Thinking Critically with Psychological Science
... a statement of procedures (operations) used to define research variables Example intelligence may be operationally defined as what an intelligence test measures ...
... a statement of procedures (operations) used to define research variables Example intelligence may be operationally defined as what an intelligence test measures ...
Classical Conditioning - Anoka
... • Author of the law of effect, the principle that forms the basis of operant conditioning • Behaviors with favorable consequences will occur more frequently. • Behaviors with unfavorable consequences will occur less frequently. • Created puzzle boxes for research on cats ...
... • Author of the law of effect, the principle that forms the basis of operant conditioning • Behaviors with favorable consequences will occur more frequently. • Behaviors with unfavorable consequences will occur less frequently. • Created puzzle boxes for research on cats ...
Reinforcement
... nimals learn an awareness or expectancy of how likely it is that the UCS will occur he environment and evolutionary history or biological predispositions make it easy for particular associations which enhance an animal’s survival f you become ill after eating mussels, you will probably have a hard t ...
... nimals learn an awareness or expectancy of how likely it is that the UCS will occur he environment and evolutionary history or biological predispositions make it easy for particular associations which enhance an animal’s survival f you become ill after eating mussels, you will probably have a hard t ...
Learning - IB Psychology.com
... • It includes a detailed description with studies and/or theories • It includes an evaluation of studies and/or theories • It includes evaluation linked to the question – It “pokes holes” in the question – It shows depth of understanding ...
... • It includes a detailed description with studies and/or theories • It includes an evaluation of studies and/or theories • It includes evaluation linked to the question – It “pokes holes” in the question – It shows depth of understanding ...
Knowledge Base - WordPress.com
... Even though I have experience using some of the tenants of behavioral learning theory I related more closely with cognitive theory when it comes to designing and developing instruction. The need to break down training objectives to smaller modules then find a way to associate them with a students pr ...
... Even though I have experience using some of the tenants of behavioral learning theory I related more closely with cognitive theory when it comes to designing and developing instruction. The need to break down training objectives to smaller modules then find a way to associate them with a students pr ...
Classical Conditioning
... 23-4. Summarize the processes and adaptive value of acquisition, higher-order conditioning, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Responses are acquired—that is, initially learned—best when the CS is presented half a second before the US. This finding demonstrates how ...
... 23-4. Summarize the processes and adaptive value of acquisition, higher-order conditioning, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Responses are acquired—that is, initially learned—best when the CS is presented half a second before the US. This finding demonstrates how ...
Learning Habituation Mere Exposure Effect Behavioral Learning
... A lasting change in behavior or mental processes that result from experience. ...
... A lasting change in behavior or mental processes that result from experience. ...
Unit 6 Learning - Helena High School
... operant conditioning research, a chamber (also known as a Skinner Box) containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; attached devices record the animal’s rate of bar pressing or key pecking. ...
... operant conditioning research, a chamber (also known as a Skinner Box) containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; attached devices record the animal’s rate of bar pressing or key pecking. ...
In operant conditioning
... OPERANT CONDITIONING In operant conditioning (also a type of associative learning), people and animals learn to do certain things—and not to do others—because of the results of what they do. In other words, they learn from the consequences of their actions. ...
... OPERANT CONDITIONING In operant conditioning (also a type of associative learning), people and animals learn to do certain things—and not to do others—because of the results of what they do. In other words, they learn from the consequences of their actions. ...
The Physiological approach:
... The behavioral approach observes a change as a result of experience, that is to look at the learning process. According to John B. Watson, in behavioral approach, there isn't a difference between other animals and humans because psychology is only concerned with behavior and not the reasoning behind ...
... The behavioral approach observes a change as a result of experience, that is to look at the learning process. According to John B. Watson, in behavioral approach, there isn't a difference between other animals and humans because psychology is only concerned with behavior and not the reasoning behind ...
Behaviorist Perspective - West Point Public Schools
... Refers to the period of time when the stimulus comes to evoke the conditioned response. ...
... Refers to the period of time when the stimulus comes to evoke the conditioned response. ...
Contiguity Theory and One Trial Learning - Learning Theories
... What is contiguity theory and one trial learning? Guthrie attempted to explain learning through association of stimuli with responses.1) Learning, in terms of behavior is a function of the environment. According to Guthrie, learning is associating a particular stimulus with a particular response. Th ...
... What is contiguity theory and one trial learning? Guthrie attempted to explain learning through association of stimuli with responses.1) Learning, in terms of behavior is a function of the environment. According to Guthrie, learning is associating a particular stimulus with a particular response. Th ...
Chapter 8 pt. 1: Learning and Classical Conditioning
... Most learning is associative learning: learning that certain events occur together. There are 3 main types of Learning: 1. Classical Conditioning 2. Operant Conditioning 3. Observational Learning ...
