PDF
... ter-type layer were more weakly correlated, while neurons within different eye-specific layers had the weakest, but still significant, correlations. If each retina independently generates spontaneous bursts of activity, there should be essentially no correlation between the patterns of spontaneous a ...
... ter-type layer were more weakly correlated, while neurons within different eye-specific layers had the weakest, but still significant, correlations. If each retina independently generates spontaneous bursts of activity, there should be essentially no correlation between the patterns of spontaneous a ...
Elastic instabilities in a layered cerebral cortex: A revised axonal
... oriented perpendicular to the outer surface of the cortex [1]. Moreover, the nerve cells in the cortex arrange themselves into six layers with the morphology differing slightly between layers. For simplicity, we assume that all the layers are equivalent in thickness and in elastic properties. Given ...
... oriented perpendicular to the outer surface of the cortex [1]. Moreover, the nerve cells in the cortex arrange themselves into six layers with the morphology differing slightly between layers. For simplicity, we assume that all the layers are equivalent in thickness and in elastic properties. Given ...
interoception and the sentient self
... cortex can be viewed as limbic sensory cortex, because it provides descending control of brainstem homeostatic integration in PB, and the cingulate cortex can be viewed as limbic motor cortex, because it projects densely to the behavioural/autonomic columns of the PAG. Lesions at cingulate cortex an ...
... cortex can be viewed as limbic sensory cortex, because it provides descending control of brainstem homeostatic integration in PB, and the cingulate cortex can be viewed as limbic motor cortex, because it projects densely to the behavioural/autonomic columns of the PAG. Lesions at cingulate cortex an ...
Bat Echolocation - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Cortex only stimulated by combination of harmonics Harmonic is amplified for that bat but not others Dual password for activation of neurons (H1-H2, not just H1) ...
... Cortex only stimulated by combination of harmonics Harmonic is amplified for that bat but not others Dual password for activation of neurons (H1-H2, not just H1) ...
Ch 48 49 Notes - Dublin City Schools
... • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of the head and upper body • Spinal nerves originate in the spinal cord and extend to parts of the body be ...
... • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of the head and upper body • Spinal nerves originate in the spinal cord and extend to parts of the body be ...
Your Nervous System - Springfield Public Schools
... Reflexes What happens when you accidentally touch something hot, such as a flame? Most likely you have noticed that your hand automatically jerks away. This type of automatic response to your environment is called a reflex. A reflex action is shown in Figure 12. In some reflex actions, the actions o ...
... Reflexes What happens when you accidentally touch something hot, such as a flame? Most likely you have noticed that your hand automatically jerks away. This type of automatic response to your environment is called a reflex. A reflex action is shown in Figure 12. In some reflex actions, the actions o ...
The Spinal Interneurons and Properties of
... projects toward the brain on the opposite side but also branches to project at least a short distance toward the tail (Fig. 2 A) (Roberts and Sillar, 1990; Li et al., 2001). EPSPs were examined for 15 neuron pairs in which the anatomy of presynaptic RB neurons and postsynaptic dlc interneurons was c ...
... projects toward the brain on the opposite side but also branches to project at least a short distance toward the tail (Fig. 2 A) (Roberts and Sillar, 1990; Li et al., 2001). EPSPs were examined for 15 neuron pairs in which the anatomy of presynaptic RB neurons and postsynaptic dlc interneurons was c ...
Brains, Bodies, and Behavior
... segment, and the segment temporarily becomes positively charged. As you can see in Figure 3.4 "The Myelin Sheath and the Nodes of Ranvier", the axon is segmented by a series of breaks between the sausage-like segments of the myelin sheath. Each of these gaps is a node of Ranvier. The electrical char ...
... segment, and the segment temporarily becomes positively charged. As you can see in Figure 3.4 "The Myelin Sheath and the Nodes of Ranvier", the axon is segmented by a series of breaks between the sausage-like segments of the myelin sheath. Each of these gaps is a node of Ranvier. The electrical char ...
- D-Scholarship@Pitt
... evidence that the postsynaptic target favors and selects inputs that are more efficient in driving the postsynaptic targets. Although these studies have provided evidence that synaptic refinement occurs through activity-dependent competition, all were performed by blocking or reducing electrical act ...
... evidence that the postsynaptic target favors and selects inputs that are more efficient in driving the postsynaptic targets. Although these studies have provided evidence that synaptic refinement occurs through activity-dependent competition, all were performed by blocking or reducing electrical act ...
Gobbi 2005 - Iowa Medical Marijuana
... compound of this class, URB597, inhibits FAAH activity with nanomolar potency and has no affinity for CB1 receptors or other cannabinoid-related targets (16, 18, 19). This high degree of selectivity is paralleled by a lack of overt cannabinoid-like actions: For example, even when administered at dos ...
... compound of this class, URB597, inhibits FAAH activity with nanomolar potency and has no affinity for CB1 receptors or other cannabinoid-related targets (16, 18, 19). This high degree of selectivity is paralleled by a lack of overt cannabinoid-like actions: For example, even when administered at dos ...
Preparation for the Dissertation report
... It is reasonable to consider that modeling the brain is fundamental for conceiving engineering systems with similar functionalities. In fact, as stated by Haykin [2], “the brain is the living proof that fault tolerant parallel computing is not only physically possible, but also fast and powerful. It ...
... It is reasonable to consider that modeling the brain is fundamental for conceiving engineering systems with similar functionalities. In fact, as stated by Haykin [2], “the brain is the living proof that fault tolerant parallel computing is not only physically possible, but also fast and powerful. It ...
Significant Mirrorings in the Process of Teaching and Learning
... plan automatically produce a shift of the attention towards those regions in which the action must be performed. In summary, the cognitive processes (perception, representation, language, memory, attention), which have always been considered belonging to distinct modules, appear actually much more i ...
... plan automatically produce a shift of the attention towards those regions in which the action must be performed. In summary, the cognitive processes (perception, representation, language, memory, attention), which have always been considered belonging to distinct modules, appear actually much more i ...
From neuroanatomy to behavior: central integration of peripheral
... of these neurons4. Recent work has suggested that these projections of melanocortin neurons to melanocortin (MC3 and MC4) receptors in the CNS determine feeding behavior, as well as energy and glucose homeostasis (Fig. 1)4,10–16. Additional work has suggested a differential regulation of these biolo ...
... of these neurons4. Recent work has suggested that these projections of melanocortin neurons to melanocortin (MC3 and MC4) receptors in the CNS determine feeding behavior, as well as energy and glucose homeostasis (Fig. 1)4,10–16. Additional work has suggested a differential regulation of these biolo ...
Evolution of Animal Neural Systems
... By nervous system we typically mean the network of neurons that underlie animal behavior. It has long been appreciated that nervous system is an imprecise term [13]. Many other cell types beside neurons are nervous, i.e. electrically excitable, and exist in systems, such as pancreatic or muscle cell ...
... By nervous system we typically mean the network of neurons that underlie animal behavior. It has long been appreciated that nervous system is an imprecise term [13]. Many other cell types beside neurons are nervous, i.e. electrically excitable, and exist in systems, such as pancreatic or muscle cell ...
The Beautiful Brain - Weisman Art Museum
... Neuron: The brain is composed of discrete nerve cells called neurons. The dendrites, a series of branched, tree-like appendages, receive inputs from other neurons. Signals are received at synapses, a small gap between neurons where chemicals (neurotransmitters) convey signals from one neuron to anot ...
... Neuron: The brain is composed of discrete nerve cells called neurons. The dendrites, a series of branched, tree-like appendages, receive inputs from other neurons. Signals are received at synapses, a small gap between neurons where chemicals (neurotransmitters) convey signals from one neuron to anot ...
Regulation of neuronal survival and death by extracellular signals
... extracellular signalling, and will not address intracellular signal transduction events that sustain survival or promote death following receptor binding and activation, as these events are covered by many excellent recent reviews (Miller and Kaplan, 2001; Airaksinen and Saarma, 2002; Hempstead, 200 ...
... extracellular signalling, and will not address intracellular signal transduction events that sustain survival or promote death following receptor binding and activation, as these events are covered by many excellent recent reviews (Miller and Kaplan, 2001; Airaksinen and Saarma, 2002; Hempstead, 200 ...
An Extended Model for Stimulus Onset Asynchrony (SOA) in Stroop
... Selective attention refers to the competition between target resources (or relevant stimuli) and distracting resources (or irrelevant stimuli). As a result, the attended stimulus creates more reliable cortical activity than the unattended ones [26]. LaBerge and Samuels [16] [17] explained selective ...
... Selective attention refers to the competition between target resources (or relevant stimuli) and distracting resources (or irrelevant stimuli). As a result, the attended stimulus creates more reliable cortical activity than the unattended ones [26]. LaBerge and Samuels [16] [17] explained selective ...
Central projections of auditory receptor neurons of crickets
... corresponding to ⬃20 m. There is no significant relationship along the A-P axis (Fig. 4B; n ⫽ 29, r2 ⫽ 0.054, P ⫽ 0.225). Nor is there a significant relationship between CF and M-L position within any of the three receptor populations (low-frequency receptors, n ⫽ 14, r2 ⫽ 0.06, P ⫽ 0.4; mid-frequenc ...
