Physiology of Cells
... bases along one side of the DNA molecule • These RNA nucleotides bind to each other with the help of RNA polymerase • The chain that results is called messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
... bases along one side of the DNA molecule • These RNA nucleotides bind to each other with the help of RNA polymerase • The chain that results is called messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
Special Topics gene expression
... A. Polymers of monomers B. Joined by peptide bond C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. nucleotide) III. Transcription – DNA to RNA A. Where does this occur? IV. Transla ...
... A. Polymers of monomers B. Joined by peptide bond C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. nucleotide) III. Transcription – DNA to RNA A. Where does this occur? IV. Transla ...
Dna * Structure, transcription and translation
... ■ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=35FwmiPE9tI ...
... ■ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=35FwmiPE9tI ...
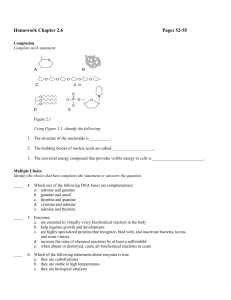
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... ____ 10. The nucleotide chains of DNA are held together by: a. carbon bonds b. hydrogen bonds c. ionic bonds d. nonpolar covalent bonds e. polar covalent bonds ____ 11. Which of the following statements about ATP is false: a. it drives the transport of certain solutes (e.g., amino acids) across cell ...
... ____ 10. The nucleotide chains of DNA are held together by: a. carbon bonds b. hydrogen bonds c. ionic bonds d. nonpolar covalent bonds e. polar covalent bonds ____ 11. Which of the following statements about ATP is false: a. it drives the transport of certain solutes (e.g., amino acids) across cell ...
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA
... Mobile DNA-----can cause mutations when move to new sites in genome. ------have no function in life cycle, probably played role in evolution. In higher eukaryotes, DNA regions encoding proteins— genes nonfunctional DNA=noncoding introns common within genes Sequencing of same protein-coding gene (Ex ...
... Mobile DNA-----can cause mutations when move to new sites in genome. ------have no function in life cycle, probably played role in evolution. In higher eukaryotes, DNA regions encoding proteins— genes nonfunctional DNA=noncoding introns common within genes Sequencing of same protein-coding gene (Ex ...
MolBioPrimer_2005-06
... Consensus sequences, e.g. TATA box 2. Chain initiation & elongation RNA synthesis begins at transcription start site, next to the promoter Again: 5' to 3' elongation ...
... Consensus sequences, e.g. TATA box 2. Chain initiation & elongation RNA synthesis begins at transcription start site, next to the promoter Again: 5' to 3' elongation ...
mRNA
... Expression refers to both RNA and protein Gene expression is regulated at both the transcriptional and translational levels – RNA and protein expression don’t always correlate ...
... Expression refers to both RNA and protein Gene expression is regulated at both the transcriptional and translational levels – RNA and protein expression don’t always correlate ...
Molecular Biology
... • The disease results from a single base change in the gene for b-globin – Altered base causes insertion an incorrect amino acid into one position of the b-globin protein – Altered protein results in distortion of red ...
... • The disease results from a single base change in the gene for b-globin – Altered base causes insertion an incorrect amino acid into one position of the b-globin protein – Altered protein results in distortion of red ...
TRANSLATION
... Protein is made 5. mRNA leaves nucleus, goes to ribosome in cytoplasm 6. tRNA assists by bringing an amino acid to the ribosome 7. tRNA matches its anticodon with the mRNA codon, putting amino acids in the correct sequence 8. amino acids bond, forming a protein click to play animation ...
... Protein is made 5. mRNA leaves nucleus, goes to ribosome in cytoplasm 6. tRNA assists by bringing an amino acid to the ribosome 7. tRNA matches its anticodon with the mRNA codon, putting amino acids in the correct sequence 8. amino acids bond, forming a protein click to play animation ...
RNA Helicase Module in an Acetyltransferase That Modifies a
... of protein complexes from yeast illustrated the interactions of KRE33 with several ribosomal proteins and a subset of ribosomal processing factors (Figure S6) (Gavin et al, 2006; Grandi et al, 2002). These facts shed light on the as yet unclear functions of the TmcA homologs as being involved in rRN ...
... of protein complexes from yeast illustrated the interactions of KRE33 with several ribosomal proteins and a subset of ribosomal processing factors (Figure S6) (Gavin et al, 2006; Grandi et al, 2002). These facts shed light on the as yet unclear functions of the TmcA homologs as being involved in rRN ...
semester 1 review
... 44. What is the function of tRNA? 45. If a sequence of nitrogenous bases on a DNA strand is ATCCGA, the corresponding sequence on the mRNA will be ___. 46. Suppose an original strand of DNA reads GTCATC. a. What would the complementary DNA strand read? b. What would the corresponding mRNA strand rea ...
