Slide 1
... • Extract selection information from conservation of secondary structure of alignments of homologous RNA sequences from different species, for different RNA families. ...
... • Extract selection information from conservation of secondary structure of alignments of homologous RNA sequences from different species, for different RNA families. ...
Select one of your Biology instructors from another class and look
... sequence of four ribonucleotides, all with equal frequency, what is the probability that any three adjacent nucleotides will be a start codon? A stop codon? In an mRNA molecule of random sequence, what is the average distance between stop codons? 8.2 If DNA consisted of only two nucleotides (say, A ...
... sequence of four ribonucleotides, all with equal frequency, what is the probability that any three adjacent nucleotides will be a start codon? A stop codon? In an mRNA molecule of random sequence, what is the average distance between stop codons? 8.2 If DNA consisted of only two nucleotides (say, A ...
splicing
... turnover determinant that lies in the 3’-UTR • Iron response elements A and E along with the large central loop of the TfR 3’-UTR can be deleted without altering the response to iron • Removing all of the IREs, or either 1 or 2 nonIRE stem loops renders the TfR mRNA ...
... turnover determinant that lies in the 3’-UTR • Iron response elements A and E along with the large central loop of the TfR 3’-UTR can be deleted without altering the response to iron • Removing all of the IREs, or either 1 or 2 nonIRE stem loops renders the TfR mRNA ...
Complete DNA Function Vocab with definitions
... inheritable traits of an organism. A single linear strand of DNA (and associated structural proteins) that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information The backbone of nucleic acid constructed from alternating ribose sugar and phosphate molecules. a part of the cell ...
... inheritable traits of an organism. A single linear strand of DNA (and associated structural proteins) that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information The backbone of nucleic acid constructed from alternating ribose sugar and phosphate molecules. a part of the cell ...
UNIT 7 – MOLECULAR GENETICS Mon, 1/23 – Mon, 2/13 Unit
... Explain the process of transcription, including mRNA editing. Distinguish among mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in terms of location and function. Describe the structure of a ribosome and explain how this structure relates to its function. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Define codon ...
... Explain the process of transcription, including mRNA editing. Distinguish among mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in terms of location and function. Describe the structure of a ribosome and explain how this structure relates to its function. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Define codon ...
Lecture 18: Powerpoint
... The catalytic site on the large subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond linking the amino acids ...
... The catalytic site on the large subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond linking the amino acids ...
DNA Replication • DNA strands separate and the nucleotides in the
... The leading strand can code continuously from 5-carbon to 3-carbon The lagging strand can only code from 5-carbon to the 3-carbon so it must reset itself to allow for this o RNA primer is added before the DNA polymerase adds the nucleotides to form the DNA o This leads to Okazaki fragments which are ...
... The leading strand can code continuously from 5-carbon to 3-carbon The lagging strand can only code from 5-carbon to the 3-carbon so it must reset itself to allow for this o RNA primer is added before the DNA polymerase adds the nucleotides to form the DNA o This leads to Okazaki fragments which are ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... DNA vs.RNA: differences • DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) and RNA (ribose nucleic acid) are both nucleotide polymers. These molecules are very similar but there are some distinct differences between them. ...
... DNA vs.RNA: differences • DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) and RNA (ribose nucleic acid) are both nucleotide polymers. These molecules are very similar but there are some distinct differences between them. ...
View/Open - Oregon State University
... 3. The genetic code is universal (all cells use the same code - only very rare exception have very slightly altered codes) 4. Codons you should know include the codon that always starts translation (AUG - specifies methionine) and three codons that STOP translation - UAA, UAG, UGA. 5. The third base ...
... 3. The genetic code is universal (all cells use the same code - only very rare exception have very slightly altered codes) 4. Codons you should know include the codon that always starts translation (AUG - specifies methionine) and three codons that STOP translation - UAA, UAG, UGA. 5. The third base ...
Translational Control
... is called a “missense mutation” bc the protein may still work, but not as before. If the change results in multiple amino acid changes or a stop codon in the middle, this is called a “nonsense mutation”. Typically these proteins do not function at all. Note: if a mutation can make a protein WORSE, i ...
... is called a “missense mutation” bc the protein may still work, but not as before. If the change results in multiple amino acid changes or a stop codon in the middle, this is called a “nonsense mutation”. Typically these proteins do not function at all. Note: if a mutation can make a protein WORSE, i ...
Transcription and Translation
... coding regions (exons) and noncoding regions (introns) Introns must be removed before primary transcript is mRNA and can leave nucleus ...
... coding regions (exons) and noncoding regions (introns) Introns must be removed before primary transcript is mRNA and can leave nucleus ...
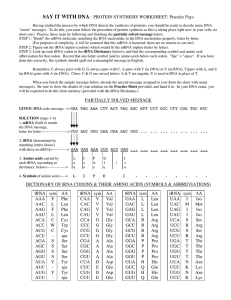
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
lesson viii - MisterSyracuse.com
... go faster, slower, repeat segments, there are also silencers that can turn off RNA polymerase. There is much more control. 18. There is a terminator in eukaryotes as well, but there are other chemicals that are thought to stop transcription, too. 19. We’re not done yet! Eukaryotes have Introns and E ...
