Learning - Reading Community Schools
... • Spontaneous Recovery-this is the recovery of what was previously an extinguished response to a stimulus. • Generalization- Responding the same to similar stimuli even though they may not be identical • Discrimination- the act of responding differently to stimuli not similar to each other ...
... • Spontaneous Recovery-this is the recovery of what was previously an extinguished response to a stimulus. • Generalization- Responding the same to similar stimuli even though they may not be identical • Discrimination- the act of responding differently to stimuli not similar to each other ...
(with Perception 6
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
behaviorism and classical conditioning
... In order to understand a behavior it must be observable. Rejects “mentalist” ideas about psychology. Views learning and experience as central in understanding behavior. ...
... In order to understand a behavior it must be observable. Rejects “mentalist” ideas about psychology. Views learning and experience as central in understanding behavior. ...
Name Crash Course-Psychology #11
... __________________________ -- is paired with the neutral stimulus -- the ___________ __________________ -- and results in drooling. >This is repeated many times until the association between the two stimuli is made, in a stage called _________________________________. >By the time you get to the aft ...
... __________________________ -- is paired with the neutral stimulus -- the ___________ __________________ -- and results in drooling. >This is repeated many times until the association between the two stimuli is made, in a stage called _________________________________. >By the time you get to the aft ...
PSY105 Neural Networks 2/5
... • We can describe patterns at one level of description that emerge due to rules followed at a lower level of description. • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
... • We can describe patterns at one level of description that emerge due to rules followed at a lower level of description. • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
Lecture8a_blanks_101
... The CS elicits a _____________________________ response (CR) after time has passed and after extinction Well, how specific is the learning? Generalization The tendency to respond to a CS that is similar to the _____________________________ CS that the animal was trained on Discrimination The ability ...
... The CS elicits a _____________________________ response (CR) after time has passed and after extinction Well, how specific is the learning? Generalization The tendency to respond to a CS that is similar to the _____________________________ CS that the animal was trained on Discrimination The ability ...
conditioning - WordPress.com
... learned. This is followed by an unconditioned response (UR). (ex: meat causes salivation). A conditioned response (CR) is a learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral or meaningless (ex: the bell in Pavlov’s experiments) Through repeated association with meat, the bell became a learn ...
... learned. This is followed by an unconditioned response (UR). (ex: meat causes salivation). A conditioned response (CR) is a learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral or meaningless (ex: the bell in Pavlov’s experiments) Through repeated association with meat, the bell became a learn ...
sensation - LackeyLand
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
Classical Conditioning
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 2. What are eliciting stimuli? 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is ...
... 2. What are eliciting stimuli? 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is ...
Notes: Classical Conditioning
... produces when only a conditioned stimulus is presented. *This will always be the same as the unconditioned response. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Sample problems: 1. Five-year-old Samantha is watching a st ...
... produces when only a conditioned stimulus is presented. *This will always be the same as the unconditioned response. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Sample problems: 1. Five-year-old Samantha is watching a st ...
Russian Physiologist Won 1904 Nobel Prize for Physiology or
... Won 1904 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine ...
... Won 1904 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine ...
vikram_slides1
... processing of S1 responses Assumptions: differential weights to different time windows Periodicity is constant and not considered same weighing window are applied across the stimulus ...
... processing of S1 responses Assumptions: differential weights to different time windows Periodicity is constant and not considered same weighing window are applied across the stimulus ...
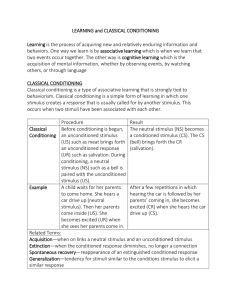
LEARNING and Classical Conditioning
... two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language CLASSICAL CONDITIONING Classical conditioning is a type of associative learning that is strongly tied to behaviorism. Cl ...
... two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language CLASSICAL CONDITIONING Classical conditioning is a type of associative learning that is strongly tied to behaviorism. Cl ...
Chapter Five Practice Quiz 2 Name: Schedule of reinforcement in
... 4. The reinforcement of each and every correct response. Continuous reinforcement 5. Development of nausea or aversive response to a particular taste because that taste was followed by a nausea reaction, occurring after only one association. Conditioned taste aversion 6. Modern theory in which class ...
... 4. The reinforcement of each and every correct response. Continuous reinforcement 5. Development of nausea or aversive response to a particular taste because that taste was followed by a nausea reaction, occurring after only one association. Conditioned taste aversion 6. Modern theory in which class ...
STUDY GUIDE Module 15 Define: Taste Aversion Spontaneous
... 3. Explain how punishment is different than negative reinforcement. 4. What is the name of the operant chamber developed by B.F. Skinner that was used to operantly condition rats to depress a lever to receive a food pellet? is often used to train complicated tricks to animals. This technique ...
... 3. Explain how punishment is different than negative reinforcement. 4. What is the name of the operant chamber developed by B.F. Skinner that was used to operantly condition rats to depress a lever to receive a food pellet? is often used to train complicated tricks to animals. This technique ...
The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... 2. The difference threshold is the smallest difference in stimulation that can be detected 50% of the time (also called jnd-just noticeable difference) ...
... 2. The difference threshold is the smallest difference in stimulation that can be detected 50% of the time (also called jnd-just noticeable difference) ...
Social Psychology Review - Grayslake Central High School
... detergents simply due to the fact that I’ve been exposed to it more. What concept is illustrated here? O Mere exposure effect ...
... detergents simply due to the fact that I’ve been exposed to it more. What concept is illustrated here? O Mere exposure effect ...
Crash Course #11 Learning
... Unconditioned or ________________________ response Describe the acquisition phase of conditioning: Conditioned or ____________________ response. Classical Conditioning: a type of ________________ in which one learns to link ______________ or more stimuli and anticipate events. B.F. ______________ an ...
... Unconditioned or ________________________ response Describe the acquisition phase of conditioning: Conditioned or ____________________ response. Classical Conditioning: a type of ________________ in which one learns to link ______________ or more stimuli and anticipate events. B.F. ______________ an ...
Reading Guide
... 3. The learned reaction to a condition stimulus is the _______________________________________. 4. __________________________________________ occurs when an animal responds to a second stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spont ...
... 3. The learned reaction to a condition stimulus is the _______________________________________. 4. __________________________________________ occurs when an animal responds to a second stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spont ...
File
... o Classical conditioning – a learning procedure in which associations are made between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus o Neutral stimulus – a stimulus that does not initially elicit any part of an unconditioned response o Unconditioned stimulus (US) – an event that elicits a certain ...
... o Classical conditioning – a learning procedure in which associations are made between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus o Neutral stimulus – a stimulus that does not initially elicit any part of an unconditioned response o Unconditioned stimulus (US) – an event that elicits a certain ...
Name: Period: Learning Reading Guide 1. What is classical
... 3. The learned reaction to a condition stimulus is the _______________________________________. 4. __________________________________________ occurs when an animal responds to a second stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spont ...
... 3. The learned reaction to a condition stimulus is the _______________________________________. 4. __________________________________________ occurs when an animal responds to a second stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spont ...