as co-factors. The noradrenergic system is most active when an individual is awake, which is important for focused attention. Elevated norepinephrine activity seems to be a contributor to anxiousness. Also, brain norepinephrine turnover is increased in conditions of str ...
Multiple sites of spike initiation in a single dendritic
... afferents project to the same neuropilar areas and, therefore, probably terminate on the same dendritic branch of a given postsynaptic cell. We have to date not performed this experiment using homolateral pairs of roots which terminate in disparate neuropilar areas. Unlike the dendritic spikes obser ...
... afferents project to the same neuropilar areas and, therefore, probably terminate on the same dendritic branch of a given postsynaptic cell. We have to date not performed this experiment using homolateral pairs of roots which terminate in disparate neuropilar areas. Unlike the dendritic spikes obser ...
Morphological and Functional Types of Neurons
... I and type II cells give off slender axon collaterals in the thalamic reticular nucleus but not in VB. Examples of both types of cell could be antidromically activated from the somatic sensory cortex. Type I and type II cells recovered histologically after intracellular recording included examples o ...
... I and type II cells give off slender axon collaterals in the thalamic reticular nucleus but not in VB. Examples of both types of cell could be antidromically activated from the somatic sensory cortex. Type I and type II cells recovered histologically after intracellular recording included examples o ...
How Simple Cells Are Made in a Nonlinear Network Model of the
... 1982), were applied to visual cortex. Figure 1, A and B (De Valois et al., 1982), shows experimental data, based on extracellular recordings of spikes, that illustrate linearity of spatial summation in a simple cell located in macaque V1 (Movshon et al., 1978; Reid et al., 1991). (Note also that sim ...
... 1982), were applied to visual cortex. Figure 1, A and B (De Valois et al., 1982), shows experimental data, based on extracellular recordings of spikes, that illustrate linearity of spatial summation in a simple cell located in macaque V1 (Movshon et al., 1978; Reid et al., 1991). (Note also that sim ...
Transgenic Targeting of Recombinant Rabies Virus Reveals
... typically led to expression levels that were too dense for our purposes. Histological and anatomical procedures. All procedures were performed in accordance with guidelines approved by University of Oregon’s Animal Care and Use Committee and the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and U ...
... typically led to expression levels that were too dense for our purposes. Histological and anatomical procedures. All procedures were performed in accordance with guidelines approved by University of Oregon’s Animal Care and Use Committee and the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and U ...
the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... Brain Reorganization Plasticity the brain’s capacity for modification, as evident in brain reorganization following damage (especially in children) and in experiments on the effects of experience on brain development Children have a surplus of neurons When one area is damaged, other areas ma ...
... Brain Reorganization Plasticity the brain’s capacity for modification, as evident in brain reorganization following damage (especially in children) and in experiments on the effects of experience on brain development Children have a surplus of neurons When one area is damaged, other areas ma ...
Learning Objectives
... The Nature of Nerve Signals 6. Define a membrane potential and a resting potential. 7. Describe the factors that contribute to a membrane potential. 8. Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9. Distinguish between gated and ungated ion channels and among ...
... The Nature of Nerve Signals 6. Define a membrane potential and a resting potential. 7. Describe the factors that contribute to a membrane potential. 8. Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9. Distinguish between gated and ungated ion channels and among ...
neural basis of deciding, choosing and acting
... movement. A main source of these signals is the superior colliculus, which receives visual inputs from the retina as well as descending inputs from many cortical areas, in particular the posterior parietal cortex, the frontal eye field and the supplementary eye field. Electrical stimulation has been ...
... movement. A main source of these signals is the superior colliculus, which receives visual inputs from the retina as well as descending inputs from many cortical areas, in particular the posterior parietal cortex, the frontal eye field and the supplementary eye field. Electrical stimulation has been ...
Communication as an emergent metaphor for neuronal operation
... However, these promises were based on the assumption that the computational model captures all the important characteristics of real biological neurons with respect to information processing. We will indicate in this article that very recent advances in neuroscience appear to invalidate this assumpt ...
... However, these promises were based on the assumption that the computational model captures all the important characteristics of real biological neurons with respect to information processing. We will indicate in this article that very recent advances in neuroscience appear to invalidate this assumpt ...
Neural Networks - Temple Fox MIS
... Predict the taste of Coors beer as a function of its chemical composition ...
... Predict the taste of Coors beer as a function of its chemical composition ...
Multifunctional Laryngeal Premotor Neurons: Their Activities during
... ELMs were identified by antidromic activation from the recurrent laryngeal nerve and by expiratory-related depolarization (Barillot et al., 1990; Shiba et al., 1999). For each ELM, the membrane potential was defined as the difference between the intracellular and extracellular potentials, using a si ...
... ELMs were identified by antidromic activation from the recurrent laryngeal nerve and by expiratory-related depolarization (Barillot et al., 1990; Shiba et al., 1999). For each ELM, the membrane potential was defined as the difference between the intracellular and extracellular potentials, using a si ...
[PPS]An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
... EVALUATING THE BIOLOGICAL PARADIGM Biological researchers have made great progress in elucidating brain-behavior relationships. Biologically based research on both causes and treatment of psychopathology is proceeding at a rapid rate, as we will see when we discuss specific psychopathologies ...
... EVALUATING THE BIOLOGICAL PARADIGM Biological researchers have made great progress in elucidating brain-behavior relationships. Biologically based research on both causes and treatment of psychopathology is proceeding at a rapid rate, as we will see when we discuss specific psychopathologies ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... • Caudate nucleus • Lentiform nucleus – composed of the putamen and the globus pallidus • Fibers of internal capsule running between and through caudate and lentiform nuclei ...
... • Caudate nucleus • Lentiform nucleus – composed of the putamen and the globus pallidus • Fibers of internal capsule running between and through caudate and lentiform nuclei ...
Recognition by Variance: Learning Rules for Spatiotemporal Patterns
... larger output when presented with it, compared to when presented with a typical background pattern. The model therefore reduces the high dimensional input to a one dimensional output. We emphasize that in the task that we consider in this paper, the selected group of learned patterns is to be distin ...
... larger output when presented with it, compared to when presented with a typical background pattern. The model therefore reduces the high dimensional input to a one dimensional output. We emphasize that in the task that we consider in this paper, the selected group of learned patterns is to be distin ...
Phantom Limbs
... visual, sensory, and motor feedback to the cortex might be an important determinant of phantom limb phenomena and pain Prosthesis: using a motor-driven prosthesis that reads electrical signals in stump muscles and effects movement of prosthesis seems to decrease PLP possibly due to reversal of cor ...
... visual, sensory, and motor feedback to the cortex might be an important determinant of phantom limb phenomena and pain Prosthesis: using a motor-driven prosthesis that reads electrical signals in stump muscles and effects movement of prosthesis seems to decrease PLP possibly due to reversal of cor ...
Harris KD. Neural signatures of cell assembly organization. Nat Rev
... timing of spike sequences also plays a part in information transmission. From a theoretical perspective, temporal coding has advantages. The set of all spike sequences is much larger than the set of instantaneous rates, and a neuron that distinguishes between sequences could therefore transmit a lar ...
... timing of spike sequences also plays a part in information transmission. From a theoretical perspective, temporal coding has advantages. The set of all spike sequences is much larger than the set of instantaneous rates, and a neuron that distinguishes between sequences could therefore transmit a lar ...
PDF file
... The additional properties discussed in this paper include: (1) In contrast with an SN where the meanings of each node are hand-selected and boundaries between conceptual modules are handcrafted, there is a class of Generative DNs (GDNs) whose learning is fully autonomous inside each network, using t ...
... The additional properties discussed in this paper include: (1) In contrast with an SN where the meanings of each node are hand-selected and boundaries between conceptual modules are handcrafted, there is a class of Generative DNs (GDNs) whose learning is fully autonomous inside each network, using t ...
Cognitive Disorders
... *Very little is known about the prevalence of dementia outside the more developed countries (Europe, North America, Australasia and Japan), so it is difficult to estimate the number of cases of dementia worldwide ...
... *Very little is known about the prevalence of dementia outside the more developed countries (Europe, North America, Australasia and Japan), so it is difficult to estimate the number of cases of dementia worldwide ...
Brain Regions Involved in USCBP Reaching Models
... BG as an Adaptive Critic • The basal ganglia’s role as an adaptive critic is not very controversial • However, each of our models uses it to learn different parameters ...
... BG as an Adaptive Critic • The basal ganglia’s role as an adaptive critic is not very controversial • However, each of our models uses it to learn different parameters ...
human motor neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells
... Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a severe and incurable neurodegenerative disease. In this disease motor neurons in spinal cord, brainstem and motor cortex are progressively lost and disconnected from their targets. As a consequence patients lose control of voluntary movement and invariably di ...
... Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a severe and incurable neurodegenerative disease. In this disease motor neurons in spinal cord, brainstem and motor cortex are progressively lost and disconnected from their targets. As a consequence patients lose control of voluntary movement and invariably di ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.















![[PPS]An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003530395_1-516558861455cb703803779680da4c5d-300x300.png)







