ribosome binding site Prokaryotic mRNAs have a ribosome binding
... • Although the expression of most genes is regulated at the level of mRNA transcription, it is more effective for the cell to regulate gene expression at the level of translation. • As with other types of regulation, translational control typically functions at the level of initiation. ...
... • Although the expression of most genes is regulated at the level of mRNA transcription, it is more effective for the cell to regulate gene expression at the level of translation. • As with other types of regulation, translational control typically functions at the level of initiation. ...
Chapter 12 - North Mac Schools
... Cells that change into specific types of specialized cells Hox genes Genes that control this differentiation early in development Mutations involving hox genes can have HUGE effect on outcome of organism ...
... Cells that change into specific types of specialized cells Hox genes Genes that control this differentiation early in development Mutations involving hox genes can have HUGE effect on outcome of organism ...
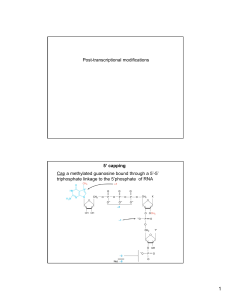
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... Gene silencing is probably often the result of more than one mechanism. Transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) is often associated with methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-depende ...
... Gene silencing is probably often the result of more than one mechanism. Transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) is often associated with methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-depende ...
Chalkboard Challenge
... 21 of 24) Examine the normal gene below. A C G T T T G C C A A G Now examine the same gene, only with a mutation. A C G T T G C C A A G What type of mutation is this? ...
... 21 of 24) Examine the normal gene below. A C G T T T G C C A A G Now examine the same gene, only with a mutation. A C G T T G C C A A G What type of mutation is this? ...
Transcription
... sequence on DNA, which is the beginning of the transcription unit). In eukaryotes transcription factors help with this binding. ...
... sequence on DNA, which is the beginning of the transcription unit). In eukaryotes transcription factors help with this binding. ...
Genetics The father of genetics is Gregor Mendel (1822
... -found in nucleus -contains genetic information Physical Structure of DNA - similar to a ladder - the sides of the ladder are made up of sugar- phosphate backbone - the rungs of a ladder are made up of the base pairs Bases -Adenine (A) -Guanine (G) -Thymine (T) -Cytosine (C) How the bases pair - A p ...
... -found in nucleus -contains genetic information Physical Structure of DNA - similar to a ladder - the sides of the ladder are made up of sugar- phosphate backbone - the rungs of a ladder are made up of the base pairs Bases -Adenine (A) -Guanine (G) -Thymine (T) -Cytosine (C) How the bases pair - A p ...
Document
... The start codon is the one that makes the tRNA insert its first amino acid The start codon is usually AUG and codes for methionine So almost all proteins begin with methionine as its first amino acid The stop codon is the one that makes the tRNA stop inserting amino acids UAA, UAG, UGA are all stop ...
... The start codon is the one that makes the tRNA insert its first amino acid The start codon is usually AUG and codes for methionine So almost all proteins begin with methionine as its first amino acid The stop codon is the one that makes the tRNA stop inserting amino acids UAA, UAG, UGA are all stop ...
gene-expression-text
... To translate an mRNA into a protein, the following ingredients are needed: mRNA template Amino acids Transfer RNA (tRNA): adaptor between amino acid and mRNA In charge of converting the nucleotide sequence code into an amino acid sequence. Ribosomes: organelles directing the translatio ...
... To translate an mRNA into a protein, the following ingredients are needed: mRNA template Amino acids Transfer RNA (tRNA): adaptor between amino acid and mRNA In charge of converting the nucleotide sequence code into an amino acid sequence. Ribosomes: organelles directing the translatio ...
Quantitative PCR
... • A method that allows to follow in real time (that is why is also called Real-Time PCR) the amplification of a target. • The target can be nucleic acids (RNA or DNA). • Taq polymerase can only synthesize DNA, so how do we study RNA using qPCR? ...
... • A method that allows to follow in real time (that is why is also called Real-Time PCR) the amplification of a target. • The target can be nucleic acids (RNA or DNA). • Taq polymerase can only synthesize DNA, so how do we study RNA using qPCR? ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... with limited RNA degradation at this temperature. Incubation at 37 degrees C strongly affected the levels of these mRNAs. Four hours of incubation at this temperature resulted in extensive RNA degradation, with mRNA levels falling to 1/10th those before incubation. When relative quantification was per ...
... with limited RNA degradation at this temperature. Incubation at 37 degrees C strongly affected the levels of these mRNAs. Four hours of incubation at this temperature resulted in extensive RNA degradation, with mRNA levels falling to 1/10th those before incubation. When relative quantification was per ...