... 44. What is the function of tRNA? 45. If a sequence of nitrogenous bases on a DNA strand is ATCCGA, the corresponding sequence on the mRNA will be ___. 46. Suppose an original strand of DNA reads GTCATC. a. What would the complementary DNA strand read? b. What would the corresponding mRNA strand rea ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
Review! Part 3 Cell cycle Order of events in cell growth and division
... to form mRNA with continoius coding squence Happens during post-transcriptional processing of tRNA and rRNA o Functional and evolutionary importance of introns Direct the synthesis of differencr proteins and may can gene activity Splicing process may help in regulating the export of mRNA into ...
... to form mRNA with continoius coding squence Happens during post-transcriptional processing of tRNA and rRNA o Functional and evolutionary importance of introns Direct the synthesis of differencr proteins and may can gene activity Splicing process may help in regulating the export of mRNA into ...
Bio1100Ch17W
... • A polypeptide destined for the ________________ system or for export has a specific ________________ (approx 20 amino acids) region at or near the leading end. • A _________________________(SRP) binds to the signal peptide and attaches it and its ribosome to a receptor protein in the ER membrane. ...
... • A polypeptide destined for the ________________ system or for export has a specific ________________ (approx 20 amino acids) region at or near the leading end. • A _________________________(SRP) binds to the signal peptide and attaches it and its ribosome to a receptor protein in the ER membrane. ...
The Master Molecule
... guanine (G); and two pyrimidines, thymine (T) and cytosine (C). The genetic code is based on these four letters, AGCT, that encode the amino acids making up the body‘s peptides and proteins. The genetic code is the same in all living creatures. Nobel Prize winner Sydney Brenner showed that a sequenc ...
... guanine (G); and two pyrimidines, thymine (T) and cytosine (C). The genetic code is based on these four letters, AGCT, that encode the amino acids making up the body‘s peptides and proteins. The genetic code is the same in all living creatures. Nobel Prize winner Sydney Brenner showed that a sequenc ...
Fishy Genetics: From DNA to Protein: The Central Dogma of Biology
... DNA is a very complex molecule. It stores the information for making proteins in the codes of its bases: A,T,C, & G. Proteins are long chain molecules (polymers) that are made of amino acids (monomers). There are 20 different amino acids. Prote ...
... DNA is a very complex molecule. It stores the information for making proteins in the codes of its bases: A,T,C, & G. Proteins are long chain molecules (polymers) that are made of amino acids (monomers). There are 20 different amino acids. Prote ...
One Gene -One polypeptide
... Overview of Protein Synthesis2 main parts 1.Transcription -nucleus a sequence of DNA nucleotides (a gene) is converted to a single-stranded RNA molecule (mRNA) mRNA leaves the nucleus to go to the ribosomes. DNA remains in the nucleus. 2.Translation –ribosomes mRNA is translated into amino ...
... Overview of Protein Synthesis2 main parts 1.Transcription -nucleus a sequence of DNA nucleotides (a gene) is converted to a single-stranded RNA molecule (mRNA) mRNA leaves the nucleus to go to the ribosomes. DNA remains in the nucleus. 2.Translation –ribosomes mRNA is translated into amino ...
12 RNA Activity
... Science and 8th grade Chemistry of Living Systems. The splitting and tagging is an extension offering information about how scientists use DNA/RNA to identify species. Link to CA Standards Geneti ...
... Science and 8th grade Chemistry of Living Systems. The splitting and tagging is an extension offering information about how scientists use DNA/RNA to identify species. Link to CA Standards Geneti ...
3.1 Class Notes Powerpoint
... Transcription is done…what now? Now we have mature mRNA transcribed from the cell’s DNA. It is leaving the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once in the cytoplasm, it finds a ribosome so that translation can begin. ...
... Transcription is done…what now? Now we have mature mRNA transcribed from the cell’s DNA. It is leaving the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once in the cytoplasm, it finds a ribosome so that translation can begin. ...
Interfering with the genome: A new generation of disease treatments
... mutant gene responsible for a disease called familial amyloid poly neuropathy. This disease is caused by a mutated gene that encodes a protein causing abnormal and damaging accumulation of proteins in the body’s tissues. It is anticipated that the first RNAi drug for this disease will hit the market ...
... mutant gene responsible for a disease called familial amyloid poly neuropathy. This disease is caused by a mutated gene that encodes a protein causing abnormal and damaging accumulation of proteins in the body’s tissues. It is anticipated that the first RNAi drug for this disease will hit the market ...
Early Earth and the Origin of Life
... Ex: Mushrooms, Molds Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Heterotrophic - external digestion Cell wall of chitin ...
... Ex: Mushrooms, Molds Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Heterotrophic - external digestion Cell wall of chitin ...