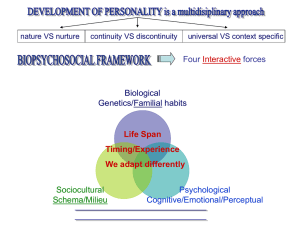
What Is Psychology?
... responses, will, mental images) Believe that mind functions by creatively combining the elements of experience ...
... responses, will, mental images) Believe that mind functions by creatively combining the elements of experience ...
Behavioral Ecology
... The study of animal behavior is one the oldest and most captivating fields of study in biology. Behavioral Ecology has taken on a more evolutionary view towards animal behavior... Animal behavior is an adaptation that has been favored for survival or reproduction means. Behavior has its roots in bo ...
... The study of animal behavior is one the oldest and most captivating fields of study in biology. Behavioral Ecology has taken on a more evolutionary view towards animal behavior... Animal behavior is an adaptation that has been favored for survival or reproduction means. Behavior has its roots in bo ...
Learning Theory Theorists (Alphabetical) Year Ideals Classroom
... Once the new information is acquired the process of assimilation with the new schema will continue until the next time we need to make an adjustment to it. Skinner believed that the best way to understand behavior is to look at the causes of an action and its consequences. This approach is called Op ...
... Once the new information is acquired the process of assimilation with the new schema will continue until the next time we need to make an adjustment to it. Skinner believed that the best way to understand behavior is to look at the causes of an action and its consequences. This approach is called Op ...
MAET 2009 Year 2 - MSU EdTech Sandbox
... Tetris is a simple game but involves multiple reinforcers. Reinforcers include: Positive Reinforcers: • Gaining points and clearing rows • High Score or improving on a previous score • Fitting blocks • Winning or advancing to the next level Negative Reinforcers: • Avoidance of losing • Build up of r ...
... Tetris is a simple game but involves multiple reinforcers. Reinforcers include: Positive Reinforcers: • Gaining points and clearing rows • High Score or improving on a previous score • Fitting blocks • Winning or advancing to the next level Negative Reinforcers: • Avoidance of losing • Build up of r ...
pleasure principle”.
... Based of the premise of imitation/observational learning = modeling (operant conditioning) and reciprocal determinism Bandura , Social Cognitive Theory Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience w ...
... Based of the premise of imitation/observational learning = modeling (operant conditioning) and reciprocal determinism Bandura , Social Cognitive Theory Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience w ...
Reinforcements from the environment ∙Operant conditioning: a type of
... The Study of operant conditioning is the exploration of behaviors that are active. 1. The Early days: The Law of Effect ∙ Edward Thorndike (1874-1949) - the first to examine active behaviors in the 1890’s -Focused on instrumental behaviors (behaviors that required an organism to do something) like s ...
... The Study of operant conditioning is the exploration of behaviors that are active. 1. The Early days: The Law of Effect ∙ Edward Thorndike (1874-1949) - the first to examine active behaviors in the 1890’s -Focused on instrumental behaviors (behaviors that required an organism to do something) like s ...
Verbal Behavior Glossary Mark L. Sundberg 2/19/04 Audience
... some aspect of a speaker’s own verbal behavior functions as an SD, or an MO, for additional speaker verbal behavior. The autoclitic relation can be thought of as verbal behavior about verbal behavior. Automatic punishment Automatic punishment is a type of conditioned punishment where a response prod ...
... some aspect of a speaker’s own verbal behavior functions as an SD, or an MO, for additional speaker verbal behavior. The autoclitic relation can be thought of as verbal behavior about verbal behavior. Automatic punishment Automatic punishment is a type of conditioned punishment where a response prod ...
The operant behaviorism of BF Skinner
... operate either successively or simultaneously in the presence of different stimuli or for different responses. Reinforcement schedules have proven useful in such areas as psychopharmacology and behavioral toxicology. The performances generated by complex schedules are also sometimes analogous to per ...
... operate either successively or simultaneously in the presence of different stimuli or for different responses. Reinforcement schedules have proven useful in such areas as psychopharmacology and behavioral toxicology. The performances generated by complex schedules are also sometimes analogous to per ...
Skinner - IB Psychology.com
... live well, we must stop building one in which it will be impossible to live at all. ...
... live well, we must stop building one in which it will be impossible to live at all. ...
The operant behaviorism of BF Skinner
... operate either successively or simultaneously in the presence of different stimuli or for different responses. Reinforcement schedules have proven useful in such areas as psychopharmacology and behavioral toxicology. The performances generated by complex schedules are also sometimes analogous to per ...
... operate either successively or simultaneously in the presence of different stimuli or for different responses. Reinforcement schedules have proven useful in such areas as psychopharmacology and behavioral toxicology. The performances generated by complex schedules are also sometimes analogous to per ...
Behavioral Learning Theory
... learning as nothing more than the achievement of new behavior based on environmental conditions. This theory is more concerned with the response generated. Input is stimulus and output is response that produces behavioral changes. This theory was pioneered by Pavlov, Edward Lee and Skinner. They des ...
... learning as nothing more than the achievement of new behavior based on environmental conditions. This theory is more concerned with the response generated. Input is stimulus and output is response that produces behavioral changes. This theory was pioneered by Pavlov, Edward Lee and Skinner. They des ...
AP Psychology Unit 6- Operant Conditioning
... if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher ...
... if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher ...
Chapter 5- Learning
... to the environment, increase the probability that the behavior will occur ...
... to the environment, increase the probability that the behavior will occur ...
