PSYC 100 Chapter 7
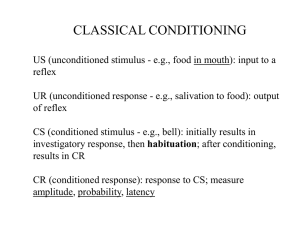
... response (CR): in classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus. Conditioned stimulus (CS): in classical conditioning, a previously neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned re ...
... response (CR): in classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus. Conditioned stimulus (CS): in classical conditioning, a previously neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned re ...
Introduction to Psychology PPT
... favorite food, you also heard the sound of a whistle. While the whistle is unrelated to the smell of the food, if the sound of the whistle was paired multiple times with the smell, the sound would eventually trigger the conditioned response. In this case, the sound of the whistle is the conditioned ...
... favorite food, you also heard the sound of a whistle. While the whistle is unrelated to the smell of the food, if the sound of the whistle was paired multiple times with the smell, the sound would eventually trigger the conditioned response. In this case, the sound of the whistle is the conditioned ...
Jeopardy
... A once neutral event that elicits a given response after a period of training in which it has been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. ...
... A once neutral event that elicits a given response after a period of training in which it has been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. ...
5. Operant Conditioning V2
... In operant conditioning, if responses are not made, the consequence doesn’t happen. In classical conditioning, responses occur regardless of responding. ...
... In operant conditioning, if responses are not made, the consequence doesn’t happen. In classical conditioning, responses occur regardless of responding. ...
Chapter 6 Editable Lecture Notecards
... Observational learning occurs when an organism’s response is influenced by the observation of others, who are called models. ...
... Observational learning occurs when an organism’s response is influenced by the observation of others, who are called models. ...
Chapter 5 Learning Outline
... 4. When responses are punished, alternatives should be introduced, that is punishing a response conveys no information about what alternative response might be acceptable. D. As punishment, spanking is physically non-injurious, intended to modify behavior, and is administered with an open hand to th ...
... 4. When responses are punished, alternatives should be introduced, that is punishing a response conveys no information about what alternative response might be acceptable. D. As punishment, spanking is physically non-injurious, intended to modify behavior, and is administered with an open hand to th ...
Slide 2 - Cengage
... Observational learning occurs when an organism’s response is influenced by the observation of others, who are called models. ...
... Observational learning occurs when an organism’s response is influenced by the observation of others, who are called models. ...
AP Ch 8 Learning Jeopardy
... Watson’s belief that psychology should be an objective science, that should study overt behavior without considering unobservable mental activity. ...
... Watson’s belief that psychology should be an objective science, that should study overt behavior without considering unobservable mental activity. ...
Jeopardy
... Watson’s belief that psychology should be an objective science, that should study overt behavior without considering unobservable mental activity. ...
... Watson’s belief that psychology should be an objective science, that should study overt behavior without considering unobservable mental activity. ...
Learning Psychology
... Work in groups of 3-4 people. Create an original skit that illustrates the principles of classical conditioning Everyone MUST be a part of the skit Skits should last between 1-2 minutes and show an understanding of the principles ...
... Work in groups of 3-4 people. Create an original skit that illustrates the principles of classical conditioning Everyone MUST be a part of the skit Skits should last between 1-2 minutes and show an understanding of the principles ...
Mod 26 Classic - WordPress.com
... automatically and involuntarily brings about the response • Must be involuntary response • Heartbeat • Breathing • Sweating • Sadness • Fear ...
... automatically and involuntarily brings about the response • Must be involuntary response • Heartbeat • Breathing • Sweating • Sadness • Fear ...
Learning - WordPress.com
... behaviours to get rewards or avoid punishment Must engage in a behaviour in order for the programmed outcome to occur Study of how voluntary behaviour is affected by its consequences ...
... behaviours to get rewards or avoid punishment Must engage in a behaviour in order for the programmed outcome to occur Study of how voluntary behaviour is affected by its consequences ...
Learning - AP Psychology
... other has yelled at you without warning several times. You now feel tense and fearful any time that you are around him or her. ...
... other has yelled at you without warning several times. You now feel tense and fearful any time that you are around him or her. ...
Classical Conditioning
... the school to safety. In November, the beeping alarm went off again, and the students again hurried out fearfully. However, this time it was only a fire drill, so there was no fire. Then for 10 days straight in December, the alarm malfunctioned and went off daily. Now no one paid any attention to it ...
