APPsynotesch9-learning
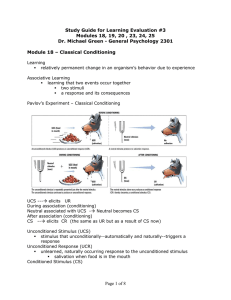
... Chapter 6 A.P. Psychology-Learning Learning-a relatively permanent change in behavior based on prior experience. Behaviorists believe learning is measured by ________________ behavior; whereas cognitivists view learning as a _____________ process Classical Conditioning Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936)-Russia ...
... Chapter 6 A.P. Psychology-Learning Learning-a relatively permanent change in behavior based on prior experience. Behaviorists believe learning is measured by ________________ behavior; whereas cognitivists view learning as a _____________ process Classical Conditioning Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936)-Russia ...
Learning Notes
... The most common example of this is disciplining (e.g. spanking) a child for misbehaving. The reason we do this is because the child begins to associate being punished with the negative behavior. (detentions) ...
... The most common example of this is disciplining (e.g. spanking) a child for misbehaving. The reason we do this is because the child begins to associate being punished with the negative behavior. (detentions) ...
Operant Conditioning
... a) Limits on Classical Conditioning i) An animal’s biology can restrict or expand its ability to be conditioned. (1) Proposed by John Garcia. (2) Supports Darwin’s theory of natural selection. (a) Conditioning is strengthened if the CS is relevant to an animal’s biology, like something associated wi ...
... a) Limits on Classical Conditioning i) An animal’s biology can restrict or expand its ability to be conditioned. (1) Proposed by John Garcia. (2) Supports Darwin’s theory of natural selection. (a) Conditioning is strengthened if the CS is relevant to an animal’s biology, like something associated wi ...
Study Guide for Learning Evaluation #4
... Spontaneous Recovery reappearance, after a rest period, of an extinguished CR Discrimination in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal a UCS ...
... Spontaneous Recovery reappearance, after a rest period, of an extinguished CR Discrimination in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal a UCS ...
History
... events are unconscious (e.g. memory retrieval, or visual processes that lead to perceptual illusions). ...
... events are unconscious (e.g. memory retrieval, or visual processes that lead to perceptual illusions). ...
Chapter 7 (Professor Powerpoint)
... – A response that is elicited by the conditioned stimulus. – Occurs after the CS is associated with the US. – Is usually similar to US Wade/Tavris, (c) 2006, Prentice Hall ...
... – A response that is elicited by the conditioned stimulus. – Occurs after the CS is associated with the US. – Is usually similar to US Wade/Tavris, (c) 2006, Prentice Hall ...
Motor Mechanisms and Behavior
... Behavior – action that can be observed and described. Genetic influence ...
... Behavior – action that can be observed and described. Genetic influence ...
Review3
... they respond to the original stimuli. For example, a drug store's bottle of private brand mouthwash might be deliberately packaged so as to resemble a name brand (such as Listerine). The consumer would assume this "me-too" product has the same characteristics as the name brand and buy it because of ...
... they respond to the original stimuli. For example, a drug store's bottle of private brand mouthwash might be deliberately packaged so as to resemble a name brand (such as Listerine). The consumer would assume this "me-too" product has the same characteristics as the name brand and buy it because of ...
Conditioning - Gordon State College
... repeatedly appear before the unconditioned stimulus (US)…about a half-second before, in most cases. The bell must come right before the food. ...
... repeatedly appear before the unconditioned stimulus (US)…about a half-second before, in most cases. The bell must come right before the food. ...
Classical & Operant Conditiong
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
a learned response - Plain Local Schools
... Discrimination: The ability to respond differently to similar but distinct stimuli, example being afraid of only white fuzzy items not all fuzzy items ...
... Discrimination: The ability to respond differently to similar but distinct stimuli, example being afraid of only white fuzzy items not all fuzzy items ...
Learning and Classical Conditioning
... radiation or drugs that led to nausea and vomiting (UCR). ...
... radiation or drugs that led to nausea and vomiting (UCR). ...
Document
... • Third-order neurons • Conduct impulses from the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex (perceptual level) ...
