From Gene to Protein
... polymerase (I, II – used in RNA synthesis and III) • Bacteria have one kind – it makes not only mRNA but also other types of RNA • Bacteria have one chromosome and many plasmids. Information is constantly being sent to ribosomes for translation into proteins needed by the bacterial cell ...
... polymerase (I, II – used in RNA synthesis and III) • Bacteria have one kind – it makes not only mRNA but also other types of RNA • Bacteria have one chromosome and many plasmids. Information is constantly being sent to ribosomes for translation into proteins needed by the bacterial cell ...
Chapter 22 (Part 2)
... larger and more complex, but many of the structural and functional properties are similar • 40S subunit contains 30 proteins and 18S RNA. • 60S subunit contains 40 proteins and 3 rRNAs. ...
... larger and more complex, but many of the structural and functional properties are similar • 40S subunit contains 30 proteins and 18S RNA. • 60S subunit contains 40 proteins and 3 rRNAs. ...
CHAPTER 17 - HCC Learning Web
... • During the elongation stage, amino acids are added one by one to the preceding amino acid at the C-terminus of the growing chain • Each addition involves proteins called elongation factors and occurs in three steps: codon recognition, peptide bond formation, and ...
... • During the elongation stage, amino acids are added one by one to the preceding amino acid at the C-terminus of the growing chain • Each addition involves proteins called elongation factors and occurs in three steps: codon recognition, peptide bond formation, and ...
Protein synthesis - Aurora City Schools
... Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three regions does a gene have and what do they do? ...
... Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three regions does a gene have and what do they do? ...
Document
... 42. The lac operon consists of three segments. These include a promoter, an operator, and three lactose-metabolizing genes. In addition, a regulator gene lies close to the lac operon. 43. The failure of lactose to bind to and remove the repressor will prevent the lac operon from functioning. As a re ...
... 42. The lac operon consists of three segments. These include a promoter, an operator, and three lactose-metabolizing genes. In addition, a regulator gene lies close to the lac operon. 43. The failure of lactose to bind to and remove the repressor will prevent the lac operon from functioning. As a re ...
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments
... B. DNA, RNA, and the Flow of Information • RNA differs from DNA in three ways: It is single single--stranded, its sugar molecule is ribose rather than deoxyribose, y , and its fourth base is uracil rather than thymine. • The central dogma of molecular biology is DNA RNA protein. Unidirectional w ...
... B. DNA, RNA, and the Flow of Information • RNA differs from DNA in three ways: It is single single--stranded, its sugar molecule is ribose rather than deoxyribose, y , and its fourth base is uracil rather than thymine. • The central dogma of molecular biology is DNA RNA protein. Unidirectional w ...
Interference with ribosomal RNA production leads to the activation of
... promotes thetranscription and processing of rRNA and the translation of the mRNAs for ribosomalproteins (which are encoded by 5’-TOP mRNAs). Here we have studied the effectsof perturbing the PeBoW complex, which comprises PES1, BOP1 and WDR12 and is required for processing the 28S rRNA. Expressing a ...
... promotes thetranscription and processing of rRNA and the translation of the mRNAs for ribosomalproteins (which are encoded by 5’-TOP mRNAs). Here we have studied the effectsof perturbing the PeBoW complex, which comprises PES1, BOP1 and WDR12 and is required for processing the 28S rRNA. Expressing a ...
DNA Transcription
... We’ve seen how DNA is replicated, but still haven’t learned exactly how genes work! The first step in understanding how genes work is to know how to “decode” the DNA. ...
... We’ve seen how DNA is replicated, but still haven’t learned exactly how genes work! The first step in understanding how genes work is to know how to “decode” the DNA. ...
Chapter 8 DNA: the universal molecule of life All living things share
... • A section of DNA with the required gene unwinds and unzips (with help of RNA polymerase) • Enzyme RNA polymerase binds to promotor region on the gene - joins complementary nucleotides that attach to exposed bases on the template DNA strand – (C to G, A to T, U to A (U not T is in RNA) to make a co ...
... • A section of DNA with the required gene unwinds and unzips (with help of RNA polymerase) • Enzyme RNA polymerase binds to promotor region on the gene - joins complementary nucleotides that attach to exposed bases on the template DNA strand – (C to G, A to T, U to A (U not T is in RNA) to make a co ...
