Mouse Nerve Growth Factor Prevents Degeneration of Axotomized
... 3-7 kg) were used as subjects in this study. Seven animals were anesthetized with halothane, intubated, and artificially ventilated, 3 animals served as unoperated controls. To facilitate brain relaxation and minimize retraction pressure, mannitol(20%) was infused systemically over 30 min (2 gm/kg, ...
... 3-7 kg) were used as subjects in this study. Seven animals were anesthetized with halothane, intubated, and artificially ventilated, 3 animals served as unoperated controls. To facilitate brain relaxation and minimize retraction pressure, mannitol(20%) was infused systemically over 30 min (2 gm/kg, ...
Local network regulation of orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus
... which may be from orexin neurons. Fast EPSCs are mediated by NMDA and non-NMDA receptors (122), whereas postsynaptic group I mGluRs provide another excitatory pathway to MCH neurons that induces a slow depolarization mediated by Na⫹/Ca2⫹ exchanger and potentiation of NMDA currents (57). Thus, somewh ...
... which may be from orexin neurons. Fast EPSCs are mediated by NMDA and non-NMDA receptors (122), whereas postsynaptic group I mGluRs provide another excitatory pathway to MCH neurons that induces a slow depolarization mediated by Na⫹/Ca2⫹ exchanger and potentiation of NMDA currents (57). Thus, somewh ...
Developments in understanding neuronal spike trains and functional
... of spike arrival defined over some finite window. Unfortunately, simple rate coding models are not sufficient to explain fast response characteristics of many neuronal circuits, particularly those involved with visual processing (Koch, 1999). Put simply, there is significant presence of neuronal pro ...
... of spike arrival defined over some finite window. Unfortunately, simple rate coding models are not sufficient to explain fast response characteristics of many neuronal circuits, particularly those involved with visual processing (Koch, 1999). Put simply, there is significant presence of neuronal pro ...
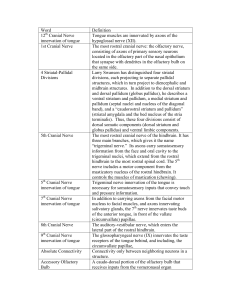
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... include locomotion towards or away from objects or other animals, and grasping of objects in feeding and other activities. Behavioral patterns present in one form or another in all animals because they are necessary for survival and reproduction. The basal and lateral nuclei of the amygdala develop ...
... include locomotion towards or away from objects or other animals, and grasping of objects in feeding and other activities. Behavioral patterns present in one form or another in all animals because they are necessary for survival and reproduction. The basal and lateral nuclei of the amygdala develop ...
Stereologic analysis of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the
... Moreover, all of the thalamic nuclei that have been implicated in schizophrenia are reciprocally connected with higher association cortices; therefore, it is not clear whether thalamic neuronal deficits in schizophrenia extend to sensory thalamic nuclei, such as the LGN. The present study was undert ...
... Moreover, all of the thalamic nuclei that have been implicated in schizophrenia are reciprocally connected with higher association cortices; therefore, it is not clear whether thalamic neuronal deficits in schizophrenia extend to sensory thalamic nuclei, such as the LGN. The present study was undert ...
PDF
... (Gorski et al., 2002, JAX stock # 005628) were crossed with Ai38 mice (Zariwala et al., 2012, JAX stock # 014538) to produce F1 hybrids. This transgenic mouse was used to observe activity of entire V1 because of its uniform expression of GCaMP3 over the cortex, and because it was difficult to entire ...
... (Gorski et al., 2002, JAX stock # 005628) were crossed with Ai38 mice (Zariwala et al., 2012, JAX stock # 014538) to produce F1 hybrids. This transgenic mouse was used to observe activity of entire V1 because of its uniform expression of GCaMP3 over the cortex, and because it was difficult to entire ...
Intrinsic and synaptic plasticity in the vestibular system
... In spontaneously firing vestibular nucleus neurons, CaMKII activity is maintained at near maximal levels by calcium influx that occurs with each action potential: decreases in CaMKII activity oppose excitability by reducing BK currents. This unusual form of plasticity might be common to spontaneousl ...