... the school to safety. In November, the beeping alarm went off again, and the students again hurried out fearfully. However, this time it was only a fire drill, so there was no fire. Then for 10 days straight in December, the alarm malfunctioned and went off daily. Now no one paid any attention to it ...
learning - Wofford
... Fixed Interval: Reward comes after a specified period of time, regardless of responses. Animal learns this and responds right around the reinforcement time. ...
... Fixed Interval: Reward comes after a specified period of time, regardless of responses. Animal learns this and responds right around the reinforcement time. ...
Verplanck
... But no effort was made to determine experimentally their ongin, and their history through differential reinforcement It is the behavior of such "rules" that this paper deals with ...
... But no effort was made to determine experimentally their ongin, and their history through differential reinforcement It is the behavior of such "rules" that this paper deals with ...
SV3 Learning Nov 22 2009
... In CC, an organism can be taught a connection between any CS and any US In OC, an organism can be taught a connection between any response and any reinforcer ...
... In CC, an organism can be taught a connection between any CS and any US In OC, an organism can be taught a connection between any response and any reinforcer ...
Basic concepts of applied behaviour analysis
... preoperational, concrete operations, formal operations). The importance of understanding the development of cognitive processes to which behavioural strategies can be applied (e.g., 11 correspondence in math; phonological awareness in reading; communicative intent in non-verbal communication). ...
... preoperational, concrete operations, formal operations). The importance of understanding the development of cognitive processes to which behavioural strategies can be applied (e.g., 11 correspondence in math; phonological awareness in reading; communicative intent in non-verbal communication). ...
CHAPTER 8 CONDITIONING AND LEARNING
... 2. conditioned emotional response – an emotional response that has been linked to a previously non-emotional stimulus by classical conditioning. 3. vicarious classical conditioning – classical conditioning brought about by observing another person react to a particular stimulus. V. Operant Condition ...
... 2. conditioned emotional response – an emotional response that has been linked to a previously non-emotional stimulus by classical conditioning. 3. vicarious classical conditioning – classical conditioning brought about by observing another person react to a particular stimulus. V. Operant Condition ...
Operant Conditioning - Everglades High School
... chance of occurring in future); behaviors followed by negative consequences are weakened. • Did pioneering work on how cats learn using puzzle box (p. 229)-read about in text ...
... chance of occurring in future); behaviors followed by negative consequences are weakened. • Did pioneering work on how cats learn using puzzle box (p. 229)-read about in text ...
Learning_ Unit 6 PP-pdf 2015-16
... chance of occurring in future); behaviors followed by negative consequences are weakened. • Did pioneering work on how cats learn using puzzle box (p. 229)-read about in text ...
... chance of occurring in future); behaviors followed by negative consequences are weakened. • Did pioneering work on how cats learn using puzzle box (p. 229)-read about in text ...
SV4 Learning Nov 22 2009
... Drug Onset Cues … function as CSs, and they elicit compensatory reactions (called drug tolerance) that diminish the effects of taking a drug like morphine (this is why bigger and bigger doses are required to bring about the same effect with extended use of a drug) What happens when DOCs are present ...
... Drug Onset Cues … function as CSs, and they elicit compensatory reactions (called drug tolerance) that diminish the effects of taking a drug like morphine (this is why bigger and bigger doses are required to bring about the same effect with extended use of a drug) What happens when DOCs are present ...
Unit 1 Exam Review - Deerfield High School
... • Take a few minutes to review your exam. In a section of your notebook, take notes on the concepts/questions that you struggled with. • In addition, answer the following question: – When you signed up for this course, what did you think psychology would be all about? How has that changed since Unit ...
... • Take a few minutes to review your exam. In a section of your notebook, take notes on the concepts/questions that you struggled with. • In addition, answer the following question: – When you signed up for this course, what did you think psychology would be all about? How has that changed since Unit ...
Verbal Behavior

Verbal Behavior is a 1957 book by psychologist B. F. Skinner that inspects human behavior, describing what is traditionally called linguistics. The book Verbal Behavior is almost entirely theoretical, involving little experimental research in the work itself. It was an outgrowth of a series of lectures first presented at the University of Minnesota in the early 1940s and developed further in his summer lectures at Columbia and William James lectures at Harvard in the decade before the book's publication. A growing body of research and applications based on Verbal Behavior has occurred since its original publication, particularly in the past decade.In addition, a growing body of research has developed on structural topics in verbal behavior such as grammar.