Sept 16 - Am i Normal part 1
... women tend to have better episodic memories. With semantic memory, men tend to remember spatial information better, whereas women generally perform better at verbal tasks, such as recalling word lists. ...
... women tend to have better episodic memories. With semantic memory, men tend to remember spatial information better, whereas women generally perform better at verbal tasks, such as recalling word lists. ...
Forgetting
... • In the 80’s and 90’s “recovered memories” were big headlines. • Individuals of all ages were claiming to suddenly remember events that had been “repressed” and forgotten for years. • Often these memories were of abuse. • Sometimes these recovered memories were corroborated with physical evidence a ...
... • In the 80’s and 90’s “recovered memories” were big headlines. • Individuals of all ages were claiming to suddenly remember events that had been “repressed” and forgotten for years. • Often these memories were of abuse. • Sometimes these recovered memories were corroborated with physical evidence a ...
Module 12 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • memory files that contain related information organized around a specific topic or category – refers to the arrangement of nodes or memory files in a certain order or hierarchy – bottom of the hierarchy are nodes with very concrete information, which are connected to nodes with somewhat more speci ...
... • memory files that contain related information organized around a specific topic or category – refers to the arrangement of nodes or memory files in a certain order or hierarchy – bottom of the hierarchy are nodes with very concrete information, which are connected to nodes with somewhat more speci ...
Readings
... patterns in LTM, (unitization) (3) decide which is the best match.(top-down processing) Understand that most information is redundant. We can identify letters and other patterns even with some features missing. Cues to identification are context and familiarity. Context is especially important i ...
... patterns in LTM, (unitization) (3) decide which is the best match.(top-down processing) Understand that most information is redundant. We can identify letters and other patterns even with some features missing. Cues to identification are context and familiarity. Context is especially important i ...
File
... contemplation, learning, emotions and memory A thick band of axons known as corpus callosum enables the right and left cerebral cortices to communicate The cerebellum coordinates movement and balance and helps in learning and remembering motor skills, as well as receiving sensory information about t ...
... contemplation, learning, emotions and memory A thick band of axons known as corpus callosum enables the right and left cerebral cortices to communicate The cerebellum coordinates movement and balance and helps in learning and remembering motor skills, as well as receiving sensory information about t ...
Elida High School Mr. Kellermeyer Blizzard Bag #3
... 14 This type of interference is the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information. 15 Researchers believe that _____________ term memory can contain 7 plus or minus 2 pieces of information. 16 This type of interference is the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of ...
... 14 This type of interference is the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information. 15 Researchers believe that _____________ term memory can contain 7 plus or minus 2 pieces of information. 16 This type of interference is the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of ...
Memory notes Explaining memory Learning required memorisation
... Kandel’s research findings indicate that any experience that results in memory produces physical changes in the brain at the neuronal level, strengthening connections between neurons involved in the process, thus making communication easier next time. These changes create and strengthen a memory cir ...
... Kandel’s research findings indicate that any experience that results in memory produces physical changes in the brain at the neuronal level, strengthening connections between neurons involved in the process, thus making communication easier next time. These changes create and strengthen a memory cir ...
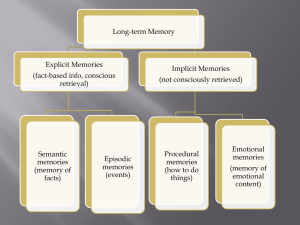
Memory Systems
... • Could learn by procedural memory but had no recollection of having learned task ...
... • Could learn by procedural memory but had no recollection of having learned task ...
Color-coded Notes
... PAST) Retroactive Interference (RETRORECENT) Positive Transfer Motivated Forgetting Repression Misinformation Effect Imagination Inflation Source Amnesia How we discern True/False memories? Children & Eyewitness AMA/APA/APSYA/APS beliefs about repression and incest Loftus Studies on false memories S ...