... Most learning is associative learning: learning that certain events occur together. There are 3 main types of Learning: 1. Classical Conditioning 2. Operant Conditioning 3. Observational Learning ...
Introduction to Psychology
... John Watson B.F. Skinner Observable behavior Learning by association Reinforcement and punishment ...
... John Watson B.F. Skinner Observable behavior Learning by association Reinforcement and punishment ...
Katie Ross EDUF 7130 Dr. Jonathan Hilpert 5 September 2015
... Expanding on the behaviorist principles of Pavlov, Thorndike, and Watson, among others, B. F. Skinner developed the principle known as operant conditioning in the 1930s. He is often regarded as the “father of operant conditioning,” because he coined the term after a series of experiments performed o ...
... Expanding on the behaviorist principles of Pavlov, Thorndike, and Watson, among others, B. F. Skinner developed the principle known as operant conditioning in the 1930s. He is often regarded as the “father of operant conditioning,” because he coined the term after a series of experiments performed o ...
Learning
... Observational Learning • Occurs when people watch the actions of others and note the reinforcements they receive for their behaviours-learning occurs as a result of vicarious rather than direct experience. ...
... Observational Learning • Occurs when people watch the actions of others and note the reinforcements they receive for their behaviours-learning occurs as a result of vicarious rather than direct experience. ...
managing behavior - Foxborough Regional Charter School
... • Behavior is a form of communication unfortunately some individuals learn that Problem Behavior is the best way for them to get their needs met ...
... • Behavior is a form of communication unfortunately some individuals learn that Problem Behavior is the best way for them to get their needs met ...
File - Teaching Future Teachers
... supplement the learning process with motivation. The model is based on Tolman's and Lewin's expectancyvalue theory, which presumes that people are motivated to learn if there is value in the knowledge presented (i.e. it fulfills personal needs) and if there is an optimistic expectation for success.[ ...
... supplement the learning process with motivation. The model is based on Tolman's and Lewin's expectancyvalue theory, which presumes that people are motivated to learn if there is value in the knowledge presented (i.e. it fulfills personal needs) and if there is an optimistic expectation for success.[ ...
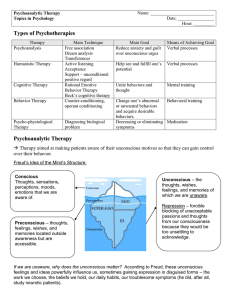
Psychoanalytic Therapy Notes
... A method used to examine the unconscious; the patients are instructed to say whatever comes to his or her mind first. Since the therapist is typically trying to uncover painful memories and feelings, the patient often experiences resistance – the reluctance of a patient either to reveal painful feel ...
... A method used to examine the unconscious; the patients are instructed to say whatever comes to his or her mind first. Since the therapist is typically trying to uncover painful memories and feelings, the patient often experiences resistance – the reluctance of a patient either to reveal painful feel ...
Review Exam 2 Text Material: Lecture Material: Be able to define or
... Topics covered include: habituation; sensitization; classical conditioning; phobias and their treatment; drug addictions; operant conditioning; schedules of reinforcement; observational learning; Social learning of fear: Minetka monkey studies; treatment for socially learned phobia, -NOT COVERED ...
... Topics covered include: habituation; sensitization; classical conditioning; phobias and their treatment; drug addictions; operant conditioning; schedules of reinforcement; observational learning; Social learning of fear: Minetka monkey studies; treatment for socially learned phobia, -NOT COVERED ...
Learning - Forensic Consultation
... Learning (relatively permanent change in behavior or mental processes resulting from practice or experience) ...
... Learning (relatively permanent change in behavior or mental processes resulting from practice or experience) ...
Test Bank 1
... accurate. For example, would students be more likely to consider a biological perspective if they discover many family members, even those adopted into other families at birth, shared the condition? Similarly, would they consider a diathesis-stress model if the condition only developed after a stres ...
... accurate. For example, would students be more likely to consider a biological perspective if they discover many family members, even those adopted into other families at birth, shared the condition? Similarly, would they consider a diathesis-stress model if the condition only developed after a stres ...
Curriculum - WordPress.com
... strategies that facilitate problem solving (cognitive process); application of problem solving skills within social context in general and within the context of democratic process; and development of cognitive skills within the academic disciplines. ...
... strategies that facilitate problem solving (cognitive process); application of problem solving skills within social context in general and within the context of democratic process; and development of cognitive skills within the academic disciplines. ...
Psychologist - PeakpsychU1
... • John Watson argued that studying the mind and introspection didn’t work because it was unscientific due to the disagreements between scientists and it’s inability to be measured • Behaviorism – The school of psychology that emphasizes the study of overt, observable behavior • Realized that you col ...
... • John Watson argued that studying the mind and introspection didn’t work because it was unscientific due to the disagreements between scientists and it’s inability to be measured • Behaviorism – The school of psychology that emphasizes the study of overt, observable behavior • Realized that you col ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections