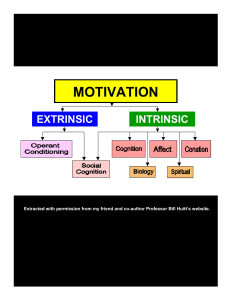
Basic Learning Processes in Infancy and Childhood - Nam
... object by grasping it in their hand can recognize its shape by sight alone; • They do not recognize that an object to which they have been habituated visually is the same as or different from the one they now are given the opportunity to hold. ...
... object by grasping it in their hand can recognize its shape by sight alone; • They do not recognize that an object to which they have been habituated visually is the same as or different from the one they now are given the opportunity to hold. ...
Chapter 8: Learning - rcook
... they are behaving well. Target a specific behavior, reward it, and watch it increase. o Ignore whining. o When children misbehave or are defiant, do not yell or hit them. Explain the misbehavior and give them a ...
... they are behaving well. Target a specific behavior, reward it, and watch it increase. o Ignore whining. o When children misbehave or are defiant, do not yell or hit them. Explain the misbehavior and give them a ...
Burrhus Frederic Skinner - Back
... stimuli, not physiology. 3. Functional analysis of stimuli and behaviors should be the goal of psychology not the “why of behaviors”. 4. We need behavior technology to resolve human problems. But our culture, government and religion erodes reinforcements to problem-free ...
... stimuli, not physiology. 3. Functional analysis of stimuli and behaviors should be the goal of psychology not the “why of behaviors”. 4. We need behavior technology to resolve human problems. But our culture, government and religion erodes reinforcements to problem-free ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Tipp City Exempted Village Schools
... • People and animals learn to do certain things & not do others because of consequences • In classical conditioning – conditioned responses are often involuntary biological behaviors • In operant conditioning – voluntary responses (we control) are conditioned ...
... • People and animals learn to do certain things & not do others because of consequences • In classical conditioning – conditioned responses are often involuntary biological behaviors • In operant conditioning – voluntary responses (we control) are conditioned ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... • Positive Reinforcement: When a response is followed by a reward or other positive event AND the probability of the organism making that response again increases in the future • Negative Reinforcement: When a response is followed by the removal of an unpleasant event or by an end to discomfort AND ...
... • Positive Reinforcement: When a response is followed by a reward or other positive event AND the probability of the organism making that response again increases in the future • Negative Reinforcement: When a response is followed by the removal of an unpleasant event or by an end to discomfort AND ...
AP Psychology 2015-2016 - Steilacoom School District
... Describe major treatment orientations used in therapy (e.g., behavioral, cognitive, humanistic) and how those orientations influence therapeutic planning. Compare and contrast different treatment formats (e.g., individual, group). Summarize effectiveness of specific treatments used to address specif ...
... Describe major treatment orientations used in therapy (e.g., behavioral, cognitive, humanistic) and how those orientations influence therapeutic planning. Compare and contrast different treatment formats (e.g., individual, group). Summarize effectiveness of specific treatments used to address specif ...
• behavior modification • biofeedback • neurofeedback • latent
... 1. Describe Pavlov’s pioneering research on classical conditioning (CC). 2. How do you create a conditioned response (CR)? 3. Think about stimulus generalization and discrimination. Predict what would be the adaptive significance of both of these responses. 4. Explain the key factor in producing ext ...
... 1. Describe Pavlov’s pioneering research on classical conditioning (CC). 2. How do you create a conditioned response (CR)? 3. Think about stimulus generalization and discrimination. Predict what would be the adaptive significance of both of these responses. 4. Explain the key factor in producing ext ...
PowerPoint slides into MS Word
... development. This theory states that when there is a discrepancy between two beliefs, two actions, or between a belief and an action, we will act to resolve conflict and discrepancies. • A second approach is Attribution Theory (Heider, 1958; Weiner, 1974). Every individual tries to explain success o ...
... development. This theory states that when there is a discrepancy between two beliefs, two actions, or between a belief and an action, we will act to resolve conflict and discrepancies. • A second approach is Attribution Theory (Heider, 1958; Weiner, 1974). Every individual tries to explain success o ...
AP Psychology: History Of Psychology Overview
... 78. Findings from a 1997 study by Dianne Tice and Roy Baumeister of procrastination among college students included all the following except: A) Procrastinators felt less stress than nonprocrastinators early in the semester. B) Procrastinators exhibited poorer performance than nonprocrastinators. C ...
... 78. Findings from a 1997 study by Dianne Tice and Roy Baumeister of procrastination among college students included all the following except: A) Procrastinators felt less stress than nonprocrastinators early in the semester. B) Procrastinators exhibited poorer performance than nonprocrastinators. C ...
Chapter 6: Introduction to Operant Conditioning Lecture Overview
... was placed just outside the door To get to the food, the cat could open the door by pressing a lever Initially, the cats tried a number of behaviors to escape befor e stumbling across correct response Thorndike was interested in how long it took the cat to escape when placed back in the box DV = the ...
... was placed just outside the door To get to the food, the cat could open the door by pressing a lever Initially, the cats tried a number of behaviors to escape befor e stumbling across correct response Thorndike was interested in how long it took the cat to escape when placed back in the box DV = the ...