... go faster, slower, repeat segments, there are also silencers that can turn off RNA polymerase. There is much more control. 18. There is a terminator in eukaryotes as well, but there are other chemicals that are thought to stop transcription, too. 19. We’re not done yet! Eukaryotes have Introns and E ...
Transcription and Translation
... Each triplet code on a DNA molecule is transcribed into a triplet codon on the mRNA molecule. • If the DNA codes for a polypeptide is T-A-C—C-C-G—T-A-G—C-T-T—A-C-T • What would the codons on the complimentary strand of mRNA codons look like? A-U-G – G-G-C – A-U-C – G-A-A – U-G-A • DNA codes: T-A-C— ...
... Each triplet code on a DNA molecule is transcribed into a triplet codon on the mRNA molecule. • If the DNA codes for a polypeptide is T-A-C—C-C-G—T-A-G—C-T-T—A-C-T • What would the codons on the complimentary strand of mRNA codons look like? A-U-G – G-G-C – A-U-C – G-A-A – U-G-A • DNA codes: T-A-C— ...
Name:
... Go to Mr. Mason’s site, and then to the link for “Genetics – Transcription” 1. What are the three steps of turning a gene into a functional protein? 2. What must be done to the DNA double helix before it can be transcribed? 3. What is the primary difference between DNA and mRNA when it comes to the ...
... Go to Mr. Mason’s site, and then to the link for “Genetics – Transcription” 1. What are the three steps of turning a gene into a functional protein? 2. What must be done to the DNA double helix before it can be transcribed? 3. What is the primary difference between DNA and mRNA when it comes to the ...
Protein Synthesis - Workforce Solutions
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against ...
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against ...
Lecture 7
... • How many amino acids would one protein contain if it was translated from an mRNA that is 690 nucleotides long? ...
... • How many amino acids would one protein contain if it was translated from an mRNA that is 690 nucleotides long? ...
DNA Damage - Columbus Labs
... An RNA molecule (messenger RNA, or mRNA), containing in its base sequence the information that specifies a particular protein, acts as a template to direct the synthesis of the polypeptide. Each amino acid is brought to the template attached to an adapter molecule specific to that amino acid. These ...
... An RNA molecule (messenger RNA, or mRNA), containing in its base sequence the information that specifies a particular protein, acts as a template to direct the synthesis of the polypeptide. Each amino acid is brought to the template attached to an adapter molecule specific to that amino acid. These ...
protein
... delivered to the cells by the blood vessels. Inside the cells, they are used for anabolism (building) of proteins or undergo deamination (removal of the amine functional group) for ATP production in cellular respiration. ...
... delivered to the cells by the blood vessels. Inside the cells, they are used for anabolism (building) of proteins or undergo deamination (removal of the amine functional group) for ATP production in cellular respiration. ...
Objectives 2
... functions: mRNA carries messages transcribed from DNA to be translated into protein, hnRNA is immature form of mRNA, tRNA carries activated amino acids, and rRNA is a structural component of ribosomes. 2) List the principal chemical building blocks that comprise nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed ...
... functions: mRNA carries messages transcribed from DNA to be translated into protein, hnRNA is immature form of mRNA, tRNA carries activated amino acids, and rRNA is a structural component of ribosomes. 2) List the principal chemical building blocks that comprise nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed ...
PowerPoint
... The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by anti-sense nucleic acids was discovered in the 1980’s (Inouye, 1988). 2. Guo and Kemphues (1995) showed that, in some cases for C. elegans genes, the sense strand inhibited just as well as the anti- ...
... The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by anti-sense nucleic acids was discovered in the 1980’s (Inouye, 1988). 2. Guo and Kemphues (1995) showed that, in some cases for C. elegans genes, the sense strand inhibited just as well as the anti- ...
21.5 RNA and Transcription
... genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes. • 15% of RNA is transfer RNA (tRNA), which translates the genetic information in mRNA into the amino acid sequence for the protein. • 80% of RNA is ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which is the most abundant type of RNA; it is combined with proteins to form riboso ...
... genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes. • 15% of RNA is transfer RNA (tRNA), which translates the genetic information in mRNA into the amino acid sequence for the protein. • 80% of RNA is ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which is the most abundant type of RNA; it is combined with proteins to form riboso ...
Transcription and Translation
... and cytosine). Clearly, it is not possible to have one base coding for each of 20 different amino acids. Similarly, using two bases would be insufficient (4n or 16 permutations of two bases, where n = the number of bases used in the code). Using three bases is more than enough (4n or 64 permutations ...
... and cytosine). Clearly, it is not possible to have one base coding for each of 20 different amino acids. Similarly, using two bases would be insufficient (4n or 16 permutations of two bases, where n = the number of bases used in the code). Using three bases is more than enough (4n or 64 permutations ...