... In spontaneously firing vestibular nucleus neurons, CaMKII activity is maintained at near maximal levels by calcium influx that occurs with each action potential: decreases in CaMKII activity oppose excitability by reducing BK currents. This unusual form of plasticity might be common to spontaneousl ...
Plasticity in gray and white: neuroimaging changes in brain structure
... imaging measures to underlying cellular and molecular events is challenging. Here we review human neuroimaging findings of structural plasticity and then discuss cellular and molecular level changes that could underlie observed imaging effects. Greater dialog between researchers in these different f ...
... imaging measures to underlying cellular and molecular events is challenging. Here we review human neuroimaging findings of structural plasticity and then discuss cellular and molecular level changes that could underlie observed imaging effects. Greater dialog between researchers in these different f ...
Missed connections: photoreceptor axon seeks target neuron for
... separated. By 40% APF (after puparium formation) R7 and R8 have reached their temporary layers, and ingrowing lamina neuron processes have further separated these layers. CadN, but not LAR, is required for R7 to reach its temporary layer at this stage. The adult projection pattern is established in ...
... separated. By 40% APF (after puparium formation) R7 and R8 have reached their temporary layers, and ingrowing lamina neuron processes have further separated these layers. CadN, but not LAR, is required for R7 to reach its temporary layer at this stage. The adult projection pattern is established in ...
Neuromodulation of in Layer II Medial Entorhinal Cortex I
... SCs and membrane potential resonance at more depolarized pothrough activation of mAChRs, tail currents were measured in 1 tentials (Yoshida and Alonso, 2007; Heys et al., 2010). As such, we M atropine, a competitive mAChR antagonist and measured sought to provide the first direct measurement of M c ...
... SCs and membrane potential resonance at more depolarized pothrough activation of mAChRs, tail currents were measured in 1 tentials (Yoshida and Alonso, 2007; Heys et al., 2010). As such, we M atropine, a competitive mAChR antagonist and measured sought to provide the first direct measurement of M c ...
Diversity of laminar connections linking periarcuate and
... Lateral prefrontal and intraparietal cortices have strong connectional and functional associations but it is unclear how their common visuomotor, perceptual and working memory functions arise. The hierarchical scheme of cortical processing assumes that prefrontal cortex issues ‘feedback’ projections ...
... Lateral prefrontal and intraparietal cortices have strong connectional and functional associations but it is unclear how their common visuomotor, perceptual and working memory functions arise. The hierarchical scheme of cortical processing assumes that prefrontal cortex issues ‘feedback’ projections ...
Vertebrate brains and evolutionary connectomics: on the origins of
... argued, and continue to argue, that there are some brain structures unique to humans, and that must explain man’s special status on this planet. Strangely, for much of the past century, many contemporary neurobiologists have taken an intermediate position, arguing that even if the neocortex is commo ...
... argued, and continue to argue, that there are some brain structures unique to humans, and that must explain man’s special status on this planet. Strangely, for much of the past century, many contemporary neurobiologists have taken an intermediate position, arguing that even if the neocortex is commo ...
Synaptic Plasticity and Connectivity Requirements to
... measure the distribution of selectivity across cells before and after training. When comparing multiple networks, we use the mean of the stimulus-pair selectivity across cells. In order to determine whether or not the information about stimulus-pairs within a given associative network is sufficient ...
... measure the distribution of selectivity across cells before and after training. When comparing multiple networks, we use the mean of the stimulus-pair selectivity across cells. In order to determine whether or not the information about stimulus-pairs within a given associative network is sufficient ...
Insular cortex – review
... that neuronal activity in our gustatory cortex can change dependent on our expectation of a tastant. They misled their subject into thinking that an aversive bitter taste would actually be less repugnant than it really was. After that, subjects reported the taste to be less aversive than when they h ...
... that neuronal activity in our gustatory cortex can change dependent on our expectation of a tastant. They misled their subject into thinking that an aversive bitter taste would actually be less repugnant than it really was. After that, subjects reported the taste to be less aversive than when they h ...
Peripheric nervous system. Vegetative nervous system
... 6. A preparation of the small intestine impregnated with silver. Neurons which axons and dendrites do not differ are seen between the mascular layers. What type of neurons are they? 7. In the intramural vegetative plexus there are seen processes of one neuron making synapses either with dendrites or ...