1. A stimulus change that increases the future frequency of behavior
... unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (US), such as salivation when food is in the mouth. e. Behavior that occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus f. A type of learning that occurs when an organism's responding is influenced by the observation of others, who ...
... unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (US), such as salivation when food is in the mouth. e. Behavior that occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus f. A type of learning that occurs when an organism's responding is influenced by the observation of others, who ...
File - Justin Daigle, MA, BCBA, LBA
... • O. Ivar Lovaas had an idea! What if we take we learned from: ...
... • O. Ivar Lovaas had an idea! What if we take we learned from: ...
Skinner`s Paper
... to be eradicated. Moreover, Skinner also believed that punishment decreased behavior and was different from negative reinforcement. To develop his theory Skinner created a device that had a lever and a food tray. Inside the box he placed a hungry rat that could get food from the tray by pressing the ...
... to be eradicated. Moreover, Skinner also believed that punishment decreased behavior and was different from negative reinforcement. To develop his theory Skinner created a device that had a lever and a food tray. Inside the box he placed a hungry rat that could get food from the tray by pressing the ...
Introduction to Operant Conditioning
... 1. Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs instantly after a behavior. A rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. 2. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. ...
... 1. Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs instantly after a behavior. A rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. 2. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. ...
Unit 13 Therapy
... supported Light exposure, supported for (SAD) Evidence-based practice – clinical decision-making that integrates the best available research and practices Eclectic approach based on evidence clinical expertise and patient characteristics Psychotherapies offer new hope, fresh perspecti ...
... supported Light exposure, supported for (SAD) Evidence-based practice – clinical decision-making that integrates the best available research and practices Eclectic approach based on evidence clinical expertise and patient characteristics Psychotherapies offer new hope, fresh perspecti ...
learning behavior
... stimulus and response, whereas; trial and error has basic instincts and motivation (drive or urge) at the base. When animals are motivated by thirst, hunger, sex or fear they show restlessness, and exploratory or appetitive behavior during the course of which it performs spontaneously a variety of m ...
... stimulus and response, whereas; trial and error has basic instincts and motivation (drive or urge) at the base. When animals are motivated by thirst, hunger, sex or fear they show restlessness, and exploratory or appetitive behavior during the course of which it performs spontaneously a variety of m ...
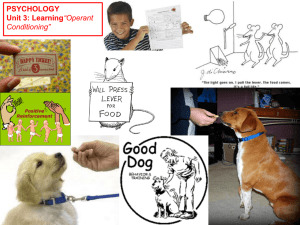
PSYCHOLOGY Unit 3: Learning“Operant Conditioning”
... ‘check-up’ might come, you have to be working hard at all times in order to be ready. In this sense, the variable schedules are more powerful and result in more consistent behaviors. This may not be as true for punishment since consistency in the application is so important, but for all other types ...
... ‘check-up’ might come, you have to be working hard at all times in order to be ready. In this sense, the variable schedules are more powerful and result in more consistent behaviors. This may not be as true for punishment since consistency in the application is so important, but for all other types ...
Chapter Excerpt
... The Scientific Revolution During the scientific revolution, a great philosophical shift occurred. Whereas religion had asserted that the spirit of a person could not be studied using scientific means, a new generation of philosophers and scientists challenged these religious beliefs. Advances in as ...
... The Scientific Revolution During the scientific revolution, a great philosophical shift occurred. Whereas religion had asserted that the spirit of a person could not be studied using scientific means, a new generation of philosophers and scientists challenged these religious beliefs. Advances in as ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in
... desired response each time it occurs. 2. Partial Reinforcement: Reinforces a response only part of the time. Though this results in slower acquisition in the beginning, it shows greater resistance to ...
... desired response each time it occurs. 2. Partial Reinforcement: Reinforces a response only part of the time. Though this results in slower acquisition in the beginning, it shows greater resistance to ...
What develops
... What examples of human behavior have you seen that seem as though they may have been inherited from our ancestors because they helped individuals survive and adapt more effectively? Why do you think they are inherited? How do the concepts of social learning and modeling relate to the mass media? How ...
... What examples of human behavior have you seen that seem as though they may have been inherited from our ancestors because they helped individuals survive and adapt more effectively? Why do you think they are inherited? How do the concepts of social learning and modeling relate to the mass media? How ...
Learning_1_1
... that by itself elicits no response). • You present the stimulus with the UCS a whole bunch of times. ...
... that by itself elicits no response). • You present the stimulus with the UCS a whole bunch of times. ...
Ch 6 Test: Learning
... 33. Being able to differentiate similar stimuli. 34. A mental awareness of an area as a result of latent learning 35. An active method of learning - particularly from a textbook 36. The danger of using only punishment to shape someone’s behavior is: a. the punisher may be reinforcing to the subject ...
... 33. Being able to differentiate similar stimuli. 34. A mental awareness of an area as a result of latent learning 35. An active method of learning - particularly from a textbook 36. The danger of using only punishment to shape someone’s behavior is: a. the punisher may be reinforcing to the subject ...