Chapter 5 Power Point: Learning
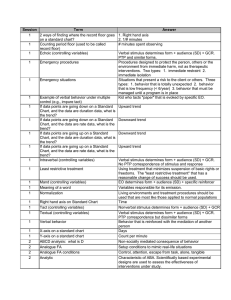
... (response) is not reinforced. • Operantly conditioned responses also can be generalized to stimuli that are only similar to the original stimulus. • Spotaneous recovery (reoccurrence of a once extinguished response) also happens in operant conditioning. ...
... (response) is not reinforced. • Operantly conditioned responses also can be generalized to stimuli that are only similar to the original stimulus. • Spotaneous recovery (reoccurrence of a once extinguished response) also happens in operant conditioning. ...
Pavlov`s Contributions to Behavior Therapy
... dure could not only produce behaviors described as neurotic through the use of conditioning principles but also eliminate such behaviors through the systematic application of counterconditioning measures--an experimentally based paradigm for the study of anxiety responses appeared, laying the groun ...
... dure could not only produce behaviors described as neurotic through the use of conditioning principles but also eliminate such behaviors through the systematic application of counterconditioning measures--an experimentally based paradigm for the study of anxiety responses appeared, laying the groun ...
Classical Conditioning
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
Operant Conditioning
... • Stimulus Generalization – response reinforced (or punished) in the presence of one stimulus to occur (or suppressed) in the presence of other similar stimuli (bird peck at circle and oval) • Stimulus Discrimination – response to occur in the presence of one stimulus but not another similar stimuli ...
... • Stimulus Generalization – response reinforced (or punished) in the presence of one stimulus to occur (or suppressed) in the presence of other similar stimuli (bird peck at circle and oval) • Stimulus Discrimination – response to occur in the presence of one stimulus but not another similar stimuli ...
Real-Life Examples of Classical Conditioning
... The greater the similarity between stimuli, the greater the possibility that a generalisation will occur. E.g. is a stimulus generalisation to the sounds of a bell occurred with one of Pavlov’s dogs, the dog might also salivate in response to the ringing of the front-door bell. ...
... The greater the similarity between stimuli, the greater the possibility that a generalisation will occur. E.g. is a stimulus generalisation to the sounds of a bell occurred with one of Pavlov’s dogs, the dog might also salivate in response to the ringing of the front-door bell. ...
Number 3 • April 1997 - Institute for Applied Behavior Analysis
... severe that they had led directly to exclusions. seen as disruptive in school. Thirdly, attempts to remove Desmond from under furniture only tended to have the effect of escalating Desmond’s tantrum but staff could not ignore a child who was beneath a table shouting at the rest of the class whenever ...
... severe that they had led directly to exclusions. seen as disruptive in school. Thirdly, attempts to remove Desmond from under furniture only tended to have the effect of escalating Desmond’s tantrum but staff could not ignore a child who was beneath a table shouting at the rest of the class whenever ...
Learning
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
Associative Learning
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
Session
... Test for evaluating whether a goal or objective is viable. If a dead man can do it, then it may not be a functional, useful goal. Absence of reinforcer for a period of time, thereby making that event more effective as a reinforcer. An instructional method wherein the client is presented with formal ...
... Test for evaluating whether a goal or objective is viable. If a dead man can do it, then it may not be a functional, useful goal. Absence of reinforcer for a period of time, thereby making that event more effective as a reinforcer. An instructional method wherein the client is presented with formal ...
Learning Psychology
... Work in groups of 3-4 people. Create an original skit that illustrates the principles of classical conditioning Everyone MUST be a part of the skit Skits should last between 1-2 minutes and show an understanding of the principles ...
... Work in groups of 3-4 people. Create an original skit that illustrates the principles of classical conditioning Everyone MUST be a part of the skit Skits should last between 1-2 minutes and show an understanding of the principles ...
Psychological Perspectives
... Reaction Patterns: specific reactionsconditioned responses-past experiencepositive response = likes negative response = dislikes ...
... Reaction Patterns: specific reactionsconditioned responses-past experiencepositive response = likes negative response = dislikes ...
Learning file RG 2 Operant Conditioning
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
Introduction
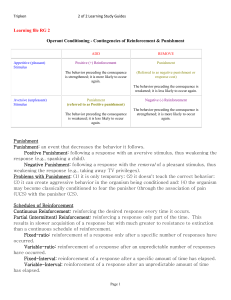
... DRO or Differential Reinforcement of Other behavior occurs when P(S*/R)=0 & P(S*/NoR)=1. Thus, a schedule of reinforcement is a rule that determines how & when a response will be reinforced. They can be simple (where a single factor determines which occurrence of the R S*) or complex (choice ...
... DRO or Differential Reinforcement of Other behavior occurs when P(S*/R)=0 & P(S*/NoR)=1. Thus, a schedule of reinforcement is a rule that determines how & when a response will be reinforced. They can be simple (where a single factor determines which occurrence of the R S*) or complex (choice ...
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or
... 33. If you try to avoid, narrow down, or remove stimuli that elicit the bad habit, you are breaking this bad habit using the strategy that involves a. cues and antecedents. b. breaking up response chains. c. negative reinforcement. d. alternate responses. 34. Which schedule of reinforcement would be ...