... 6. A preparation of the small intestine impregnated with silver. Neurons which axons and dendrites do not differ are seen between the mascular layers. What type of neurons are they? 7. In the intramural vegetative plexus there are seen processes of one neuron making synapses either with dendrites or ...
Nervous Tissue
... Ligand-gated Channel Ligand-gated channels – open and close in response to a specific ...
... Ligand-gated Channel Ligand-gated channels – open and close in response to a specific ...
Drug-drug interactions in inpatient and outpatient settings in Iran: a
... excitatory neurotransmission. They act on different parts of the brain and various molecular targets and cause different behavioral responses like amnesia, unconsciousness, analgesia, and immobility [1]. The association between the specific sites of CNS and the functions of general anesthetics has b ...
... excitatory neurotransmission. They act on different parts of the brain and various molecular targets and cause different behavioral responses like amnesia, unconsciousness, analgesia, and immobility [1]. The association between the specific sites of CNS and the functions of general anesthetics has b ...
Neuroscience - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... Synapse formation during nervous system development and degeneration in the pathogenesis of human neurological diseases are highly regulated processes. Subtle changes in the environment of the complex neuronal network may cause either breakdown or creation of synaptic connections. Drug discovery scr ...
... Synapse formation during nervous system development and degeneration in the pathogenesis of human neurological diseases are highly regulated processes. Subtle changes in the environment of the complex neuronal network may cause either breakdown or creation of synaptic connections. Drug discovery scr ...
The Integrated Nature of Motor Cortical Function
... elbow, and shoulder regions. This shows that intrinsic connections exist between the representations of distal hand and more proximal muscles. Within this massive pattern of intrinsic connections, physiologically identified motor cortical points controlling antagonistic muscles are also linked by in ...
... elbow, and shoulder regions. This shows that intrinsic connections exist between the representations of distal hand and more proximal muscles. Within this massive pattern of intrinsic connections, physiologically identified motor cortical points controlling antagonistic muscles are also linked by in ...
Dendrite structure
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
Hypothalamus15
... large-diameter hypothalamic neurons from same nuclei of the middle zone. - Axons deliver these hormones down the infundibular stalk and terminate on fenestral capillaries (“leaky”) of the posterior pit - this is 1 place lacking a ...
... large-diameter hypothalamic neurons from same nuclei of the middle zone. - Axons deliver these hormones down the infundibular stalk and terminate on fenestral capillaries (“leaky”) of the posterior pit - this is 1 place lacking a ...
Dendrite structure
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
This article was originally published in the Encyclopedia of
... behavioral no-go response. Strikingly, when stimulation is applied during go trials in which the monkey should respond, the response is cancelled or delayed, concomitant with reduced electrical activity in the motor cortex. The strength of the suppressive effect depends on the stimulation timing, wi ...
... behavioral no-go response. Strikingly, when stimulation is applied during go trials in which the monkey should respond, the response is cancelled or delayed, concomitant with reduced electrical activity in the motor cortex. The strength of the suppressive effect depends on the stimulation timing, wi ...
Pierre Berthet Computational Modeling of the Basal Ganglia – Functional Pathways
... neocortex, seems to be capable of much more, but some argue that it all comes down to enriching the information that is going to be used to perform a movement, be it planning, fine tuning, estimating the outcome, or even building a better representation of the world in order to compute the best moto ...
... neocortex, seems to be capable of much more, but some argue that it all comes down to enriching the information that is going to be used to perform a movement, be it planning, fine tuning, estimating the outcome, or even building a better representation of the world in order to compute the best moto ...
Frequency-Dependent Recruitment of Fast Amino Acid and Slow
... of GnRH neurons located in the rostral preoptic area were found to receive monosynaptic inputs from the AVPV in a sex-dependent manner. AVPV stimulation frequencies ⬍1 Hz generated short-latency action potentials in GnRH neurons with GABA and glutamate mediating ⬎90% of the evoked fast synaptic curr ...
... of GnRH neurons located in the rostral preoptic area were found to receive monosynaptic inputs from the AVPV in a sex-dependent manner. AVPV stimulation frequencies ⬍1 Hz generated short-latency action potentials in GnRH neurons with GABA and glutamate mediating ⬎90% of the evoked fast synaptic curr ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.