医学分子生物学
... downstream and as far away as 50 kb from the transcription start site. In some cases, promoter-proximal elements occur downstream from the start site as well. (b) Most yeast genes contain only one regulatory region, called an upstream activating sequence (UAS), and a TATA box, which is ≈90 base pair ...
... downstream and as far away as 50 kb from the transcription start site. In some cases, promoter-proximal elements occur downstream from the start site as well. (b) Most yeast genes contain only one regulatory region, called an upstream activating sequence (UAS), and a TATA box, which is ≈90 base pair ...
Genetic Code Review.cwk
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNAis transcribed from DNAin the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNAto bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases ...
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNAis transcribed from DNAin the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNAto bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases ...
Slide 1
... Coding region – contains nucleotide sequence that encodes a specific protein product (this region will be translated) In eukaryotes: introns and exons Non-coding regions – contains nucleotide sequence that will get transcribed BUT not translated *Un-translated regions (UTR’s) Promoter regions – sequ ...
... Coding region – contains nucleotide sequence that encodes a specific protein product (this region will be translated) In eukaryotes: introns and exons Non-coding regions – contains nucleotide sequence that will get transcribed BUT not translated *Un-translated regions (UTR’s) Promoter regions – sequ ...
Chapter 2 DNA, RNA, Transcription and Translation I. DNA
... shorter with each cell division eventually DNA damage occurs at chromosome ends sends a signal to stabilize p53transcription of several genes (e.g. p21) CKI (cdk inhibitor protein) bind to and inhibit G1/S-cdk and S-cdk.=> block entry into S phase (Alberts, p10071018). ...
... shorter with each cell division eventually DNA damage occurs at chromosome ends sends a signal to stabilize p53transcription of several genes (e.g. p21) CKI (cdk inhibitor protein) bind to and inhibit G1/S-cdk and S-cdk.=> block entry into S phase (Alberts, p10071018). ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 3. The two different mechanisms by which DNA transposons can move are called: A. retrotransposition and replication B. bridge and fuse C. ITR and LTR D. replicative and nonreplicative transposition ...
... 3. The two different mechanisms by which DNA transposons can move are called: A. retrotransposition and replication B. bridge and fuse C. ITR and LTR D. replicative and nonreplicative transposition ...
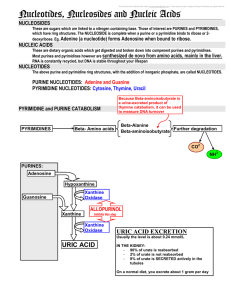
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... This document was created by Alex Yartsev ([email protected]); if I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me. ...
... This document was created by Alex Yartsev ([email protected]); if I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me. ...
rna interference
... regulate gene activity: certain parts of the genome are transcribed into microRNAs, short RNA molecules that fold back on themselves in a hairpin shape to create a double strand. When the RNA interference machinery detects these double strands, it will also destroy all mRNAs that match the micro RNA ...
... regulate gene activity: certain parts of the genome are transcribed into microRNAs, short RNA molecules that fold back on themselves in a hairpin shape to create a double strand. When the RNA interference machinery detects these double strands, it will also destroy all mRNAs that match the micro RNA ...
May 4, 2004 B4730/5730 Plant Physiological Ecology
... traits • Two copies of alleles determines traits ...
... traits • Two copies of alleles determines traits ...
Model 1: Elongation Phase of Translation
... 4. What would happen if all the tRNAs in a cell with anticodons for lysine carried glycine amino acids instead of lysine amino acids? Circle the correct answer. A. Translation would still occur but the protein product would contain glycines in place of lysines B. Translation would stop at the first ...
... 4. What would happen if all the tRNAs in a cell with anticodons for lysine carried glycine amino acids instead of lysine amino acids? Circle the correct answer. A. Translation would still occur but the protein product would contain glycines in place of lysines B. Translation would stop at the first ...
SDS-PAGE of protein purified with the AllPrep RNA/Protein
... SDS-PAGE of protein purified with the AllPrep RNA/Protein Kit We would like to inform you that the RNA-stabilizing agent in Buffer APL (lysis buffer) causes precipitation of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Therefore, an SDS-containing buffer should not be used to equilibrate the Protein Cleanup spin c ...