... 33. If you try to avoid, narrow down, or remove stimuli that elicit the bad habit, you are breaking this bad habit using the strategy that involves a. cues and antecedents. b. breaking up response chains. c. negative reinforcement. d. alternate responses. 34. Which schedule of reinforcement would be ...
PSYC 305
... Research on learning has been influenced by this approach to psychology that emphasizes the study of observable behavior and the role of the environment as a determinant of behavior. ...
... Research on learning has been influenced by this approach to psychology that emphasizes the study of observable behavior and the role of the environment as a determinant of behavior. ...
527880MyersMod_LG_20
... MODULE 20 PREVIEW Learning helps us adapt to our environment. For example, through classical conditioning we learn to anticipate events, such as being fed or experiencing pain. In his famous studies, Pavlov presented a neutral stimulus just before an unconditioned stimulus, which normally triggered ...
... MODULE 20 PREVIEW Learning helps us adapt to our environment. For example, through classical conditioning we learn to anticipate events, such as being fed or experiencing pain. In his famous studies, Pavlov presented a neutral stimulus just before an unconditioned stimulus, which normally triggered ...
The Science of Psychology
... also can be generalized to stimuli that are only similar to the original stimulus. • Spotaneous recovery (reoccurrence of a once extinguished response) also happens in operant conditioning. ...
... also can be generalized to stimuli that are only similar to the original stimulus. • Spotaneous recovery (reoccurrence of a once extinguished response) also happens in operant conditioning. ...
Chapter 6: Behaviour
... = a process which manifests itself by adaptive changes in individual behaviour as a result of experience ...
... = a process which manifests itself by adaptive changes in individual behaviour as a result of experience ...
Ch. 6 Learning King 3rd Edition Updated 3-15
... • Douglas Merritte died in 1925, at age 6, from the hydrocephaly. According to stories passed down by his family, Merritte never learned to walk and either crawled or had to be carried. It’s unclear whether he ever spoke. • The other baby, Albert Barger, lived a long life, but not quite long enough ...
... • Douglas Merritte died in 1925, at age 6, from the hydrocephaly. According to stories passed down by his family, Merritte never learned to walk and either crawled or had to be carried. It’s unclear whether he ever spoke. • The other baby, Albert Barger, lived a long life, but not quite long enough ...
Operant Conditioning
... • Stimulus Generalization – response reinforced (or punished) in the presence of one stimulus to occur (or suppressed) in the presence of other similar stimuli (bird peck at circle and oval) • Stimulus Discrimination – response to occur in the presence of one stimulus but not another similar stimuli ...
... • Stimulus Generalization – response reinforced (or punished) in the presence of one stimulus to occur (or suppressed) in the presence of other similar stimuli (bird peck at circle and oval) • Stimulus Discrimination – response to occur in the presence of one stimulus but not another similar stimuli ...
Operant Conditioning
... Rocky hit him – rewarded by toy Children alone in room for 20 minutes w/ a rubber doll and other toys from film Children who viewed the film were more aggressive than those who had not seen ...
... Rocky hit him – rewarded by toy Children alone in room for 20 minutes w/ a rubber doll and other toys from film Children who viewed the film were more aggressive than those who had not seen ...
Chp 9
... People’s behaviors are largely the result of their experiences with environmental stimuli. › The “writing” of our behavior is called conditioning. Learning is the relationships among stimuli and responses. Learning involves a behavior change. › Note that this does not include mental events. Learning ...
... People’s behaviors are largely the result of their experiences with environmental stimuli. › The “writing” of our behavior is called conditioning. Learning is the relationships among stimuli and responses. Learning involves a behavior change. › Note that this does not include mental events. Learning ...
Learning Objectives
... conditioned response; describe higher-order conditioning; and discuss the informational view of classical conditioning. OBJECTIVE 8.4 – Describe and give examples of the following concepts as they relate to classical conditioning: a. extinction; b. spontaneous recovery; c. stimulus generalization; a ...
... conditioned response; describe higher-order conditioning; and discuss the informational view of classical conditioning. OBJECTIVE 8.4 – Describe and give examples of the following concepts as they relate to classical conditioning: a. extinction; b. spontaneous recovery; c. stimulus generalization; a ...
PSYC 101 - Study Guide for Mid Term
... Presented food by remote control Other conditioning stimuli also presented by remote control A tube carried the saliva from the dog's mouth to container where it was measured. Tie off stomach - Pavlovian Pouch Stimulus - Any event or object in the environment to which organisms response. Reflex - An ...
... Presented food by remote control Other conditioning stimuli also presented by remote control A tube carried the saliva from the dog's mouth to container where it was measured. Tie off stomach - Pavlovian Pouch Stimulus - Any event or object in the environment to which organisms response. Reflex - An ...
Verbal Behavior

Verbal Behavior is a 1957 book by psychologist B. F. Skinner that inspects human behavior, describing what is traditionally called linguistics. The book Verbal Behavior is almost entirely theoretical, involving little experimental research in the work itself. It was an outgrowth of a series of lectures first presented at the University of Minnesota in the early 1940s and developed further in his summer lectures at Columbia and William James lectures at Harvard in the decade before the book's publication. A growing body of research and applications based on Verbal Behavior has occurred since its original publication, particularly in the past decade.In addition, a growing body of research has developed on structural topics in verbal behavior such as grammar.