Unit #3 Retake Ticket Unit 3 Retake Ticket
... Double OR Single stranded? Which sugar does it have? List all nitrogen bases ...
... Double OR Single stranded? Which sugar does it have? List all nitrogen bases ...
Translation Notes
... • Ribosomes consist of two subunits. – The large subunit has three binding sites for tRNA. – The small subunit binds to mRNA. ...
... • Ribosomes consist of two subunits. – The large subunit has three binding sites for tRNA. – The small subunit binds to mRNA. ...
protein - Warren County Schools
... •A three-letter code is used because there are 20 different amino acids that are used to make proteins. •If a two-letter code were used there would not be enough codons to select all 20 amino acids. •That is, there are 4 bases in RNA, so 42 (4x 4)=16; where as 43 (4x4x4)=64. ...
... •A three-letter code is used because there are 20 different amino acids that are used to make proteins. •If a two-letter code were used there would not be enough codons to select all 20 amino acids. •That is, there are 4 bases in RNA, so 42 (4x 4)=16; where as 43 (4x4x4)=64. ...
Transcription and Translation
... Transcription occurs in the nucleus, and translation occurs in the cytoplasm on ribosomes. • Figure comparing eukaryotic and prokaryotic transcription and translation. ...
... Transcription occurs in the nucleus, and translation occurs in the cytoplasm on ribosomes. • Figure comparing eukaryotic and prokaryotic transcription and translation. ...
Document
... – Termination: release of the RNA polymerase from the DNA • special sequences denote this region • differs between prokaryotes and eukaryotes ...
... – Termination: release of the RNA polymerase from the DNA • special sequences denote this region • differs between prokaryotes and eukaryotes ...
2.7 DNA Transcription_translation
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries copies of instructions for assembling amino acids into ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries copies of instructions for assembling amino acids into ...
Lecture 25: Protein Synthesis
... Starting state for elongation • eIF4 complex stays bound to 5´ cap • Other initiation factors have fallen off • Large (60S) subunit bound • Met-tRNA and AUG codon are in P site • A and E sites empty ...
... Starting state for elongation • eIF4 complex stays bound to 5´ cap • Other initiation factors have fallen off • Large (60S) subunit bound • Met-tRNA and AUG codon are in P site • A and E sites empty ...
分子生物學小考(一) 範圍ch3~ch7
... (B) "Transcription Repressor" is a sequence upstream of promoter that has negative effects on gene (C) "Transcription Insulator" is a sequence that acts as a neutral barrier for nearby genes (D) "General Transcription Factor" is a transcription factors requires for the basal level of transcription ( ...
... (B) "Transcription Repressor" is a sequence upstream of promoter that has negative effects on gene (C) "Transcription Insulator" is a sequence that acts as a neutral barrier for nearby genes (D) "General Transcription Factor" is a transcription factors requires for the basal level of transcription ( ...
protein synthesis worksheet
... “unzipped” and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome. The strand of mRNA is then read in order to make protein. They are read 3 bases at a time. These bases are called codons. tRNA is ...
... “unzipped” and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome. The strand of mRNA is then read in order to make protein. They are read 3 bases at a time. These bases are called codons. tRNA is ...
Molecular genetics of gene expression
... Transcription factors: proteins that bind to promoters to affect transcription • Transcriptional activators- Recruits the RNA polymerase complex to the transcription start site by binding to either sequences in the promoter or distant cis-acting elements to increase transcription. • Transcriptional ...
... Transcription factors: proteins that bind to promoters to affect transcription • Transcriptional activators- Recruits the RNA polymerase complex to the transcription start site by binding to either sequences in the promoter or distant cis-acting elements to increase transcription. • Transcriptional ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
Bio 139 Exam Review Outline: Exam #3
... Ch. 7 DNA structure & function: Know functions of three RNA types (messenger, ribosomal, transfer). RNA polymerase: synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. What is a codon? How many nucleotides does it take to encode one amino acid?(3) What is the “genetic code” and how is it “degenerate”? Know that so ...
... Ch. 7 DNA structure & function: Know functions of three RNA types (messenger, ribosomal, transfer). RNA polymerase: synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. What is a codon? How many nucleotides does it take to encode one amino acid?(3) What is the “genetic code” and how is it “degenerate”? Know that so ...
Physiology of Cells
... bases along one side of the DNA molecule • These RNA nucleotides bind to each other with the help of RNA polymerase • The chain that results is called messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
... bases along one side of the DNA molecule • These RNA nucleotides bind to each other with the help of RNA polymerase • The chain that results is called messenger RNA (mRNA) ...