... PAST) Retroactive Interference (RETRORECENT) Positive Transfer Motivated Forgetting Repression Misinformation Effect Imagination Inflation Source Amnesia How we discern True/False memories? Children & Eyewitness AMA/APA/APSYA/APS beliefs about repression and incest Loftus Studies on false memories S ...
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... in synaptic changes in the neural network. His research showed that learning (forming memories) means growing new connections or strengthening connections between neurons. Kandel went on to study synaptic changes due to memory in the hippocampus. In other words, what changes occur in the hippocampus ...
... in synaptic changes in the neural network. His research showed that learning (forming memories) means growing new connections or strengthening connections between neurons. Kandel went on to study synaptic changes due to memory in the hippocampus. In other words, what changes occur in the hippocampus ...
Memory
... • The circuit of neurons is called a “cell assembly” • Eventually, the neurons in the cell assembly change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
... • The circuit of neurons is called a “cell assembly” • Eventually, the neurons in the cell assembly change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
Slide outlines
... • "My theory ... is that the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the exciting fact, and that our feeling of the same changes as they occur is the emotion. Common sense says, we lose our fortune, are sorry and weep; we meet a bear, are frightened and run; we are insulted by a rival, and ...
... • "My theory ... is that the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the exciting fact, and that our feeling of the same changes as they occur is the emotion. Common sense says, we lose our fortune, are sorry and weep; we meet a bear, are frightened and run; we are insulted by a rival, and ...
Memory Capacity of a Hebbian Learning Model with Inhibition
... The University of Chicago Department of Statistics Master’s Seminar ...
... The University of Chicago Department of Statistics Master’s Seminar ...
Forgetting - Cloudfront.net
... – Occurs when information already in memory interferes with new information – Because of proactive interference, new learning is disrupted by old habits. – Psychologists have found that recall of later items can be improved by making them distinctive from early items. For example, people being fed g ...
... – Occurs when information already in memory interferes with new information – Because of proactive interference, new learning is disrupted by old habits. – Psychologists have found that recall of later items can be improved by making them distinctive from early items. For example, people being fed g ...
Memory_Ch7_all - Arizona State University
... A more effective way to encode information is through elaborative rehearsal – making connections between the new item and memories you already have ...
... A more effective way to encode information is through elaborative rehearsal – making connections between the new item and memories you already have ...
Memory kaleidoscope: enhancing memory to improve learning
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
Memory Manipulation - Hunting Hills High School
... In 1974 researchers designed an experiment to test the reliability of memory, and whether it could be manipulated after the fact. ...
... In 1974 researchers designed an experiment to test the reliability of memory, and whether it could be manipulated after the fact. ...
Who You Know: Prominent Psychologists (Word Associations
... Darley and Latane – Kitty Genovese; diffusion of responsibility and pluralistic ignorance; bystander effect James – functionalism (all activities of mind serve a function, survival of species) Wundt – first psychology lab, introspection and structuralism (all human mental experience, no matter how c ...
... Darley and Latane – Kitty Genovese; diffusion of responsibility and pluralistic ignorance; bystander effect James – functionalism (all activities of mind serve a function, survival of species) Wundt – first psychology lab, introspection and structuralism (all human mental experience, no matter how c ...
emotion_08
... • "My theory ... is that the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the exciting fact, and that our feeling of the same changes as they occur is the emotion. Common sense says, we lose our fortune, are sorry and weep; we meet a bear, are frightened and run; we are insulted by a rival, and ...
... • "My theory ... is that the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the exciting fact, and that our feeling of the same changes as they occur is the emotion. Common sense says, we lose our fortune, are sorry and weep; we meet a bear, are frightened and run; we are insulted by a rival, and ...
Cognitive Neuroscience of Language: 18: Memory and language
... and rehearsal, where rehearsal is equivalent (but not identical with) subvocal rehearsal Left posterior parietal cortex is implicated in storage ...
... and rehearsal, where rehearsal is equivalent (but not identical with) subvocal rehearsal Left posterior parietal cortex is implicated in storage ...