... SDS-PAGE of protein purified with the AllPrep RNA/Protein Kit We would like to inform you that the RNA-stabilizing agent in Buffer APL (lysis buffer) causes precipitation of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Therefore, an SDS-containing buffer should not be used to equilibrate the Protein Cleanup spin c ...
Lecture Notes
... nucleus and its subsequent transport to the cytoplasm. © 2003 John Wiley and Sons Publishers ...
... nucleus and its subsequent transport to the cytoplasm. © 2003 John Wiley and Sons Publishers ...
Gene Expression/Mutations
... - It doesn’t make sense for DNA to have introns if there is no function because it goes to so much work to keep them and remove them. - Study done where they spliced out introns of a plant leaf and crossed it: the resulting leaf was very different than original leaf. - It is thought that introns add ...
... - It doesn’t make sense for DNA to have introns if there is no function because it goes to so much work to keep them and remove them. - Study done where they spliced out introns of a plant leaf and crossed it: the resulting leaf was very different than original leaf. - It is thought that introns add ...
Protein Translation
... 1.5% encode proteins < = > 98.5% not protein encoding ~ 31,000 genes encoding 100,000 - 200,000 proteins How are 100,000 to 200,000 proteins produced from ...
... 1.5% encode proteins < = > 98.5% not protein encoding ~ 31,000 genes encoding 100,000 - 200,000 proteins How are 100,000 to 200,000 proteins produced from ...
BASIC BIOLOGY FOR MATHEMATICIANS AND COMPUTER …
... So correct amino acids are added Protein has correct amino acid sequence D:\cell biol 3611\protein synth sorting\TRANSLATION.MOV ...
... So correct amino acids are added Protein has correct amino acid sequence D:\cell biol 3611\protein synth sorting\TRANSLATION.MOV ...
Introduction to molecular biology
... • Proteins are coded in the genes in ADN located in the nucleus. DNA stays always in the nucleus. • Ribosomes are factories to build proteins located in the cytoplasm. mRNA carries the mesage from the nucleus to the ribosomes. There is an intermediate step called mRNA maturation in which introns are ...
... • Proteins are coded in the genes in ADN located in the nucleus. DNA stays always in the nucleus. • Ribosomes are factories to build proteins located in the cytoplasm. mRNA carries the mesage from the nucleus to the ribosomes. There is an intermediate step called mRNA maturation in which introns are ...
Chap.1
... Each three-nucleotides group, called a codon, translates to an amino acid (the protein building block). Transfer RNA (tRNA): Decodes the mRNA molecules to amino acids. It connects to the mRNA with one side and holds the appropriate amino acid on its other side. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Part of the ribo ...
... Each three-nucleotides group, called a codon, translates to an amino acid (the protein building block). Transfer RNA (tRNA): Decodes the mRNA molecules to amino acids. It connects to the mRNA with one side and holds the appropriate amino acid on its other side. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Part of the ribo ...
Bio background
... Several types exist, classified by function mRNA – this is what is usually being referred to when a Bioinformatician says “RNA”. This is used to carry a gene’s message out of the nucleus. tRNA – transfers genetic information from mRNA to an amino acid sequence rRNA – ribosomal RNA. Part of the ...
... Several types exist, classified by function mRNA – this is what is usually being referred to when a Bioinformatician says “RNA”. This is used to carry a gene’s message out of the nucleus. tRNA – transfers genetic information from mRNA to an amino acid sequence rRNA – ribosomal RNA. Part of the ...
BIOLOGY CONTENT STANDARDS REVIEW
... information from DNA into mRNA. Ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 18. Describe DNA replication. 19. Describe transcription and translation (include the terms nucleus, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, rRNA, tRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, and amino acids). Th ...
... information from DNA into mRNA. Ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 18. Describe DNA replication. 19. Describe transcription and translation (include the terms nucleus, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, rRNA, tRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, and amino acids). Th ...
Recombinant DNA I
... IV. Control of gene expression by DNA Methylation • Addition of CH3 to selected C’s in DNA can inactivate genes, e.g. high levels are seen in inactivated X chromosome of female mammals. • Mammals have about 5% methylation. • Not essential in eukarotyes, since Drosophila has 0% methylation. • First ...
... IV. Control of gene expression by DNA Methylation • Addition of CH3 to selected C’s in DNA can inactivate genes, e.g. high levels are seen in inactivated X chromosome of female mammals. • Mammals have about 5% methylation. • Not essential in eukarotyes, since Drosophila has 0% methylation. • First ...