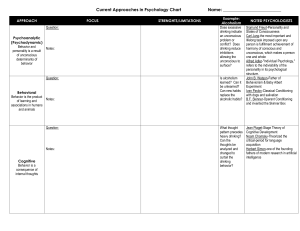
Current Approaches in Psychology Chart Name
... Ivan Pavlov-Classical Conditioning with dogs and salivation B.F. Skinner-Operant Conditioning and invented the Skinner Box ...
... Ivan Pavlov-Classical Conditioning with dogs and salivation B.F. Skinner-Operant Conditioning and invented the Skinner Box ...
The Behavior Analyst, 18
... Jack Michael Quotes “An environment change, such as a stimulus onset or offset, usually has more than one effect on behavior” (Michael, 1995, p. ...
... Jack Michael Quotes “An environment change, such as a stimulus onset or offset, usually has more than one effect on behavior” (Michael, 1995, p. ...
Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences 1
... Use of physical force with the intention to cause an individual to experience pain (not injury) for purposes of correction or control of the individual's behavior. ...
... Use of physical force with the intention to cause an individual to experience pain (not injury) for purposes of correction or control of the individual's behavior. ...
Behaviorism - Kolten E
... • U.S most influential behavioral scientist • He taught by reinforcement. He believed we are likely to continue what is rewarded. • He believed that we do have such a thing as a mind, but that it is simply more productive to study observable behavior rather than internal mental events. • He believed ...
... • U.S most influential behavioral scientist • He taught by reinforcement. He believed we are likely to continue what is rewarded. • He believed that we do have such a thing as a mind, but that it is simply more productive to study observable behavior rather than internal mental events. • He believed ...
Operant Conditioning
... These terms both refer to learned changes in behavior that occur as a result of the consequences of the behavior. “Instrumental ” refers to the fact that the behavior is instrumental in bringing about a given consequence. “Operant” refers to the fact that the behavior operates on the environment, th ...
... These terms both refer to learned changes in behavior that occur as a result of the consequences of the behavior. “Instrumental ” refers to the fact that the behavior is instrumental in bringing about a given consequence. “Operant” refers to the fact that the behavior operates on the environment, th ...
139 Chapter 13 Assignment
... 139 Chapter 13 Assignment 1. Watson’s 1913 paper-what was his main idea? 2. What approach did Watson advocate for psychology to become a science? Against what approach was he arguing? 3. History of Behaviorism: Pavlov, Watson, Thorndike, Skinner 4. Principle of classical conditioning: S-R associatio ...
... 139 Chapter 13 Assignment 1. Watson’s 1913 paper-what was his main idea? 2. What approach did Watson advocate for psychology to become a science? Against what approach was he arguing? 3. History of Behaviorism: Pavlov, Watson, Thorndike, Skinner 4. Principle of classical conditioning: S-R associatio ...
9. What evidence led Thorndike to propose the “law of effect”? • Law
... Cat in a puzzle box: Thorndike used a fish reward to entice cats to find their way out of a puzzle box through a series of maneuvers. The cats’ performance tended to improve with successive trials. B.F. Skinner elaborated on Thorndike’s research 10. What is operant conditioning, and how is opera ...
... Cat in a puzzle box: Thorndike used a fish reward to entice cats to find their way out of a puzzle box through a series of maneuvers. The cats’ performance tended to improve with successive trials. B.F. Skinner elaborated on Thorndike’s research 10. What is operant conditioning, and how is opera ...
Principles of Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning, and
... • Copying what other’s are doing, although no real learning takes place (We see, so we do.) • Imitation after watching someone do something, that the observer couldn’t do before. • Disinhibition occurs when an observer sees a someone engage in a threatening activity without being punished, then enga ...
... • Copying what other’s are doing, although no real learning takes place (We see, so we do.) • Imitation after watching someone do something, that the observer couldn’t do before. • Disinhibition occurs when an observer sees a someone engage in a threatening activity without being punished, then enga ...
Reinforcement - Eagan High School
... Negative reinforcement • Anything that increases the likelihood of a behavior by following it with the REMOVAL of something undesirable • Ex. Headache/meds, mom/nag, torture, • Seatbelt ding in car ...
... Negative reinforcement • Anything that increases the likelihood of a behavior by following it with the REMOVAL of something undesirable • Ex. Headache/meds, mom/nag, torture, • Seatbelt ding in car ...
19. The person who studied operant conditioning
... Across 3. When a conditioned response is successfully made to one stimulus but not to another similar stimulus 6. The type of conditioning that involves learning associations between two previously unrelated stimuli 7. One major example of a primary reinforcer 10. Skinner expanded this guy's Law of ...
... Across 3. When a conditioned response is successfully made to one stimulus but not to another similar stimulus 6. The type of conditioning that involves learning associations between two previously unrelated stimuli 7. One major example of a primary reinforcer 10. Skinner expanded this guy's Law of ...
Verbal Behavior

Verbal Behavior is a 1957 book by psychologist B. F. Skinner that inspects human behavior, describing what is traditionally called linguistics. The book Verbal Behavior is almost entirely theoretical, involving little experimental research in the work itself. It was an outgrowth of a series of lectures first presented at the University of Minnesota in the early 1940s and developed further in his summer lectures at Columbia and William James lectures at Harvard in the decade before the book's publication. A growing body of research and applications based on Verbal Behavior has occurred since its original publication, particularly in the past decade.In addition, a growing body of research has developed on structural topics in verbal behavior such as grammar.