... • Third-order neurons • Conduct impulses from the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex (perceptual level) ...
The Learning Approach: Classical Conditioning
... A cat who was conditioned to salivate when he heard a tin of cat food being opened no longer salivates to the noise because the tin and tin can opener are no longer presented together. A cat who was conditioned to salivate when he heard a tin of cat food being opened no longer salivates to the noise ...
... A cat who was conditioned to salivate when he heard a tin of cat food being opened no longer salivates to the noise because the tin and tin can opener are no longer presented together. A cat who was conditioned to salivate when he heard a tin of cat food being opened no longer salivates to the noise ...
Neurophysiology Complete
... to Na ions when a neuron is activated by a stimulus of adequate intensity Depolarization: the interior becomes less negative, exterior becomes less positive Action potential: when depolarization reaches a certain point so that the membrane polarity changes Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and ...
... to Na ions when a neuron is activated by a stimulus of adequate intensity Depolarization: the interior becomes less negative, exterior becomes less positive Action potential: when depolarization reaches a certain point so that the membrane polarity changes Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and ...
Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences 1
... Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences ...
... Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences ...
Chapter 8 - Learning - North Cobb High School Class Websites
... Skinner “ _______________” the animal to get closer to the bar before giving it food. For example, if the animal approached the bar, he might initially give it a pellet of food for getting close to the bar. Eventually, the animal learned that it had to press the bar in order to get any food. ...
... Skinner “ _______________” the animal to get closer to the bar before giving it food. For example, if the animal approached the bar, he might initially give it a pellet of food for getting close to the bar. Eventually, the animal learned that it had to press the bar in order to get any food. ...
Conditioned Learning
... • Noticed that the dogs began to salivate before the food was presented – At the sight of food, the food dish, the presence of the researchers, or the sound of their approaching footsteps. ...
... • Noticed that the dogs began to salivate before the food was presented – At the sight of food, the food dish, the presence of the researchers, or the sound of their approaching footsteps. ...
Module 26 notes - Bremerton School District
... Early behaviorists believed that learned behaviors of various animals could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. However, later behaviorists suggested that animals learn the predictability of a stimulus, meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus. ...
... Early behaviorists believed that learned behaviors of various animals could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. However, later behaviorists suggested that animals learn the predictability of a stimulus, meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus. ...
doc psych 100 review summary
... According to Hebb “set” occurs when two stimuli are presented one after the other and the response to the second is controlled or modified by the first. o The cell assembly theory explains set: The mechanism of thought is a recurrent neural loop that received sensory input from another loop but that ...
... According to Hebb “set” occurs when two stimuli are presented one after the other and the response to the second is controlled or modified by the first. o The cell assembly theory explains set: The mechanism of thought is a recurrent neural loop that received sensory input from another loop but that ...
Psychologists and Their Contributions - Har
... 51. Brocca’s Area: The left frontal lobe that directs muscle movement involved in speech. He did his studies with a subject who could only speak one word, “Tan”. The person damaged in this area has speech that makes sense but has difficulty speaking 52. Wernicke’s Area: An area of the left temporal ...
... 51. Brocca’s Area: The left frontal lobe that directs muscle movement involved in speech. He did his studies with a subject who could only speak one word, “Tan”. The person damaged in this area has speech that makes sense but has difficulty speaking 52. Wernicke’s Area: An area of the left temporal ...
studyguidesection1-teacher-website-ch8
... 3. During the initial phase of the experiment, Pavlov and his associates placed food or meat powder (unconditioned stimulus UCS/ US) on the tongue of one of the dogs. The food or meat powder (UCS/US) automatically produced saliva (unconditioned response UCR/UR) in the dog’s mouth; the production of ...
... 3. During the initial phase of the experiment, Pavlov and his associates placed food or meat powder (unconditioned stimulus UCS/ US) on the tongue of one of the dogs. The food or meat powder (UCS/US) automatically produced saliva (unconditioned response UCR/UR) in the dog’s mouth; the production of ...
Learning PP 1
... “Education is what survives when what has been learned has been forgotten.” B.F. Skinner ...
... “Education is what survives when what has been learned has been forgotten.” B.F. Skinner ...