Protein Synthsis
... Therefore, it is very important for the mRNA to have a clear START and STOP ...
... Therefore, it is very important for the mRNA to have a clear START and STOP ...
From DNA to Protein
... the protein encoded (Figure 15.2). C. The one gene–one polypeptide hypothesis represents the analysis of this study. D. The pathway from gene to polypeptide uses transcription and translation (Figure 15.3). 1. Transcription is the process by which DNA is used to create an RNA copy. 2. Translation is ...
... the protein encoded (Figure 15.2). C. The one gene–one polypeptide hypothesis represents the analysis of this study. D. The pathway from gene to polypeptide uses transcription and translation (Figure 15.3). 1. Transcription is the process by which DNA is used to create an RNA copy. 2. Translation is ...
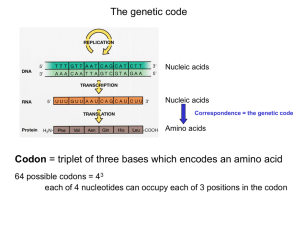
AUG
... 61 codons encode amino acids, 3 codons do not specify amino acids Specialized codons: - for start of translation - AUG - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
... 61 codons encode amino acids, 3 codons do not specify amino acids Specialized codons: - for start of translation - AUG - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
Multiple choice questions
... Occurs at the ends of coding regions Can be induced by specific RNA stem-loops Is similar in prokaryotes and in the nucleus of eukaryotes Can involve the action of several proteins Is always linked to translation Can be regulated ...
... Occurs at the ends of coding regions Can be induced by specific RNA stem-loops Is similar in prokaryotes and in the nucleus of eukaryotes Can involve the action of several proteins Is always linked to translation Can be regulated ...
Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events
... Glutamate receptor ion channel GluR-B changes glutamine->arginine Reduces Ca2+-permeability. ...
... Glutamate receptor ion channel GluR-B changes glutamine->arginine Reduces Ca2+-permeability. ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... determined by the DNA. Three Stages of Translation: Initiation- assemble components to start process Elongation- add amino acids in repeated cycles ...
... determined by the DNA. Three Stages of Translation: Initiation- assemble components to start process Elongation- add amino acids in repeated cycles ...
Biol-1406_Ch10Notes.ppt
... Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes • The intestinal bacterium Escherichia coli _______ lives on what its host eats • Specific ________ are needed to metabolize the type of food that comes along • e.g. in newborn mammals, E.coli are bathed in milk, containing the milk sugar ___________ • The lactose ___ ...
... Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes • The intestinal bacterium Escherichia coli _______ lives on what its host eats • Specific ________ are needed to metabolize the type of food that comes along • e.g. in newborn mammals, E.coli are bathed in milk, containing the milk sugar ___________ • The lactose ___ ...
Sample Exam #2 ( file)
... For a complete translation (including termination) of a protein synthesis containing 330 amino acids would require an mRNA coding region of ____________ bases long. A. 993 B. 663 C. 660 D. 330 E. 990 ...
... For a complete translation (including termination) of a protein synthesis containing 330 amino acids would require an mRNA coding region of ____________ bases long. A. 993 B. 663 C. 660 D. 330 E. 990 ...
REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION, TRANSLATION TAKS
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
Gene Regulation
... • Inducible enzymes catabolic pathways – Break down larger molecules – Turn on in the presence of starting product ...
... • Inducible enzymes catabolic pathways – Break down larger molecules – Turn on in the presence of starting product ...
Transcription and Translation
... No effect if it is the same amino acid Redundancy! Missense – codes for a different amino acid Nonsense – codes for a stop codon Can be harmful to the organism if a useless or less active protein is created. ...
... No effect if it is the same amino acid Redundancy! Missense – codes for a different amino acid Nonsense – codes for a stop codon Can be harmful to the organism if a useless or less active protein is created. ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... pathway are often found in the same operon – All under the control of the same promoter region – Thus these genes are transcribed all together into one continuous mRNA strand: polycistronic mRNA • Proteins are then synthesized from that mRNA ...
... pathway are often found in the same operon – All under the control of the same promoter region – Thus these genes are transcribed all together into one continuous mRNA strand: polycistronic mRNA • Proteins are then synthesized from that mRNA ...