... corresponding to ⬃20 m. There is no significant relationship along the A-P axis (Fig. 4B; n ⫽ 29, r2 ⫽ 0.054, P ⫽ 0.225). Nor is there a significant relationship between CF and M-L position within any of the three receptor populations (low-frequency receptors, n ⫽ 14, r2 ⫽ 0.06, P ⫽ 0.4; mid-frequenc ...
UShape Representation in the Inferior Temporal Cortex of MonkeysU
... Mathematically, the network is designed to solve an approximation problem in a high-dimensional space [13]. Learning to recognize an object is assumed to be equivalent to finding a surface in this space that provides the best fit to a set of training data corresponding to the object's familiar views ...
... Mathematically, the network is designed to solve an approximation problem in a high-dimensional space [13]. Learning to recognize an object is assumed to be equivalent to finding a surface in this space that provides the best fit to a set of training data corresponding to the object's familiar views ...
Editorial overview: Neurobiology of cognitive behavior: Complexity
... We live in an age when our phones incorporate real-time traffic updates to help us navigate complex urban environments, Roombas map the layout of our apartments to optimize their cleaning strategies, and cars are beginning to drive themselves. But, amazing though today’s artificial cognition systems ...
... We live in an age when our phones incorporate real-time traffic updates to help us navigate complex urban environments, Roombas map the layout of our apartments to optimize their cleaning strategies, and cars are beginning to drive themselves. But, amazing though today’s artificial cognition systems ...
Cortical and Brainstem Control of Motor Function
... performs motor and sensory functions for the face and head (i.e., cranial nerves). similar to spinal cord for functions from the head down. Contains centers for stereotypic movement and ...
... performs motor and sensory functions for the face and head (i.e., cranial nerves). similar to spinal cord for functions from the head down. Contains centers for stereotypic movement and ...
Olfactory modulation by dopamine in the context of aversive learning
... The insect olfactory system has evolved several modulatory systems to maximize foraging efficiency for resources that are patchy in their distribution. For instance, the flowers of Datura wrightii (a host plant of the moth Manduca sexta) open in the early evening, making them a temporally patchy res ...
... The insect olfactory system has evolved several modulatory systems to maximize foraging efficiency for resources that are patchy in their distribution. For instance, the flowers of Datura wrightii (a host plant of the moth Manduca sexta) open in the early evening, making them a temporally patchy res ...
The Ventral Striatopallidum and Extended Amygdala in
... aversion (Goodson & Wang, 2006) via Vasotoxin-positive neurons. The intraamygdaloid bed nucleus of the stria terminalis contains only a few cells bordering the dorsal part of the medial nucleus laterally. It is interspersed by fibers projecting to the stria terminalis. The medial sublenticular EA is ...
... aversion (Goodson & Wang, 2006) via Vasotoxin-positive neurons. The intraamygdaloid bed nucleus of the stria terminalis contains only a few cells bordering the dorsal part of the medial nucleus laterally. It is interspersed by fibers projecting to the stria terminalis. The medial sublenticular EA is ...
Impaired Reelin-Dab1 Signaling Contributes to
... at P24 compared to WT. (D) At P7, more Cux1-positive neurons are present in bin1 (MZ) and bin 3 in the CKO compared to WT. (E) In utero electroporation with pCAG-GFP at E16.5 demonstrates markedly delayed migration of Tsc2 CKO neurons at P0 compared to WT. (F) Migration of neurons born on E16.5 (lat ...
... at P24 compared to WT. (D) At P7, more Cux1-positive neurons are present in bin1 (MZ) and bin 3 in the CKO compared to WT. (E) In utero electroporation with pCAG-GFP at E16.5 demonstrates markedly delayed migration of Tsc2 CKO neurons at P0 compared to WT. (F) Migration of neurons born on E16.5 (lat ...
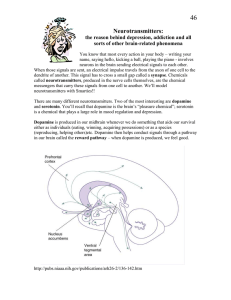
Neurotransmitters:
... You know that most every action in your body – writing your name, saying hello, kicking a ball, playing the piano - involves neurons in the brain sending electrical signals to each other. When those signals are sent, an electrical impulse travels from the axon of one cell to the dendrite of another. ...
... You know that most every action in your body – writing your name, saying hello, kicking a ball, playing the piano - involves neurons in the brain sending electrical signals to each other. When those signals are sent, an electrical impulse travels from the axon of one cell to the dendrite of another. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.